Figure 4. The migration, deformability and adhesion capacity of MV4-11 cells is modulated by CD97 knock down.
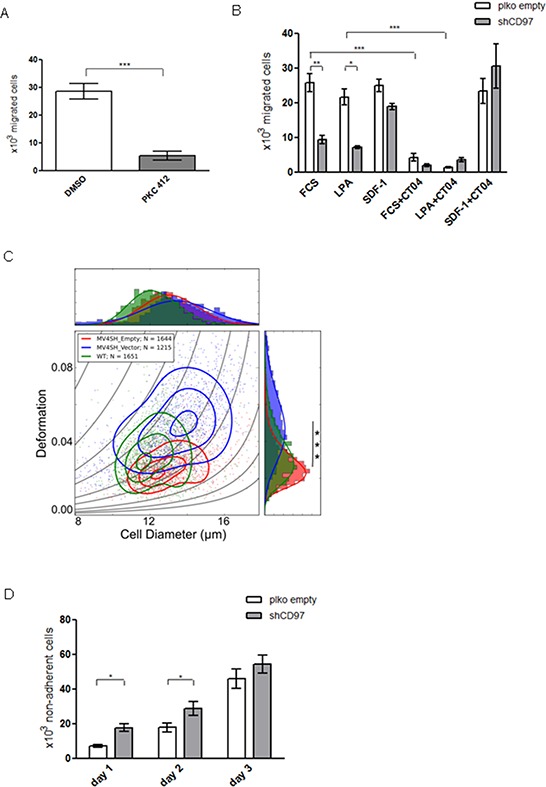
A. Trans-well migration of MV4-11 cells towards FCS in a Boyden chamber assay was significantly inhibited after treatment with PKC412. Data is represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, p < 0.001 (***). B. Migration capacity of CD97 knock down MV4-11 cells is significantly decreased in comparison to control cells towards FCS and LPA but not affected towards SDF-1. Pre-treatment of the cells with the Rho inhibitor CT04 resulted in decreased migration potency of both cell types towards FCS and LPA whereas migration towards SDF-1 was not impaired. Data is represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, p < 0.05 (*); p < 0.01 (**); p < 0.001 (***). C. RT-DC on MV4-11 cells. Mechanical properties (wildtype - green, empty vector - red, CD97 down-regulated - blue) were determined in separate experiments and revealed distinct populations in size and deformation (indicated by 1d projection at top and right). Data acquisition was carried out in a 20 μm x 20 μm channel at a flow rate of 0.04 μl/s and summarize n = 2,688 (wildtype), n = 2009 (empty vector) and n = 2404 (CD97) single cell measurements. Curved lines are isoelasticity lines and contour lines represent 90%, 50% and 20% of maximum intensity, respectively. Statistical significance between wildtype and CD97 knock down (***p < 0.00001). D. Adhesion of CD97 knock down and control MV4-11 cells to a MSC monolayer was compared at 1, 2 and 3 days by counting the cells in the supernatant. Data is represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, p < 0.05 (*).
