Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akinkugbe O. O., Lewis E. A., Montefiore D., Okubadejo O. A. Trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in typhoid. Br Med J. 1968 Sep 21;3(5620):721–722. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5620.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. E., Kennedy A. C., McGeachie J., McDonald G. A. Sulphamethoxazole-trimethoprim therapy in urinary tract infection with reference to its haematological effects. Scott Med J. 1969 Oct;14(10):355–360. doi: 10.1177/003693306901401004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie J., Macqueen I. A., Livingstone D. Effect of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole on typhoid and salmonella carriers. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 8;3(5718):318–319. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5718.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
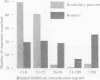
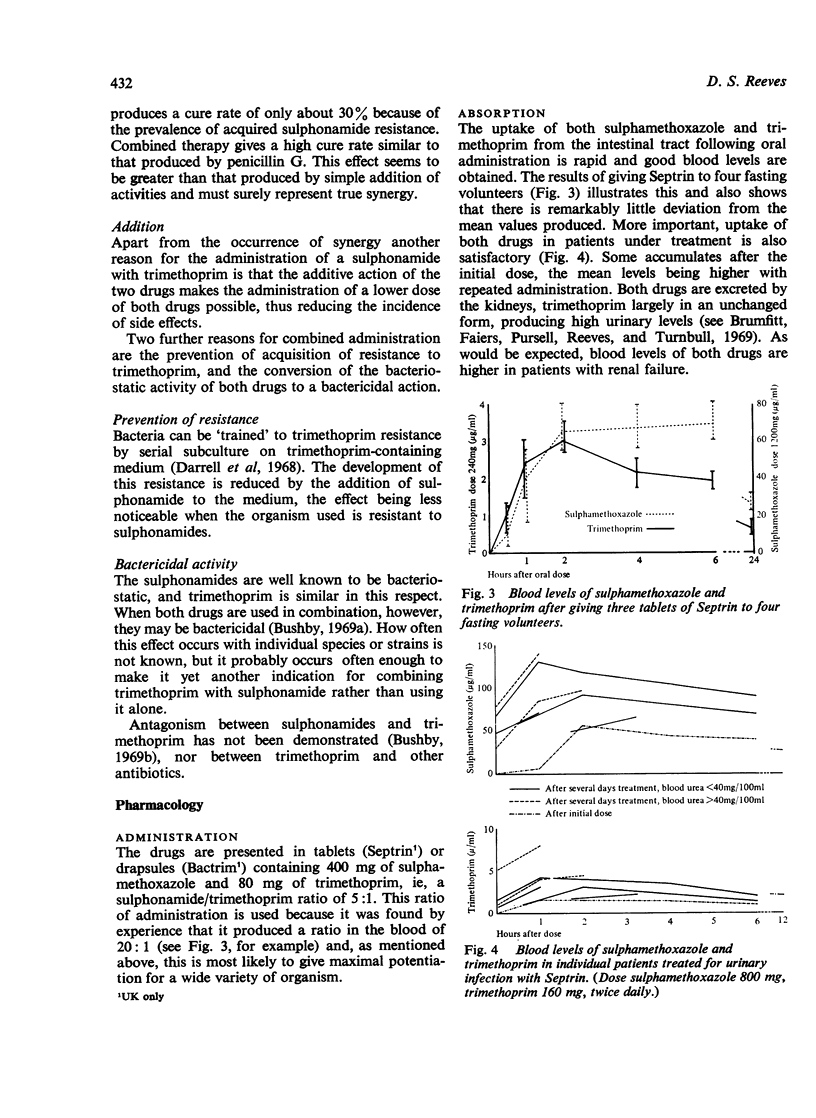
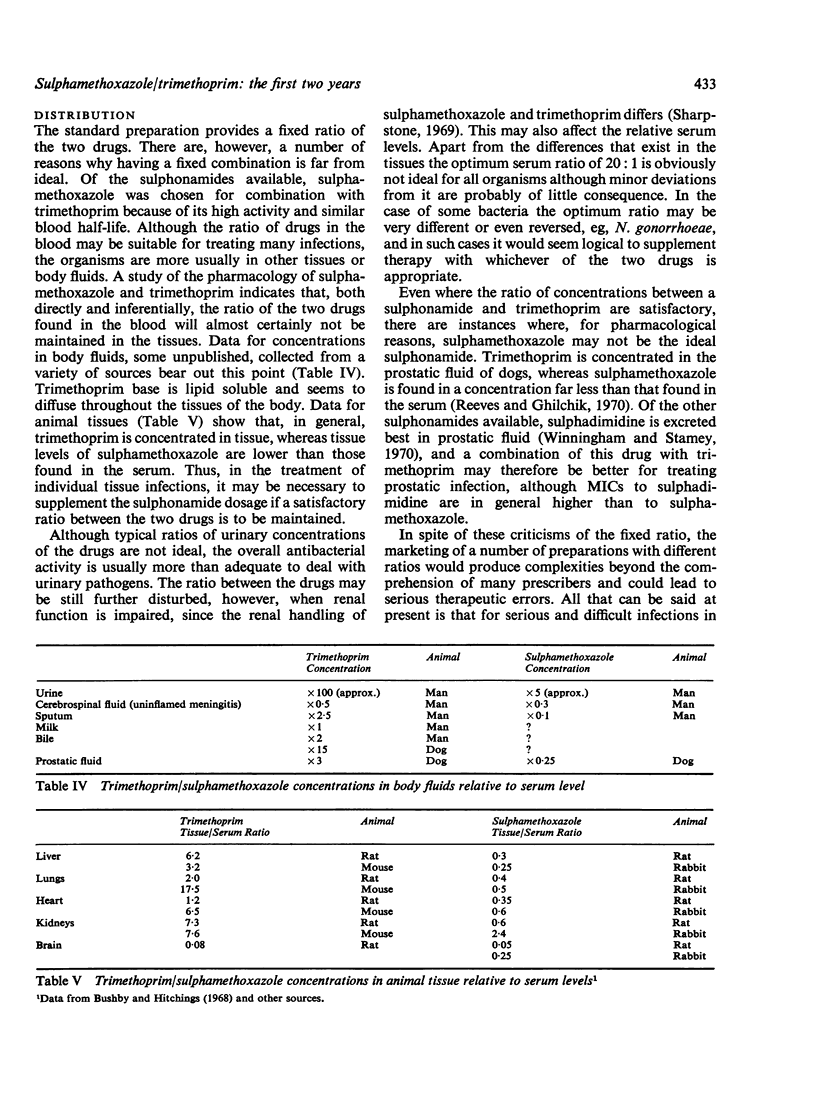
- Brumfitt W., Faiers M. C., Pursell R. E., Reeves D. S., Turnbull A. R. Bacteriological, pharmacological and clinical studies with trimethoprim-sulphonamide combinations with particular reference to the treatment of urinary infections. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Percival A. Laboratory control of antibiotic therapy in urinary tract infection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):329–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushby S. R. Combined antibacterial action in vitro of trimethoprim and sulphonamides. The in vitro nature of synergy. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushby S. R., Hitchings G. H. Trimethoprim, a sulphonamide potentiator. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 May;33(1):72–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhni E. Chemotherapeutic activity of the combination of trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in infections of mice. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER R. G., WALD M. SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF PROTEUS SEPTICAEMIA WITH A NEW DRUG TRIMETHOPRIM. Med J Aust. 1964 Jul 18;2:93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. R., Nicol C. S. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Feb;46(1):31–33. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. E., Montgomery W. G. Combined trimethoprim-sulfisoxazole therapy of urinary infections. Clinical studies. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven J. L., Pugsley D. J., Blowers R. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in acute osteomyelitis due to penicillin-resistant staphylococci in Uganda. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 25;3(5716):201–203. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5716.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka G. W., Knight G. J. Therapeutic trial of trimethoprim as a potentiator of sulphonamides in gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1967 Sep;43(3):161–165. doi: 10.1136/sti.43.3.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka G. W. Therapeutic trial of some genital infections with trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Trimethoprim: laboratory and clinical studies. