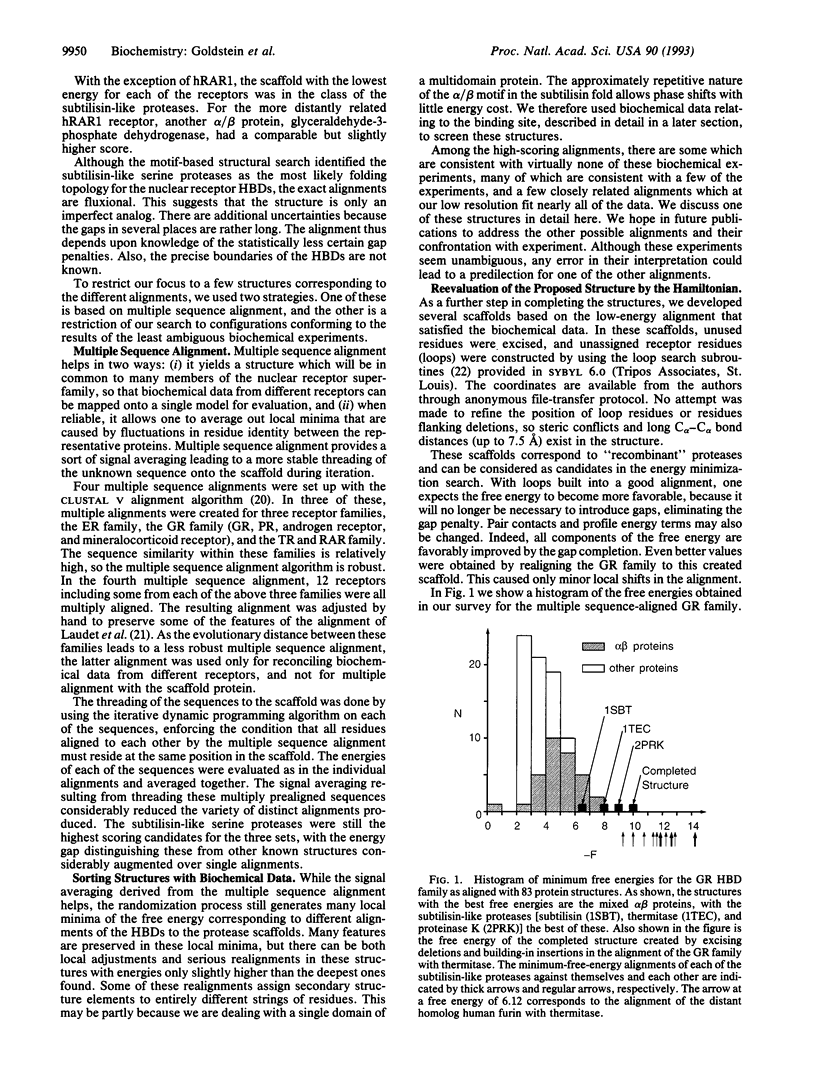
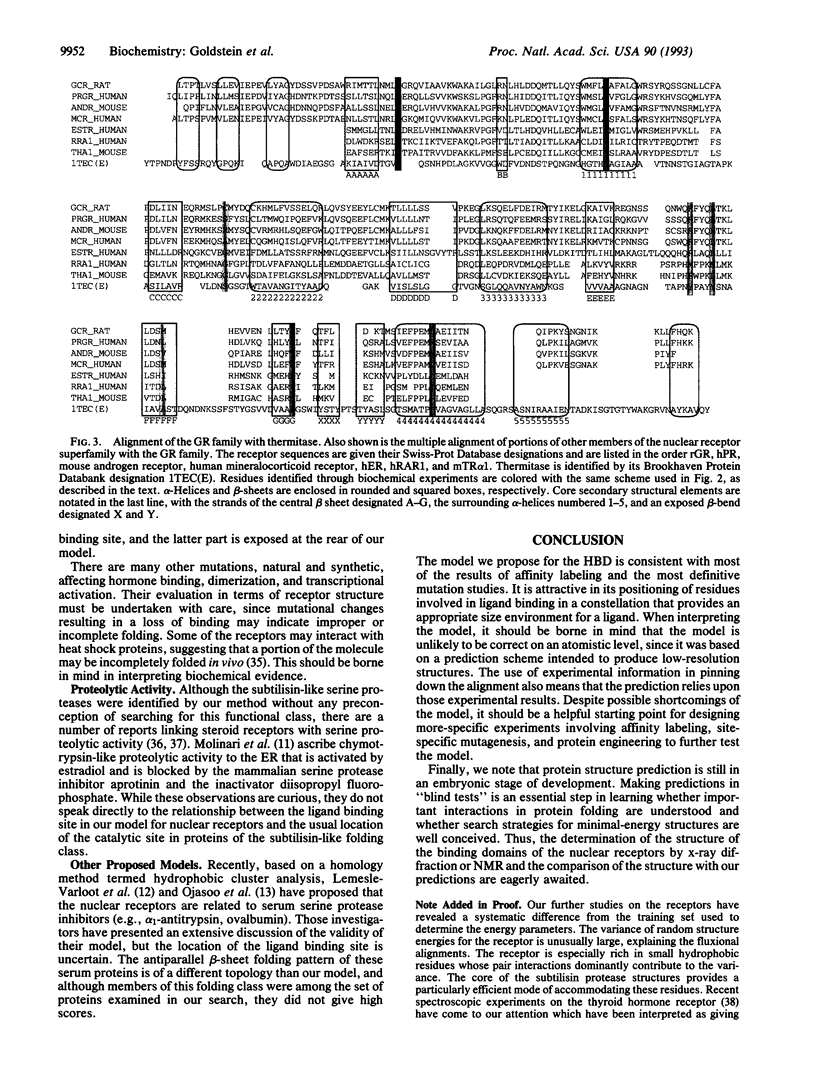
Abstract
We have used a motif-based structural search method to identify structural homologs of the hormone binding domains of the nuclear receptors from among a set of known protein structures and have found the closest similarity with members of the subtilisin-like serine proteases. These proteins consist of an open twisted sheet of parallel beta-strands flanked on both sides by alpha-helices. The alignment with the protease scaffold was refined by using multiple sequence prealignment of different sets of nuclear receptors, and alternative model structures were screened by considering their consistency with the results of biochemical experiments defining the ligand binding pocket. In the most favored model, nearly all of the residues thought to be involved in ligand binding map to a pocket of appropriate dimensions where the subtilisin-like proteases have their active site. The three-dimensional model that we propose for the hormone binding domains of the nuclear receptors provides a framework for the design of experiments to further investigate nuclear receptor structure and function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. E., Kimlinger W. R. Protease substrates inhibit binding of 3H-R5020 to the G-fragment in chick oviduct cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändeén C. I. Relation between structure and function of alpha/beta-proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Aug;13(3):317–338. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J., Strömstedt P. E., Persson B., Cederlund E., Gustafsson J. A., Jörnvall H. Identification of hormone-interacting amino acid residues within the steroid-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor in relation to other steroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6842–6846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti P. K., Garabedian M. J., Yamamoto K. R., Simons S. S., Jr Creation of "super" glucocorticoid receptors by point mutations in the steroid binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22075–22078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielian P. S., White R., Lees J. A., Parker M. G. Identification of a conserved region required for hormone dependent transcriptional activation by steroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A. V., Reva B. A. A search for the most stable folds of protein chains. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):497–499. doi: 10.1038/351497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan S., Bashirelahi N., Young J. D., Cohen S. P. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) inhibits 17 beta-estradiol binding to estrogen receptor from human prostate. Life Sci. 1987 Dec 21;41(25):2767–2776. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90470-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia T., Benhamou B., Gofflo D., Vergezac A., Philibert D., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Switching agonistic, antagonistic, and mixed transcriptional responses to 11 beta-substituted progestins by mutation of the progesterone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2071–2078. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1337143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godzik A., Skolnick J. Sequence-structure matching in globular proteins: application to supersecondary and tertiary structure determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12098–12102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. A., Luthey-Schulten Z. A., Wolynes P. G. Optimal protein-folding codes from spin-glass theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4918–4922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. A., Luthey-Schulten Z. A., Wolynes P. G. Protein tertiary structure recognition using optimized Hamiltonians with local interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9029–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow K. W., Smith D. N., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Greene G. L., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Identification of cysteine 530 as the covalent attachment site of an affinity-labeling estrogen (ketononestrol aziridine) and antiestrogen (tamoxifen aziridine) in the human estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17476–17485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Hänni C., Coll J., Catzeflis F., Stéhelin D. Evolution of the nuclear receptor gene superfamily. