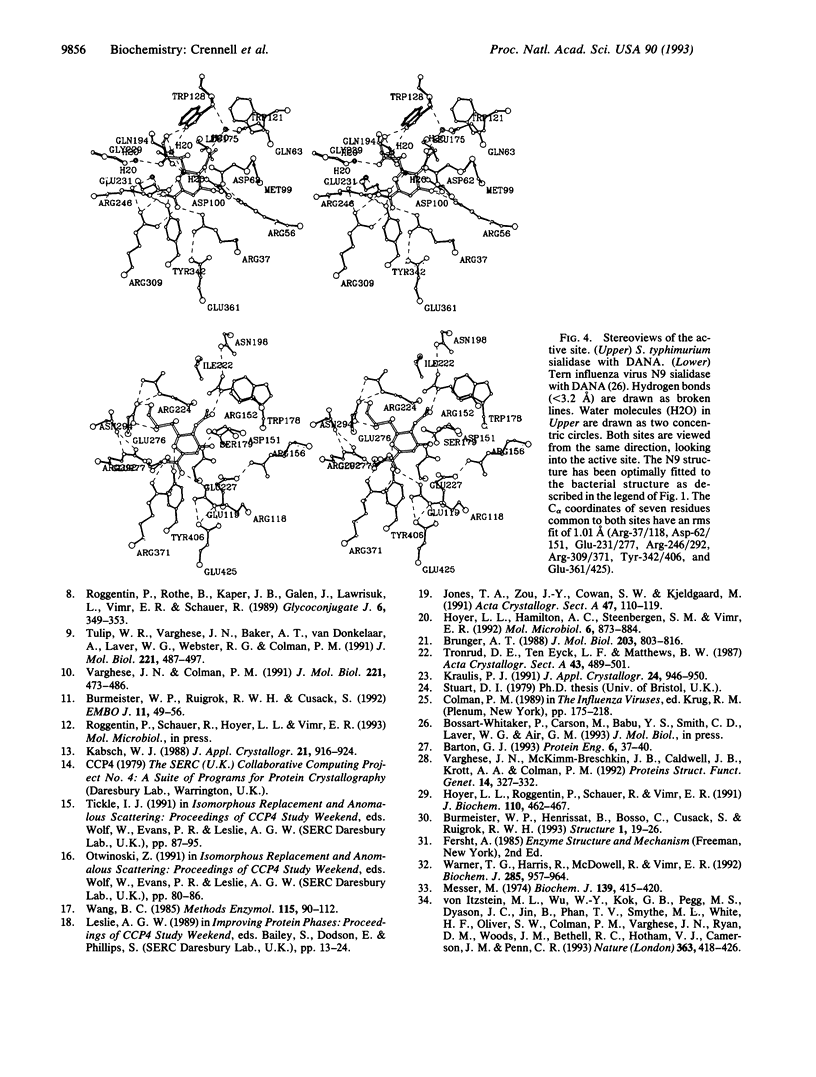
Abstract
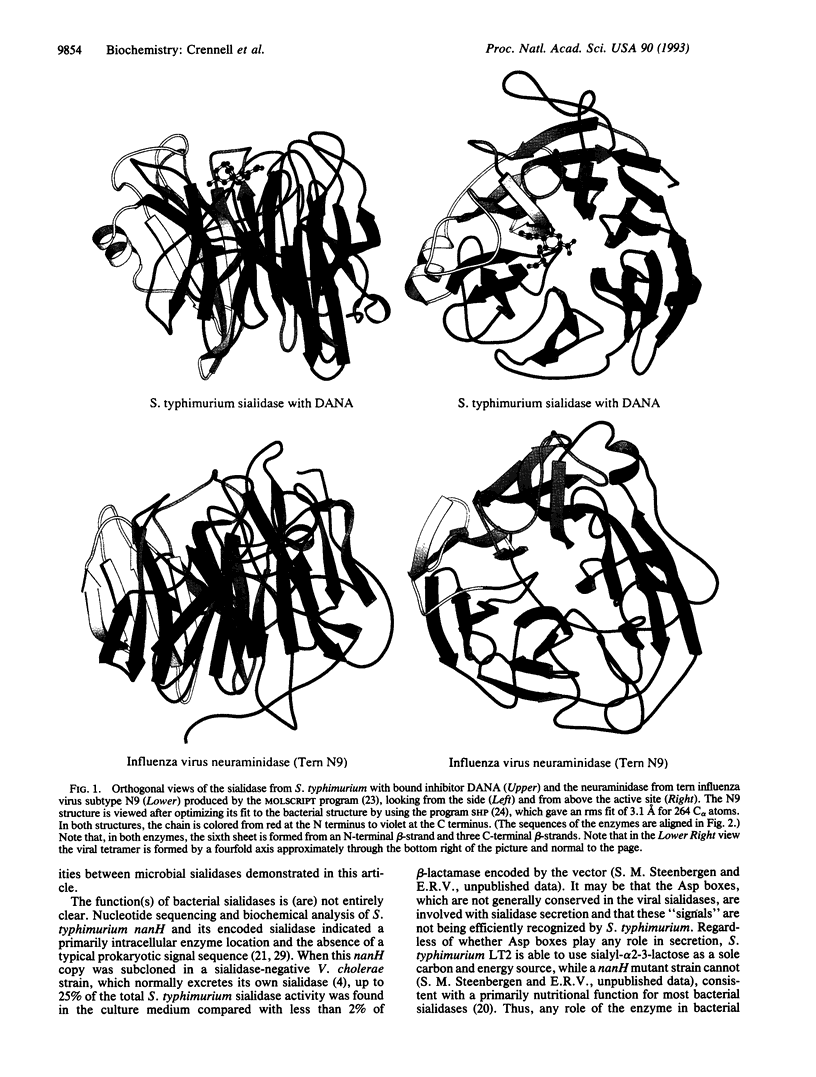
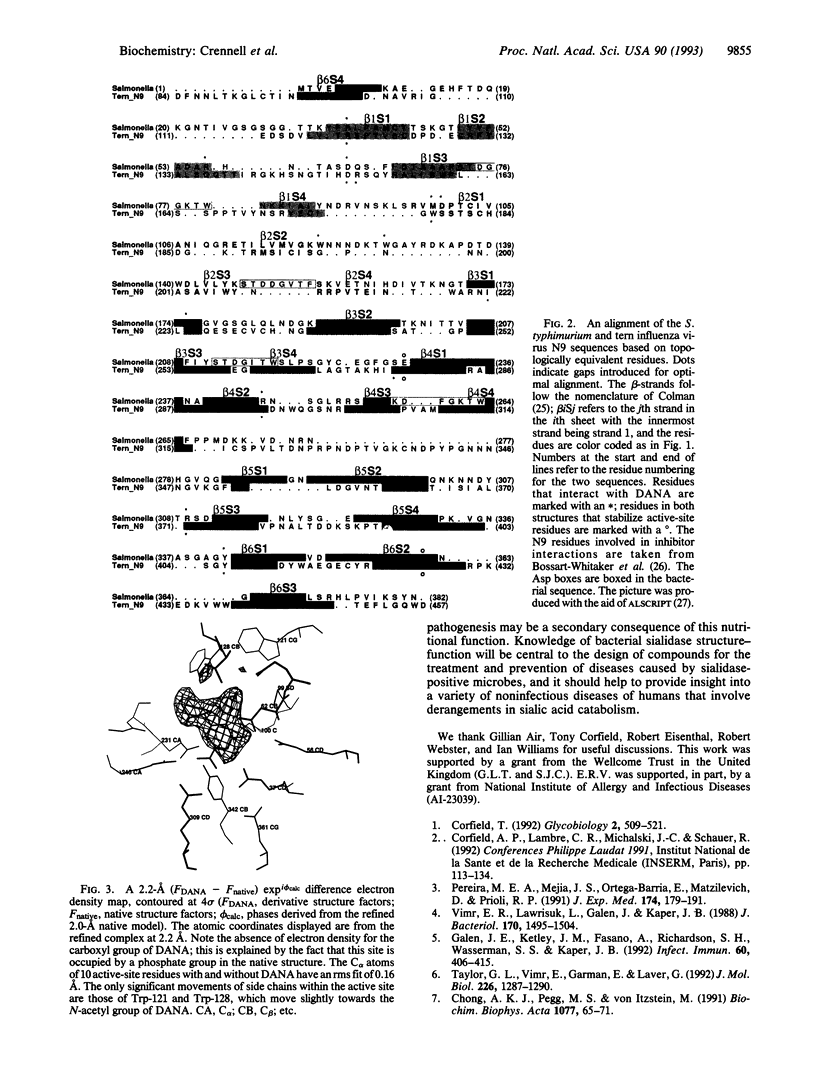
Sialidases (EC 3.2.1.18 or neuraminidases) remove sialic acid from sialoglycoconjugates, are widely distributed in nature, and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases. The three-dimensional structure of influenza virus sialidase is known, and we now report the three-dimensional structure of a bacterial sialidase, from Salmonella typhimurium LT2, at 2.0-A resolution and the structure of its complex with the inhibitor 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid at 2.2-A resolution. The viral enzyme is a tetramer; the bacterial enzyme, a monomer. Although the monomers are of similar size (approximately 380 residues), the sequence similarity is low (approximately 15%). The viral enzyme contains at least eight disulfide bridges, conserved in all strains, and binds Ca2+, which enhances activity; the bacterial enzyme contains one disulfide and does not bind Ca2+. Comparison of the two structures shows a remarkable similarity both in the general fold and in the spatial arrangement of the catalytic residues. However, an rms fit of 3.1 A between 264 C alpha atoms of the S. typhimurium enzyme and those from an influenza A virus reflects some major differences in the fold. In common with the viral enzyme, the bacterial enzyme active site consists of an arginine triad, a hydrophobic pocket, and a key tyrosine and glutamic acid, but differences in the interactions with the O4 and glycerol groups of the inhibitor reflect differing kinetics and substrate preferences of the two enzymes. The repeating "Asp-box" motifs observed among the nonviral sialidase sequences occur at topologically equivalent positions on the outside of the structure. Implications of the structure for the catalytic mechanism, evolution, and secretion of the enzyme are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brünger A. T. Crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing. Application to a 2.8 A resolution structure of aspartate aminotransferase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):803–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister W. P., Henrissat B., Bosso C., Cusack S., Ruigrok R. W. Influenza B virus neuraminidase can synthesize its own inhibitor. