Abstract
Context:
Laryngeal mask airway supreme (LMA-S) has an inflatable cuff while i-gel has a noninflatable cuff made of thermoplastic elastomer.
Aims:
To study the efficacy of ventilation and the laryngeal seal pressures (LSPs) with either device. Our secondary objectives were to compare the ease of insertion, adequacy of positioning the device, hemodynamic response to device insertion, and any postoperative oropharyngeal morbidity.
Settings and Design:
A prospective, randomized, single-blinded study at Teaching Medical School in South India.
Materials and Methods:
Forty-two patients posted for surgery under general anesthesia were randomly divided into two groups - LMA-S and i-gel. After a standardized premedication and anesthesia induction sequence, the supra-glottic devices were introduced. Ease of insertion was assessed from the number of attempts taken to insert, insertion time, and any maneuvers required to insert the device. Position of the device was assessed by the ease of gastric catheter placement and the fibreoptic grading of laryngeal visualization. Efficacy of ventilation was determined from the LSP, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP), and end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2)values. Any postoperative oropharyngeal morbidity was also recorded.
Statistical Analysis:
Descriptive analysis was reported as a mean and standard deviation, median, and range of continuous variables. Demographics were analyzed using a unpaired t-test for parametric data and Chi-square test for nonparametric data. Respiratory and hemodynamic data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA to find statistical difference within and between the two groups.
Results:
LMA-S was successfully inserted in 95% of patients and i-gel in 85.5% of patients. There was a significant difference (P = 0.021) in the LSPs between the two groups (18.15 cmH2O in LMA-S and 21.28 cmH2O in the i-gel group). There was no significant difference in the PIPs, leak fraction, and the EtCO2values.
Conclusion:
Both devices are suitable for positive pressure ventilation (PPV) in anesthetized paralyzed patients. However, i-gel gives a better laryngeal seal when compared to LMA-S and may be chosen preferentially for PPV.
Keywords: I-gel, laryngeal mask airway supreme, laryngeal seal pressure, ventilation
INTRODUCTION
The laryngeal mask airway (LMA) was described by A.I.J Brain as the missing link between facemask and tracheal tube and was first used in Royal Hospital London UK in 1981.[1] The LMA-classic became available in 1989. Recently, two new devices have been developed: The LMA-supreme (LMA-S) (IntaventOrthofix, Maidenhead, UK) and i-gel (Intersurgical Ltd, Wokingham, England). I-gel is the innovative second generation supraglottic airway device from intersurgical, launched in 2007.[2] These devices with gastric access tubes are being increasingly used in surgery requiring general anesthesia and positive pressure ventilation (PPV).[3,4,5] I-gel has a noninflatable cuff that achieves a mirrored impression of the pharyngeal, laryngeal, and perilaryngeal structures, creating an anatomical seal. LMA-S is made of polyvinyl chloride with an inflatable cuff. Both devices have been successfully used in spontaneously breathing patients under anesthesia[6] and also in resuscitation and emergency scenarios and “cannot intubate, cannot ventilate” situations.[7]
As there are very few studies comparing the i-gel and LMA-S, especially in South Indian population, we proposed to assess the suitability of these two devices for PPV in this population. Our primary objective was to compare the efficacy of ventilation with either device. Our secondary objectives were to compare the ease of insertion, adequacy of positioning the device, hemodynamic response to device insertion, and any postoperative oropharyngeal morbidity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
After approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee (MD/MS/2012/23), this randomized prospective single-blinded study was conducted at a medical teaching school between 2013 and 2014. Forty-two, American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status 1 and 2 adult patients of either sex, aged between 18 and 60 years scheduled for elective surgeries of <4 h duration were enrolled into the study. Patients with a potentially difficult airway (cervical spine disease, Mallampatti classification III or IV or mouth opening of <2.5 cm), risk of aspiration, surgery spanning >4 h, and patients posted for laparoscopic surgeries were excluded. A written informed consent was taken from each patient recruited for the study. Of the expected 2400 elective surgery cases to be performed under general anesthesia 42 patients were selected by computer generated randomization chart. Patients were randomized to either LMA-S or i-gel group by sealed envelope technique.