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):202–209. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid Z., Hassan A., Wahab M. F., Sanborn W. R., Kent D. C., Hathout S. E. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in enteric fevers. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 8;3(5718):323–324. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5718.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowle A. S., Zorab P. A. Esch. coli endocarditis successfully treated with oral trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole. Br Heart J. 1970 Jan;32(1):127–129. doi: 10.1136/hrt.32.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharagozloo R. A., Naficy K., Mouin M., Nassirzadeh M. H., Yalda R. Comparative trial of tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in eradication of Vibrio cholerae El Tor. Br Med J. 1970 Oct 31;4(5730):281–282. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5730.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghilchik M. W., Morris A. S., Reeves D. S. Immunosuppressive powers of the antibacterial agent trimethoprim. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):393–394. doi: 10.1038/227393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg R. N., Kolbe R. Trimethoprim in the treatment of urinary infections in hospital. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):545–547. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. T., Drew C. D., Johnson T. B., Jarvis J. D. Trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in the treatment of chronic chest infections. Chemotherapy. 1969;14(3):151–157. doi: 10.1159/000220624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. T. Single-blind comparative trial of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole and ampicillin in the treatment of exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 22;4(5681):470–473. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5681.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. B., Fein S. A., Brodsky I. Effects of trimethoprim on folate metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 Sep-Oct;9(5):550–560. doi: 10.1002/cpt196895550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamat S. A. Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole and chloramphenicol in enteric fever. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 8;3(5718):320–322. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5718.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal S., Bhalla K. K. Comparison of tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in acute episodes in chronic chest infections. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):91–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal S., Modawal K. K., Fowle A. S., Peach B., Popham R. D. Acute brucellosis treated with trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 1;3(5717):256–257. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5717.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcovitch H., Norman A. P. Treatment of nocardiosis. Lancet. 1970 Aug 15;2(7668):362–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzaria R. N., Walton I. G., Pickering D. Neonatal meningitis treated with trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole. Br Med J. 1969 May 24;2(5655):511–512. