Abstract
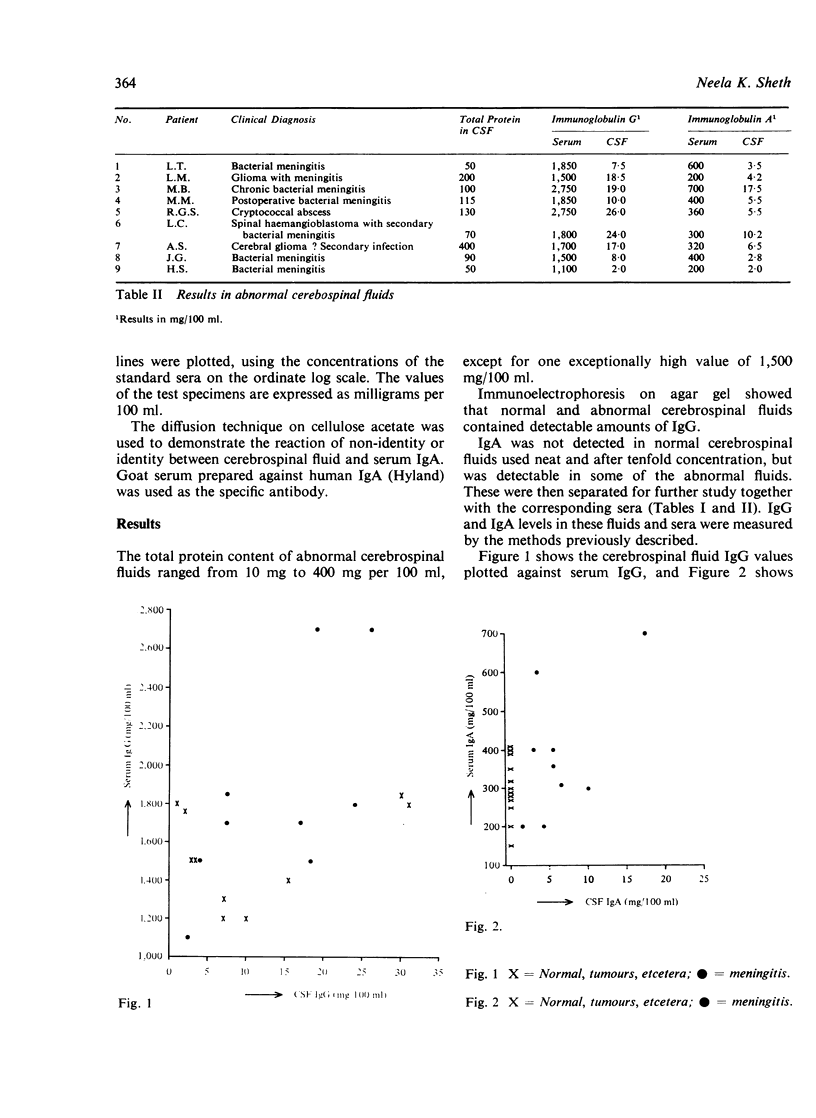
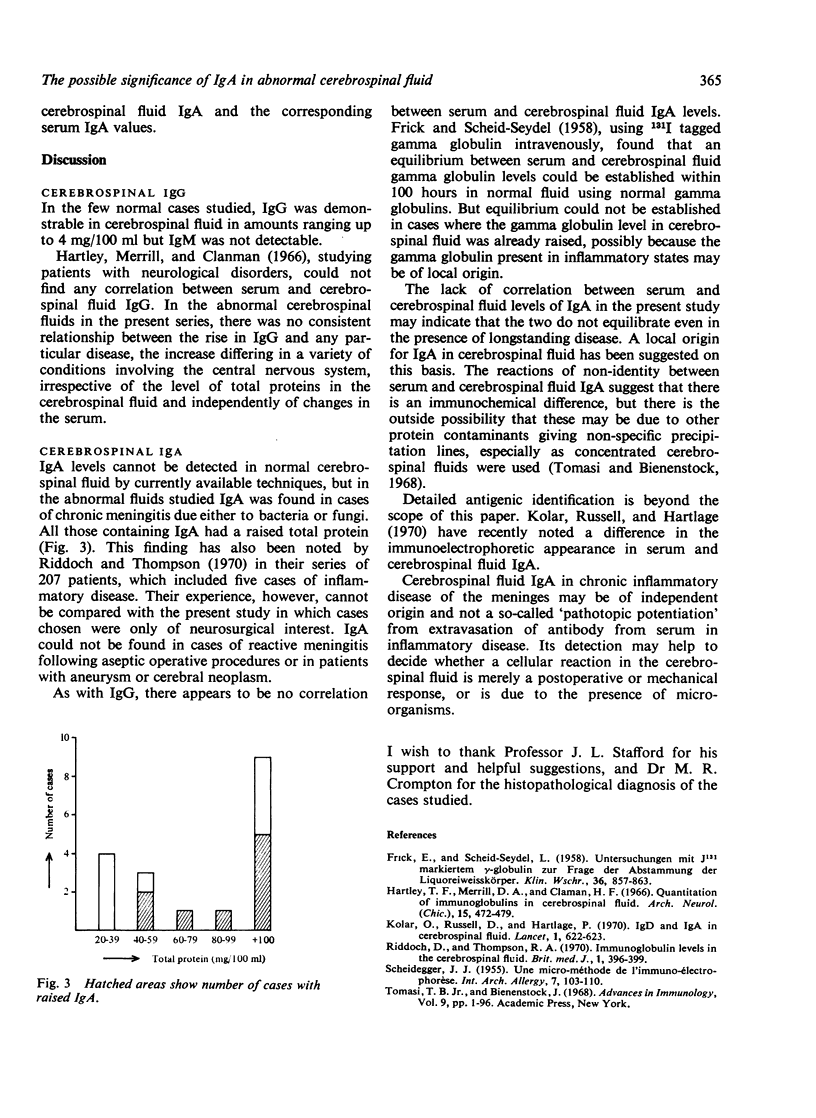
In a study of 21 patients with disease of the central nervous system IgA, which is normally absent, could be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid in the presence of meningitis of bacterial or fungal origin: the concentration of IgA in the cerebrospinal fluid could not, however, be correlated with serum levels. A reaction of non-identity has been demonstrated between serum and cerebrospinal fluid IgA using the diffusion technique on cellulose acetate.