Patients were advised a fasting period of at least 6 h. They were premedicated with tablet ranitidine 150 mg, tablet metoclopramide 10 mg, and tablet diazepam 10 mg orally on the night before surgery and the morning of surgery. In the preanesthetic preparing room, an 18 gauge venous cannula was secured and ringer's solution administered at 10 ml/kg over 30 min. Injection glycopyrrolate 0.2 mg and injection midazolam 0.03 mg/kg were administered intravenously 10–15 min before anesthesia induction. In the operating theatre, patients were positioned supine on the operating table with head resting on a doughnut. Standard monitoring of pulse oximetry, electro-cardiography, noninvasive blood pressure recording, and capnography were established. All patients were preoxygenated with 6 L/min of 100% oxygen for 3 min. Anesthesia was induced with injection fentanyl 2 mg/kg and injection 2.5 mg/kg intravenously. After confirmation of bag and mask ventilation, injection vecuronium 0.1 mg/kg was administered intravenously and patient ventilated with nitrous oxide 4 L/min, oxygen 2 L/min, and isoflurane 1.5% for 3 min before insertion of airway device was attempted.
LMA-S and i-gel were lubricated and prepared. The size of the airway device was selected based on patient's body weight in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations. For LMA-S, size 3 was used for 30–50 kg, size 4 for 50–70 kg, and size 5 for 70–100 kg body weight. For i-gel, size 3 was used for 30–60 kg, size 4 for 50–90 kg, and size 5 for >90 kg body weight. In the group, LMA-S the cuff was inflated with air to attain a cuff pressure of 60 cmH2O (44 mmHg). The aneroid blood pressure monitoring set was modified for the purpose [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
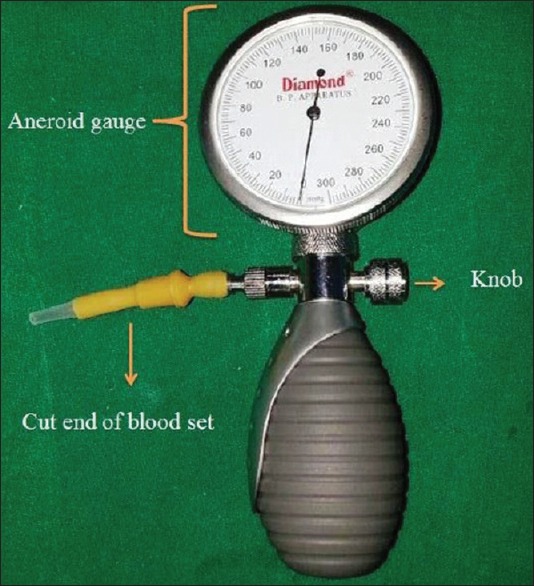

The modified aneroid blood pressure monitoring set used for measuring cuff pressure. (The blood pressure cuff is disconnected and a latex tube with luer fitting cut from a blood administration set is connected to the manometer. The luer fitting can be connected to the inflating port of the laryngeal mask airway-supreme and the cuff inflated with the use of the latex bulb. The precision-release knob is pressed to regulate the pressure)
The appearance of the first square wave end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2) trace denoted successful establishment of effective ventilation. If ventilation was not adequate, then gentle manipulation of the airway device, chin lift, jaw thrust, head extension, and neck flexion were tried. If unsuccessful, the device was removed for another insertion attempt. Two insertion attempts were allowed. In case of failure of insertion, the airway was secured according to the decision of the attending anesthesiologist.
Time for insertion was defined as the time from picking the device to the appearance of first square-wave capnograph trace.
Anesthesia was maintained with oxygen: Nitrous oxide mixture with isoflurane. Initial ventilator tidal volume was set at 8 ml/kg body weight. Volume controlled ventilation was adjusted to achieve an EtCO2 of 30–35 mmHg through tidal volumes of 8–10 ml/kg and respiratory rate of 10–16 breath/min. Hemodynamic parameters were recorded at preinduction, postinduction, and postinsertion at 1 min, 2 min, and 3 min.
Once the device was in place and ventilation was satisfactory, a gastric tube was inserted through the gastric drain tube port (size 14 FG for LMA-S and 12 FG for i-gel). Ease of insertion was graded subjectively on a scale from 1 to 3 (1 - easy, 2 - difficult, 3 - impossible).
The laryngeal seal pressure (LSP) was measured by transiently stopping ventilation and providing a fresh gas flow of 3 L/min. The adjustable pressure-limiting valve was adjusted to 40 cmH2O, and the airway pressure was monitored to see if it has reached a plateau. The plateau pressure was taken as seal pressure.