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister W. P., Ruigrok R. W., Cusack S. The 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of influenza B neuraminidase and its complex with sialic acid. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong A. K., Pegg M. S., von Itzstein M. Influenza virus sialidase: effect of calcium on steady-state kinetic parameters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 8;1077(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield T. Bacterial sialidases--roles in pathogenicity and nutrition. Glycobiology. 1992 Dec;2(6):509–521. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.6.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen J. E., Ketley J. M., Fasano A., Richardson S. H., Wasserman S. S., Kaper J. B. Role of Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase in the function of cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):406–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.406-415.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. L., Hamilton A. C., Steenbergen S. M., Vimr E. R. Cloning, sequencing and distribution of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 sialidase gene, nanH, provides evidence for interspecies gene transfer. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(7):873–884. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. L., Roggentin P., Schauer R., Vimr E. R. Purification and properties of cloned Salmonella typhimurium LT2 sialidase with virus-typical kinetic preference for sialyl alpha 2----3 linkages. J Biochem. 1991 Sep;110(3):462–467. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer M. Identification of N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminyl-lactose in Echidna milk. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):415–420. doi: 10.1042/bj1390415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Mejia J. S., Ortega-Barria E., Matzilevich D., Prioli R. P. The Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase contains sequences similar to bacterial neuraminidases, YWTD repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor, and type III modules