These data seem to suggest that cerebrospinal fluid IgA is produced independently of serum IgA and can be detected in measurable amounts where microorganisms are the cause of inflammatory disease of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF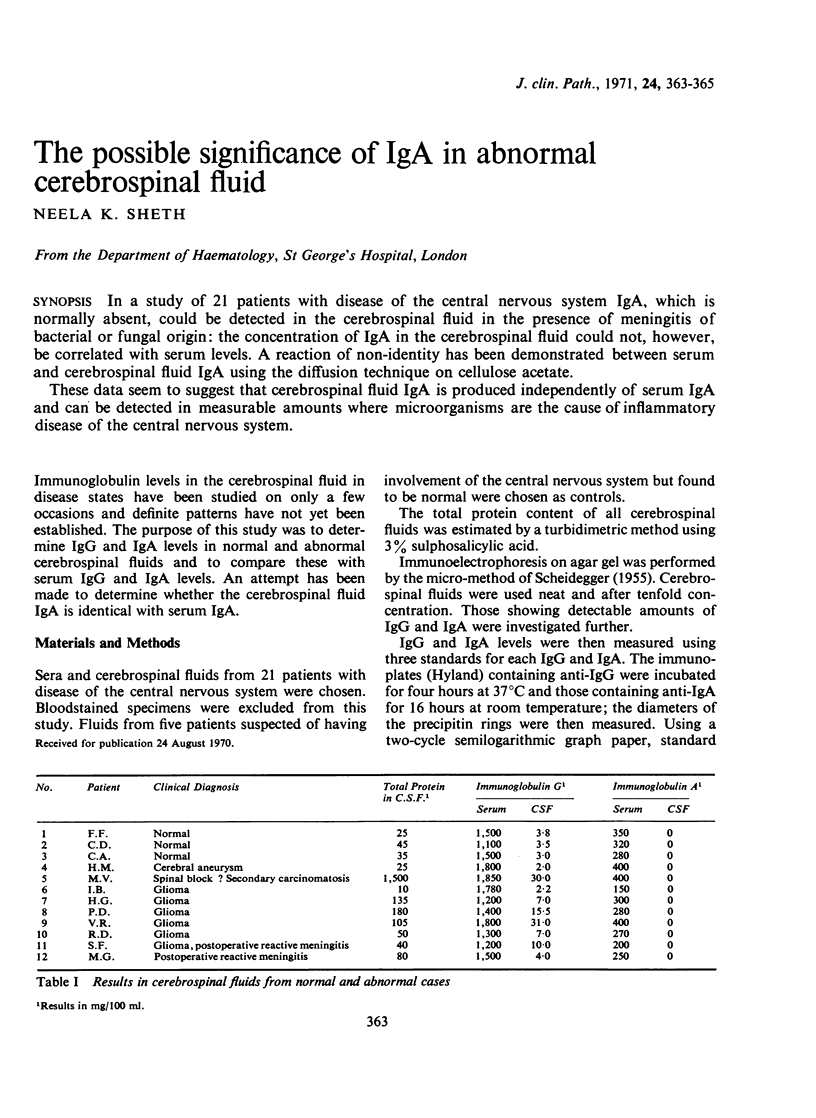
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRICK E., SCHEID-SEYDEL L. Untersuchungen mit J 131-markiertem gamma-Globulin zur Frage der Abstammung der Liquoreiweisskörper. Klin Wochenschr. 1958 Sep 15;36(18):857–863. doi: 10.1007/BF01485232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley T. F., Merrill D. A., Claman H. N. Quantitation of immunoglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid. Arch Neurol. 1966 Nov;15(5):472–479. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470170026003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolar O., Russell D., Hartlage P. IgD and IgA in cerebrospinal fluid. Lancet. 1970 Mar 21;1(7647):622–623. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddoch D., Thompson R. A. Immunoglobulin levels in the cerebrospinal fluid. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 14;1(5693):396–399. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5693.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