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5655.511-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray I. G., Mahgoub E. S. Treatment of nocardiosis. Lancet. 1970 Aug 15;2(7668):362–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noall E. W., Sewards H. F., Waterworth P. M. Successful Treatment of a Case of Proteus Septicaemia. Br Med J. 1962 Oct 27;2(5312):1101–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5312.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady F., Chamberlain D. A., Stark J. E., Cattell W. R., Sardeson J. M., Fry I. F., Spiro F. I., Waters A. H. Long-term, low-dosage, trimethoprim-sulphonamide in the control of chronic bacteriuria. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva I. P., Salokannel S. J., Takkunen J. T. Thrombocytopenia in heart failure. Preliminary report. Acta Med Scand. 1970 May;187(5):429–430. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb02966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Ridley M., Rimmer D., Lynn R. In-vitro activity of twelve antibacterial agents against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1970 Feb 7;1(7641):263–265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90635-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley D. J., Mwanje L., Pearson C., Blowers R. Use of trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in tropical Africa: typhoid fever, salmonella typhi carriage and staphylococcus aureus sepsis. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Faiers M. C., Pursell R. E., Brumfitt W. Trimethoprim--sulphamethoxazole: comparative study in urinary infection in hospital. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):541–544. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Ghilchik M. Secretion of the antibacterial substance trimethoprim in the prostatic fluid of dogs. Br J Urol. 1970 Feb;42(1):66–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1970.tb11909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savidge R. S. Trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in ulcerative colitis. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):101–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Koechlin B. A., Weinfeld R. E. Spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of trimethoprim in body fluids. Chemotherapy. 1969;14(Suppl):22–29. doi: 10.1159/000220652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udall V. Toxicology of sulphonamide-trimethoprim combinations. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):42–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterworth P. M. Practical aspects of testing sensitivity to trimethoprim and sulphonamide. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Brumfitt W., Condie A. P., Reeves D. S. The treatment of bacteriuria in pregnant women with sulphamethoxazole and thrimethoprim. A microbiological, clinical and toxicological study. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winningham D. G., Stamey T. A. Diffusion of sulfonamides from plasma into prostatic fluid. J Urol. 1970 Oct;104(4):559–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J., Grimble A. S. Sulphamethoxazole combined with 2-4-diamino-pyrimidines in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Feb;46(1):34–36. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]