The position of the airway tube was assessed by passing a flexible intubating fibrescope (FOB) through the airway tube of the supreme LMA/i-gel, to a position 1 cm proximal to the end of the tube. The laryngeal view was scored on a four-point scale. 1 - only vocal cords visible, 2 - vocal cords plus posterior epiglottis visible, 3 - vocal cords plus anterior epiglottis visible, and 4 - vocal cords not visible.
After 15 min of anesthesia induction the inspired tidal volume (ITV), expired tidal volume (ETV), and airway pressure achieved were recorded. The difference between ITV and ETV was used to calculate leak volume (LV), that is, LV = ITV – ETV. The leak fraction (LF) is the LV divided by ITV. Maximum peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) was recorded to see if it exceeded the LSP that was determined for each patient. This determined the feasibility of PPV with the particular supraglottic airway device. Any requirement of intraoperative repositioning or replacement of the device due to an excessive air leak or airway obstruction was noted.
At the end of surgery, the effects of the neuromuscular blocking drug were reversed with intravenous neostigmine 0.04 mg/kg and glycopyrrolate 0.01 mg/kg. The airway device was removed upon return of spontaneous breathing and eye opening of the patient. The device was inspected for the presence of any visible blood. One hour after extubation, patients were assessed for jaw pain, hoarseness, and difficulty in swallowing.
Statistical methods
The sample size was calculated based on previous studies where the standard deviation of 3.5 to demonstrate a mean difference of 3 cmH2O in LSP with the power set at 0.8 and alpha set at 0.05. Our sample size was 21 patients in each group.
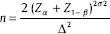
All data were recorded in Microsoft excel chart, and statistical analysis was done by Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, IBM, USA) software version 19. Descriptive analysis was reported as a mean and standard deviation, median, and range of continuous variables. Demographics were analyzed using a unpaired t-test for parametric data and Chi-square test for nonparametric data. Respiratory and hemodynamic data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA to find statistical difference within and between the two groups.
RESULTS
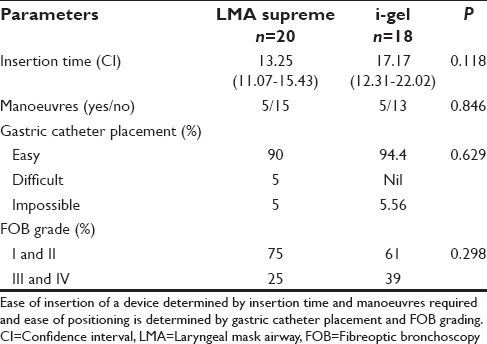
Patient demographic characteristics age, sex, and weight were comparable in both groups [Table 1]. There was a significant difference in the mean duration of surgery between the two groups (P = 0.02). In the first attempt, LMA-S device was inserted successfully in 76% of patients and i-gel in 71% of patients. In the second attempt, LMA-S device was inserted successfully in 19% of patients and i-gel in 14% of patients. The overall rate of successful insertion in LMA-S group was 95.24% and in the i-gel group was 85.71%. We were unable to insert LMA device in one patient in LMA-S group and in 3 patients of the i-gel group. There was no significant difference between the two groups with regard to the number of attempts, success rate [Figure 2], insertion time, and requirement of manoeuvres [Table 2]. In several patients in the i-gel group, the head ring had to be removed to get a better mouth opening for introducing the device into the mouth. There was no significant difference between the two groups with regard to ease of gastric catheter placement or the FOB grading of laryngeal view [Table 2].
Table 1.
Demographic data and duration of surgery
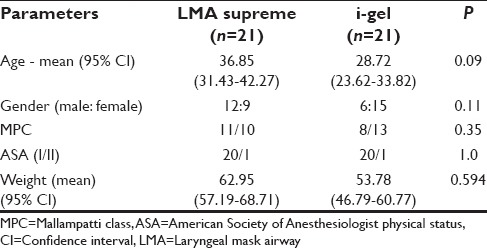
Figure 2.
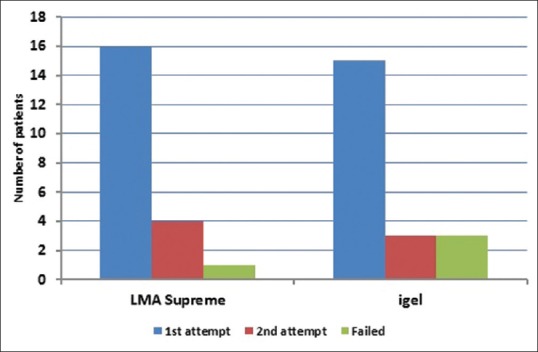
Bar diagram showing the number of attempts and failed insertions
Table 2.