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Kliewer S. A., Provencal J., Wright P. E., Evans R. M. Structure of the retinoid X receptor alpha DNA binding domain: a helix required for homodimeric DNA binding. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1117–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.8388124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemesle-Varloot L., Ojasoo T., Mornon J. P., Raynaud J. P. A model for the determination of the 3D-spatial distribution of the functions of the hormone-binding domain of receptors that bind 3-keto-4-ene steroids. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):369–388. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90363-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Bowie J. U., Eisenberg D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):83–85. doi: 10.1038/356083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinari A. M., Abbondanza C., Armetta I., Medici N., Minucci S., Moncharmont B., Nigro V., Puca G. A. Proteolytic activity of the purified hormone-binding subunit in the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4463–4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. Interaction of hsp90 with steroid receptors: organizing some diverse observations and presenting the newest concepts. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):C69–C76. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90198-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese J. C., Wooge C. H., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Identification of two cysteines closely positioned in the ligand-binding pocket of the human estrogen receptor: roles in ligand binding and transcriptional activation. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2160–2166. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenkin P. S., Yarmush D. L., Fine R. M., Wang H. J., Levinthal C. Predicting antibody hypervariable loop conformation. I. Ensembles of random conformations for ringlike structures. Biopolymers. 1987 Dec;26(12):2053–2085. doi: 10.1002/bip.360261207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Leunissen J. A., Dijkstra B. W. Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinases. Protein Eng. 1991 Oct;4(7):719–737. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.7.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Pumphrey J. G., Rudikoff S., Eisen H. J. Identification of cysteine 656 as the amino acid of hepatoma tissue culture cell glucocorticoid receptors that is covalently labeled by dexamethasone 21-mesylate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9676–9680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippl M. J. Calculation of conformational ensembles from potentials of mean force. An approach to the knowledge-based prediction of local structures in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):859–883. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippl M. J., Weitckus S. Detection of native-like models for amino acid sequences of unknown three-dimensional structure in a data base of known protein conformations. Proteins. 1992 Jul;13(3):258–271. doi: 10.1002/prot.340130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömstedt P. E., Berkenstam A., Jörnvall H., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. Radiosequence analysis of the human progestin receptor charged with [3H]promegestone. A comparison with the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12973–12977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]