Abstract
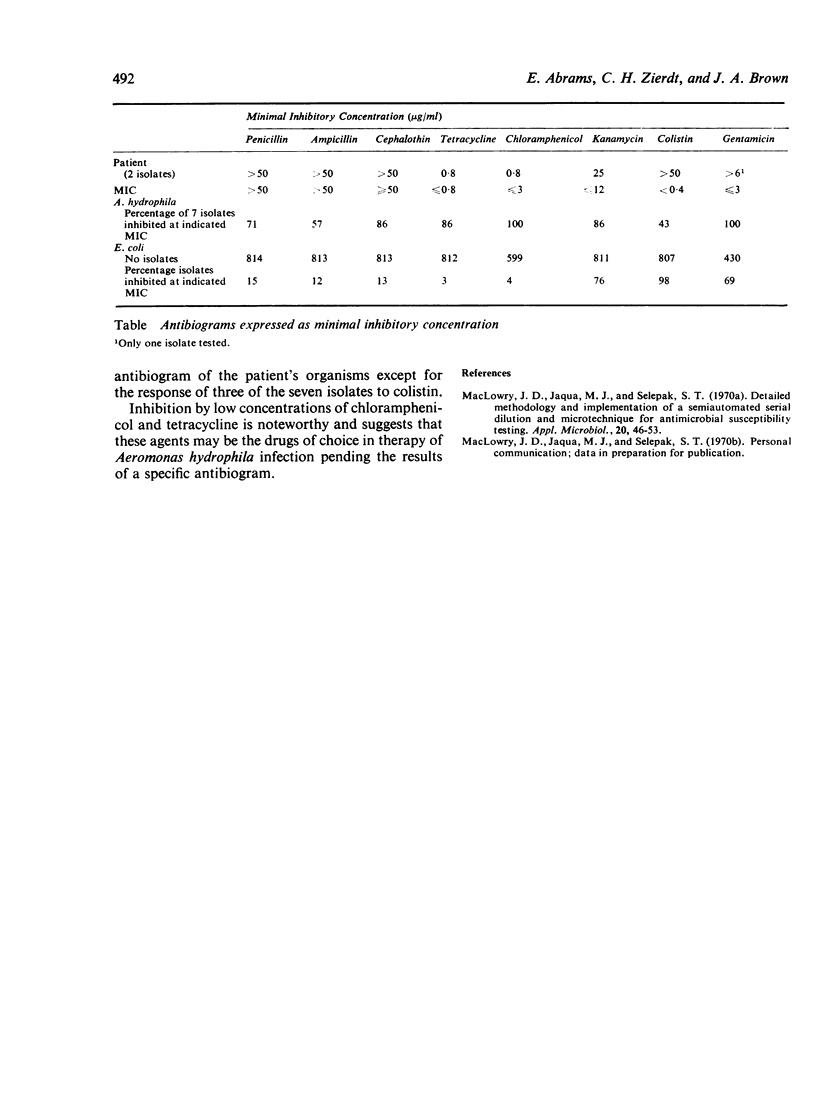
A Gram-negative bacillus isolated from the blood of a leukaemic patient with septicaemia was identified on the basis of common tests as Escherichia coli. However, the organism's antibiogram was atypical of E. coli and led to its re-examination and correct identification as Aeromonas hydrophila. A. hydrophila is sensitive to chloramphenicol and tetracycline, characteristics useful in differentiation from E. coli. A simple test differentiating this organism from the Enterobacteriaceae is the oxidase test. A. hydrophila is oxidase positive.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MacLowry J. D., Jaqua M. J., Selepak S. T. Detailed methodology and implementation of a semiautomated serial dilution microtechnique for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):46–53. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.46-53.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