Ease of insertion and assessment of positioning between the two groups
There was a significant difference in the LSP between the two groups with a P = 0.021 [Table 3]. Ventilation was adequate in all the patients in both groups. EtCO2 was maintained between 30 and 35 mmHg without altering the initial setting of ventilation [Figure 3]. In spite of Grade III and IV FOB view in 12 patients of both groups, ventilation was adequate in these patients. There was no significant difference between the two groups with regard to mean EtCO2 values, PIP, LV, and LF.
Table 3.
Efficacy of ventilation in the two groups
Figure 3.
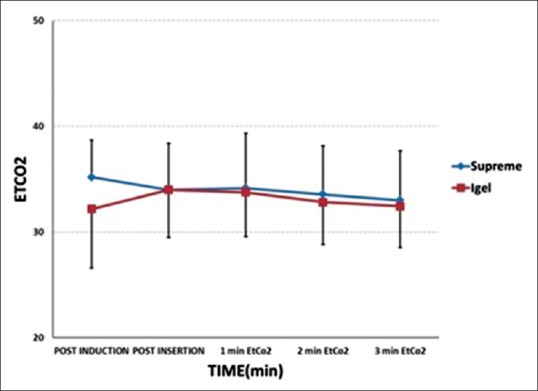
Changes in mean end-tidal carbon dioxide in the two groups
None of the patients in either group reported any postoperative oropharyngeal morbidity. Blood on the supraglottic device was observed in one patient in LMA-S in whom the device could not be inserted in 2 attempts.
There was no significant difference in heart rate between the two groups. There was a significant fall in mean blood pressures (MBPs) after induction compared to baseline in both groups [Figure 4]. At 3 min after insertion of the devices, there was a significant rise in MBP in LMA-S group when compared to the i-gel group.
Figure 4.
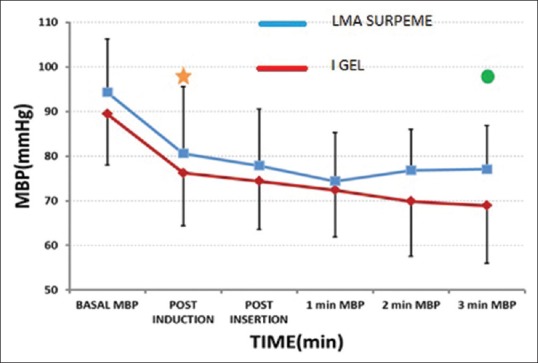
Changes in mean arterial pressures in the two groups. (-*- Laryngeal mask airway supreme, -.- i-gel) *significant fall in mean arterial pressure from baseline to postinduction in both groups, P = 0.05. O significant difference in mean arterial pressure between the groups at 3 min postinsertion = 0.003
DISCUSSION
In our study, the first attempt success rate was higher in the LMA-S group, and more placement failures occurred in the i-gel group. This is similar to the observations made by Fernández et al.[8] and Ragazzi et al.[7] in their studies which compared the insertion success rate between the two devices when inserted by operators without prior airway management expertise. Russo et al.[9] and Theiler et al.[10] have, however, reported a success rate of 95% when insertions were done by senior registrars. The higher rate of failure of i-gel insertion can be attributed to the overlap in size selection according to body weight as recommended by the manufacturer. For patients weighing between 50 and 60 kg either size 3 or 4 was chosen depending on the subjective assessment of neck size and oropharyngeal space by the resident. The three patients in whom insertion was not possible weighed 50 kg, 57 kg, and 55 kg, respectively. Size 4 i-gel was selected in two of the patients. Probably insertion would have been successful if size 3 i-gel was used. In four patients between 50 and 60 kg in whom size 3 i-gel was used, the airway was secured in the first attempt. This problem with size selection has been reported by Janakiraman et al.[11] Saran et al.[12] have also observed a similar problem with size selection of i-gel in pediatric patients.
The mean insertion time in group LMA-S was 13.2 ± 4.6 s and in group i-gel was 17.17 ± 9.7 s. Fernández et al.[8] have also observed longer insertion time (32.5 s) with i-gel compared to LMA-S (27.1 s) and lower first attempt placement rates with i-gel (86%) compared to with LMA-S (95.2%). Insertion of both devices has taken much longer time than in our study. The longer insertion times in either group could be due to the inadequate jaw relaxation because of the absence of neuromuscular blockade in their study. Theiler et al.[10] have attributed the longer insertion time for i-gel to the bulky design of the airway device. Chauhan et al.[13] have observed significantly lower insertion times with i-gel (11.12 ± 1.814 s) when compared with LMA-proseal (15.13 ± 2.91 s).