of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):179–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggentin P., Rothe B., Kaper J. B., Galen J., Lawrisuk L., Vimr E. R., Schauer R. Conserved sequences in bacterial and viral sialidases. Glycoconj J. 1989;6(3):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01047853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Vimr E., Garman E., Laver G. Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic study of neuraminidase from Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1287–1290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulip W. R., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., van Donkelaar A., Laver W. G., Webster R. G., Colman P. M. Refined atomic structures of N9 subtype influenza virus neuraminidase and escape mutants. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Colman P. M. Three-dimensional structure of the neuraminidase of influenza virus A/Tokyo/3/67 at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Caldwell J. B., Kortt A. A., Colman P. M. The structure of the complex between influenza virus neuraminidase and sialic acid, the viral receptor. Proteins. 1992 Nov;14(3):327–332. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Lawrisuk L., Galen J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and expression of the Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase gene nanH in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1495–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1495-1504.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. G., Harris R., McDowell R., Vimr E. R. Photolabelling of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 sialidase. Identification of a peptide with a predicted structural similarity to the active sites of influenza-virus sialidases. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):957–964. doi: 10.1042/bj2850957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Itzstein M., Wu W. Y., Kok G. B., Pegg M. S., Dyason J. C., Jin B., Van Phan T., Smythe M. L., White H. F., Oliver S. W. Rational design of potent sialidase-based inhibitors of influenza virus replication. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):418–423. doi: 10.1038/363418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]