Abstract
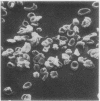
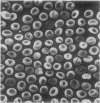
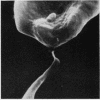
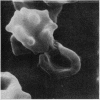
Examination by scanning electron microscopy of erythrocytes from three cases of microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia demonstrated the presence of adherent cells. Although in some cases this appeared to be due to a thin strand, presumably fibrin, between the erythrocytes, in most instances there was intimate contact and this was invariably associated with damage to the red cell surface membrane.
It is considered that the adherence is predominantly due to altered physico-chemical properties of the surface membrane of the red blood cell and that further morphological abnormalities may result from the intravascular stresses to which the paired cells are subjected.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAIN M. C., DACIE J. V., HOURIHANE D. O. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the possible role of vascular lesions in pathogenesis. Br J Haematol. 1962 Oct;8:358–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Brain M. C. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Experimental models of microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Nov;61(11 Pt 1):1134–1137. doi: 10.1177/003591576806111P132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Rubenberg M. L., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: mechanisms of red-cell fragmentation: in vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mc Kay D. G. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Pathology, diagnosis and therapy of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Nov;61(11 Pt 1):1129–1134. doi: 10.1177/003591576806111P131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder E. Effect of basic proteins on the adhesiveness of red cells. Nature. 1966 Jan 15;209(5020):307–308. doi: 10.1038/209307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenberg M. L., Regoeczi E., Bull B. S., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the experimental production of haemolysis and red-cell fragmentation by defibrination in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):627–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salsbury A. J., Clarke J. A. New method for detecting changes in the surface appearance of human red blood cells. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jul;20(4):603–610. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Jones D. B., Nelson D. A. Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia in rats with malignant hypertension. Blood. 1968 Aug;32(2):278–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]