Gastric tube insertion was impossible in 5% of patients in either group. FOB grading was found to be Grade II in the patient in whom gastric tube could not be passed in LMA-S group. The FOB grading was 4 in the patient in the i-gel group in whom gastric tube could not be passed. 25% of LMA-S and 38.8% of the i-gel group had Grade III and IV FOB visualization. In spite of Grade III and IV in 12 patients, ventilation was adequate which is interpreted by the normal EtCO2 range in this group of patients. Van Zundert et al.[14] have reported a lack of correlation between the fiberoptic view and effective airway maintenance. Parthasarathy et al.[15] have also observed that clinical airway patency without signs of obstruction could be present while using LMA even though endoscopy might reveal obstruction.
The feasibility of PPV was determined by the factors such as LSP, PIP, LF, and EtCO2 changes. Our study shows a significant difference in the LSP between the two groups (P = 0.021), with the better seal in the i-gel group. Helmy et al.[16] reported similar findings in their study in spontaneously ventilating patients. Bikramjit Das et al.[17] have also observed higher seal airway leak pressures with i-gel when compared with classic LMA when used for controlled ventilation in children. Russo et al.[9] have observed higher LSP with either device (25.7 ± 5.7 cmH2O with LMA-S and 26.5 ± 5.1 cmH2O with i-gel). Ragazzi et al.[7] have noted significantly higher LSP with LMA-S (28 cmH2O) than with i-gel (24 cmH2O). The difference could be explained to be due to the different end points for LMA-S cuff inflation. They have inflated the supreme LMA cuff with a definite volume as per the manufacturer's recommendations. Chauhan et al.[13] have also observed higher mean airway sealing pressures in proseal-LMA group (29.55 ± 3.53 cmH2O) than in i-gel group (26.73 ± 2.52 cmH2O), despite filling the proseal-LMA cuff to 60 cmH2O pressure. Seet et al.[18] in their study found that filling the cuff with a specific volume had raised intra-cuff pressure to as high as 114 ± 57 mmHg in routine care group contributing to a higher LSP. Unlike our study Fernández et al.[8] and Theiler et al.[10] found that both devices have similar LSP and provide an adequate seal. In our study, there was no significant difference in LV, LF, and PIP between the groups. These findings are similar to the study of Maharjan.[19]
None of the patients in either group had any postoperative sore throat, hoarseness of voice, or dysphagia. As the mean duration of surgery in the i-gel group was less, postoperative oropharyngeal morbidity could not be compared satisfactorily between the two groups. Our findings contradicted those observed by Ragazzi et al.[7] They reported that significantly more patients complained of transient laryngeal pain with LMA-S compared with i-gel. In their study, the LMA-S cuffs were inflated with 30 and 40 ml of air, respectively, without monitoring cuff pressures. Zhang et al.[20] in their study found that LMA-S with intra-cuff pressure of 80 cmH2O had a higher incidence of postoperative pharyngolaryngeal events. Seet et al.[18] recommended the routine use of manometry to limit the intra-cuff pressure to <60 cmH2O to reduce postoperative pharyngolaryngeal complications. The lower incidence in our study was probably because the LMA-S cuff was inflated to 60 cmH2O of pressure and not with a specific volume.
Our observation of an increase in blood pressure 3 min after insertion of the device in the LMA-S group could be attributed to the minimal sympathetic response caused by inflation of the cuff.
The limitations of our study were that the investigator had limited exposure in inserting the supraglottic airway devices. The insertion of i-gel took 22–40 s for the initial cases while after gaining experience it was 8–15 s. However with LMA-S, insertion time for the initial cases was between 8 and 25 s and in later cases was also 8–16 s. I-gel owing to its bulky design requires more time for skill development. Another limitation of the study was that the FOB views in LMA-S and i-gel group do not give a similar picture. In LMA-S, the gastric drainage tube is within the ventilating port and the FOB has to be introduced either into the right or left of the draining tube. This requires bending of the FOB tip and gives a distorted view of larynx compared to a straight visualization of the larynx, when observed through i-gel.
