Figure 4. Inhibition of c-MYC protein expression and DNA-binding activity by shikonin, its derivatives, 10058-F4 and 10074-G5 in U937 cells.
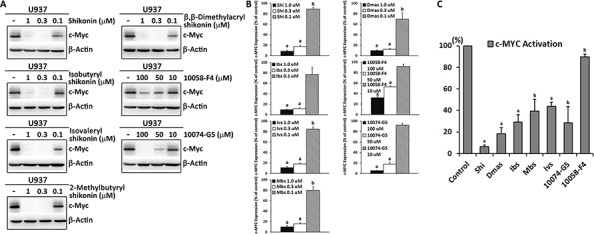
A. Western blot analysis of c-MYC expression after 24 h treatment with these compounds. β-Actin was used as loading control. B. Digitalized graphs of c-MYC protein levels as quantified by FluorChem Q. Data were normalized to β-actin expression and represented as means ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3). a, p < 0.01 vs. control; b, p < 0.05 vs. control, calculated by two-tailed Student's t test. C. Determination of DNA binding activity of c-MYC by Trans-AM ELISA-based kit. Nuclear extracts were obtained after treatment of U937 cells with 0.3 μM shikonin and its derivatives or 50 μM 10058-F4 and 10074-G5 for 24 h. Protein/oligonucleotide binding activity was measured by colorimetric analysis with 10 μg of nuclear extracts. The absorbance at 450 nm was recorded by an ELISA plate reader. Results are presented as percentage with respect to the untreated control and represented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3). a, p < 0.01 vs. control; b, p < 0.05 vs. control, calculated by two-tailed Student's t test. Shi, shikonin; Ibs, isobutyrylshikonin; Dmas, β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin; Ivs, isovalerylshikonin; Mbs, 2-methylbutyrylshikonin.
