Abstract
A convenient and reliable method for serogrouping meningococci, based on immunospecific precipitation haloes in antiserum-agar plates, is described. It gave concordant results with conventional slide-agglutination in 900 strains of groups A, B or C tested. The antiserum-agar can also be used as a primary isolation medium for detecting nasopharyngeal carriers of a certain serogroup if antibiotics are added.
Full text
PDF

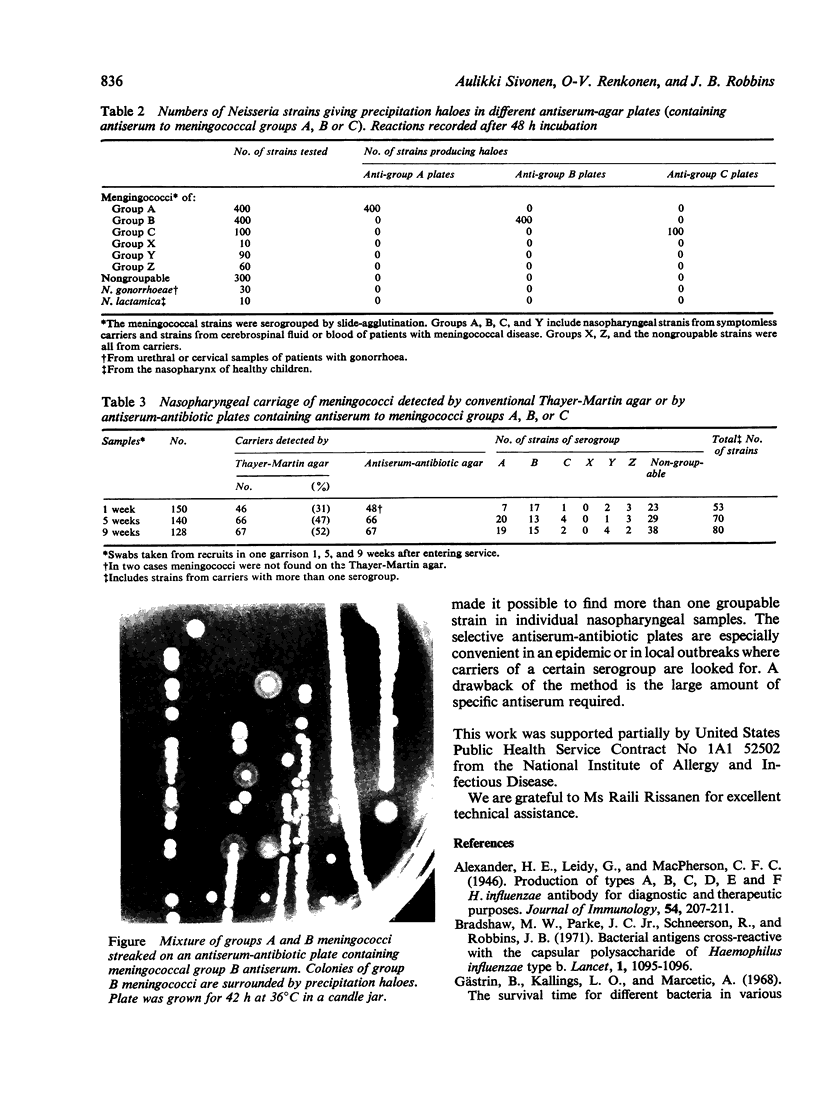

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradshaw M. W., Schneerson R., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Bacterial antigens cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1095–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Käyhty H., Weckström P., Sivonen A., Renkonen O. V. Effect of group-A meningococcal vaccine in army recruits in Finland. Lancet. 1975 Nov 8;2(7941):883–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Mäkelä P. H., ELO O., Pettay O., Renkonen O. V., Sivonen A. Vaccination against meningococcal group A disease in Finland 1974-75. Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(3):169–174. doi: 10.3109/inf.1976.8.issue-3.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATERUS K. W. Serological typing of meningococci by means of micro-precipitation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1961;27:305–315. doi: 10.1007/BF02538460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Peenen P. F., Suiter L. E., Mandel A. D., Mitchell M. S. Field evaluation of Thayer-Martin medium for identification of meningococcus carriers. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Nov;82(3):329–333. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]