CONCLUSION
We conclude that both devices are suitable for PPV in anesthetized paralyzed patients. However, i-gel gives a better laryngeal seal when compared to LMA-S and may be chosen preferentially for PPV. Ease of insertion, ease of gastric tube placement, and fibreoptic visualization of glottis were comparable in both groups.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest
REFERENCES
- 1.Brain AI. The laryngeal mask – A new concept in airway management. Br J Anaesth. 1983;55:801–5. doi: 10.1093/bja/55.8.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.I-gel User Guide. 7th ed. Wokingham, UK: Intersurgical Ltd.; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Timmermann A, Cremer S, Eich C, Kazmaier S, Bräuer A, Graf BM, et al. Prospective clinical and fiberoptic evaluation of the Supreme laryngeal mask airway. Anesthesiology. 2009;110:262–5. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181942c4d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Verghese C, Ramaswamy B. LMA-Supreme – A new single-use LMA with gastric access: A report on its clinical efficacy. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101:405–10. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gatward JJ, Cook TM, Seller C, Handel J, Simpson T, Vanek V, et al. Evaluation of the size 4 i-gel airway in one hundred non-paralysed patients. Anaesthesia. 2008;63:1124–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chew EE, Hashim NH, Wang CY. Randomised comparison of the LMA Supreme with the I-Gel in spontaneously breathing anaesthetised adult patients. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2010;38:1018–22. doi: 10.1177/0310057X1003800609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ragazzi R, Finessi L, Farinelli I, Alvisi R, Volta CA. LMA Supreme™ vs i-gel™ – A comparison of insertion success in novices. Anaesthesia. 2012;67:384–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.07002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fernández Díez A, Pérez Villafañe A, Bermejo González JC, Marcos Vidal JM. Supreme laryngeal mask airway vs the I-gel supraglottic airway in patients under general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation with no neuromuscular block: A randomized clinical trial. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2009;56:474–8. doi: 10.1016/s0034-9356(09)70437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Russo SG, Cremer S, Galli T, Eich C, Bräuer A, Crozier TA, et al. Randomized comparison of the i-gel™, the LMA Supreme™, and the laryngeal tube suction-D using clinical and fibreoptic assessments in elective patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2012;12:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-12-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Theiler LG, Kleine-Brueggeney M, Kaiser D, Urwyler N, Luyet C, Vogt A, et al. Crossover comparison of the laryngeal mask Supreme and the i-gel in simulated difficult airway scenario in anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:55–62. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181a4c6b9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Janakiraman C, Chethan DB, Wilkes AR, Stacey MR, Goodwin N. A randomised crossover trial comparing the i-gel supraglottic airway and classic laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia. 2009;64:674–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2009.05898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Saran S, Mishra SK, Badhe AS, Vasudevan A, Elakkumanan LB, Mishra G. Comparison of i-gel supraglottic airway and LMA-ProSeal™ in pediatric patients under controlled ventilation. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2014;30:195–8. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.130013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chauhan G, Nayar P, Seth A, Gupta K, Panwar M, Agrawal N. Comparison of clinical performance of the I-gel with LMA proseal. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2013;29:56–60. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.105798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Van Zundert TC, Brimacombe JR. Similar oropharyngeal leak pressures during anaesthesia with i-gel, LMA-ProSeal and LMA-Supreme laryngeal masks. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2012;63:35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parthasarathy S, Hemavathi B, Ravishankar M. Fibreoptic assessment of position of laryngeal mask airway. J Anaesth Clin Pharmacol. 1999;15:321–4. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Helmy AM, Atef HM, El-Taher EM, Henidak AM. Comparative study between I-gel, a new supraglottic airway device, and classical laryngeal mask airway in anesthetized spontaneously ventilated patients. Saudi J Anaesth. 2010;4:131–6. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.71250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Das B, Mitra S, Samanta A, Vijay BS. Comparison of i-gel™ supraglottic device with classic laryngeal mask airway in anesthetized paralyzed children undergoing elective surgery. Anesth Essays Res. 2012;6:180–3. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.108305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Seet E, Yousaf F, Gupta S, Subramanyam R, Wong DT, Chung F. Use of manometry for laryngeal mask airway reduces postoperative pharyngolaryngeal adverse events: A prospective, randomized trial. Anesthesiology. 2010;112:652–7. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181cf4346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Maharjan SK. I-gel for positive pressure ventilation. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2013;52:255–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang L, Seet E, Mehta V, Subramanyam R, Ankichetty SP, Wong DT, et al. Oropharyngeal leak pressure with the laryngeal mask airway Supreme™ at different intracuff pressures: A randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2011;58:624–9. doi: 10.1007/s12630-011-9514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


