Abstract
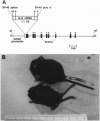
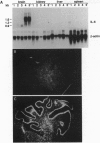
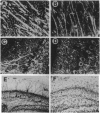
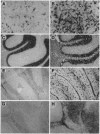
Cytokines are thought to be important mediators in physiologic and pathophysiologic processes affecting the central nervous system (CNS). To explore this hypothesis, transgenic mice were generated in which the cytokine interleukin 6 (IL-6), under the regulatory control of the glial fibrillary acidic protein gene promoter, was overexpressed in the CNS. A number of transgenic founder mice and their offspring exhibited a neurologic syndrome the severity of which correlated with the levels of cerebral IL-6 expression. Transgenic mice with high levels of IL-6 expression developed severe neurologic disease characterized by runting, tremor, ataxia, and seizure. Neuropathologic manifestations included neuro-degeneration, astrocytosis, angiogenesis, and induction of acute-phase-protein production. These findings indicate that cytokines such as IL-6 can have a direct pathogenic role in inflammatory, infectious, and neurodegenerative CNS diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham C. R. The role of the acute-phase protein alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in brain dysfunction and injury. Res Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80047-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley J. E., Bishop G. A., St John T., Frelinger J. A. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Strauss S., Schreiter-Gasser U., Ganter U., Schlegel P., Witt I., Yolk B., Berger M. Interleukin-6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin indicate an acute-phase state in Alzheimer's disease cortices. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 8;285(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80737-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Cutri A., Wilson A., Harrison L. C. Evidence for IL-6 production by and effects on the pancreatic beta-cell. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1188–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Goldman J. E. Regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in CNS development and in pathological states. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Jun;8(4-6):283–292. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston M., Mucke L. Molecular profile of reactive astrocytes--implications for their role in neurologic disease. Neuroscience. 1993 May;54(1):15–36. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90380-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I., Costa F., Grau Veciana J. M. Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease: a golgi study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 May-Jun;7(3):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Leist T. P., Meager A., Gallo P., Leppert D., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):449–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Malipiero U. V., Leist T. P., Zinkernagel R. M., Schwab M. E., Fontana A. On the cellular source and function of interleukin 6 produced in the central nervous system in viral diseases. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):689–694. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Frei K., Rordorf C., Lazdins J., Tavolato B., Fontana A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jul;23(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Woodward J., Young D. G., Krebs J. F., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 injected into mammalian brain stimulates astrogliosis and neovascularization. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2485–2490. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02485.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Adelman D. C., Sreedharan S. P. Neuroimmunology. Adv Immunol. 1990;48:161–190. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60754-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Bukasa K., Sindic C. J., Van Damme J., Van Snick J. Elevated levels of the 26K human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin 6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the central nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):320–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis J. D., Lee M., Davidson D. R., Hill R. E. Isolation of two cDNAs encoding novel alpha 1-antichymotrypsin-like proteins in a murine chondrocytic cell line. Gene. 1991 Oct 15;106(2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90201-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laterra J., Goldstein G. W. Astroglial-induced in vitro angiogenesis: requirements for RNA and protein synthesis. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1231–1239. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A. P., Pitha P. M., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines by astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or a neurotropic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Achim C. L., Ge N., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Wiley C. A. Spectrum of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neocortical damage. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Ge N., Achim C. L., Hansen L. A., Wiley C. A. Selective neuronal vulnerability in HIV encephalitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Nov;51(6):585–593. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199211000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 and related cytokines in brain development: normal and pathological. Dev Neurosci. 1992;14(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000111642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro B., Itin A., Sachs L., Keshet E. Pattern of interleukin 6 gene expression in vivo suggests a role for this cytokine in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucke L., Oldstone M. B., Morris J. C., Nerenberg M. I. Rapid activation of astrocyte-specific expression of GFAP-lacZ transgene by focal injury. New Biol. 1991 May;3(5):465–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata-Salamán C. R. Immunoregulators in the nervous system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1991 Summer;15(2):185–215. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. M., Liu D., Setter E., Bhargava M., Goldberg I. D. Interleukin-6 stimulates motility of vascular endothelium. EXS. 1991;59:194–205. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7494-6_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Cowan N. J. Intragenic sequences affect the expression of the gene encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Neurochem. 1991 Aug;57(2):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Raine C. S., Brosnan C. F. Proliferation of astrocytes in vitro in response to cytokines. A primary role for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Taniguchi H., Yoda K., Shimizu M., Sakiyama S. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for mouse cytoskeletal beta-actin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2829–2829. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Wong R. K. Cellular mechanism of neuronal synchronization in epilepsy. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):745–747. doi: 10.1126/science.7079735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Szikora J. P., Renauld J. C., Van Roost E., Boon T., Simpson R. J. cDNA cloning of murine interleukin-HP1: homology with human interleukin 6. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):193–197. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe M. N., Sarna G. S., Wadhwa M., Hayes G. M., Loughlin A. J., Tinker A., Cuzner M. L. Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Sep;33(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90110-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong V. W., Moumdjian R., Yong F. P., Ruijs T. C., Freedman M. S., Cashman N., Antel J. P. Gamma-interferon promotes proliferation of adult human astrocytes in vitro and reactive gliosis in the adult mouse brain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7016–7020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N., Martin J. L., Stella N., Magistretti P. J. Arachidonic acid stimulates glucose uptake in cerebral cortical astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4042–4046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]