Abstract
By screening an Arabidopsis expression library with an antiserum against chloroplast envelope proteins, we have isolated a partial cDNA with an open reading frame that encodes a polypeptide similar to P-type cation-transporting ATPases. The corresponding genomic clone was isolated and the complete coding sequence was deduced after identification and mapping of introns. The gene has been designated PEA1 (plastid envelope ATPase) and the predicted polypeptide PEA1p. PEA1p has 946 amino acids and a molecular mass of 104 kDa. This protein is 40-44% identical to various mammalian plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPases but lacks the C-terminal calmodulin binding domain present in the mammalian polypeptides. When aligned with mammalian plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPases, PEA1p has a 70- to 80-amino acid N-terminal region that extends beyond the N terminus of these enzymes. This extension has some similarity to the transit peptide of the plastid envelope phosphate translocator and may function to target the protein to the plastid. Antibodies raised against a portion of PEA1p recognize a single 90- to 95-kDa polypeptide in chloroplast inner envelope preparations. Transcript abundance as determined by RNase protection was found to be 7- to 9-fold higher in roots than in leaves. Possible roles for a plastid envelope calcium pump are suggested.
Full text
PDF


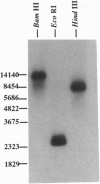
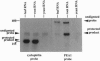
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand J. J., Becker D. W. Evidence for direct roles of calcium in photosynthesis. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1984 Aug;16(4):239–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00744278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., MacLennan D. H. Functional consequences of alterations to polar amino acids located in the transmembrane domain of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6262–6267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce R., Joyard J. Biochemistry and function of the plastid envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:173–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreses-Werringloer U., Fischer K., Wachter E., Link T. A., Flügge U. I. cDNA sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the precursor of the 37-kDa inner envelope membrane polypeptide from spinach chloroplasts. Its transit peptide contains an amphiphilic alpha-helix as the only detectable structural element. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 30;195(2):361–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Mulligan J. T., Ramer S. W., Spottswood M., Davis R. W. Lambda YES: a multifunctional cDNA expression vector for the isolation of genes by complementation of yeast and Escherichia coli mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügge U. I., Fischer K., Gross A., Sebald W., Lottspeich F., Eckerskorn C. The triose phosphate-3-phosphoglycerate-phosphate translocator from spinach chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA clone and import of the in vitro synthesized precursor protein into chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):39–46. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S., Short T. W., Ray P. M., Pratt L. H., Briggs W. R. Light-mediated changes in two proteins found associated with plasma membrane fractions from pea stem sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8003–8007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Gunning D. A., Budelier K. A., Brown S. M. Structure and expression of cytosolic cyclophilin/peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase of higher plants and production of active tomato cyclophilin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9519–9523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour S. J., Hajela R. K., Thomashow M. F. Cold Acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):745–750. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Franklin A. E., Hoffman N. E. Primary structure and characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana calnexin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6560–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Kirtley M. R. Structural features of cation transport ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Jun;24(3):271–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00768848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving H. R., Gehring C. A., Parish R. W. Changes in cytosolic pH and calcium of guard cells precede stomatal movements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreimer G., Melkonian M., Holtum J. A., Latzko E. Stromal free calcium concentration and light-mediated activation of chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):423–428. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. M., Sullivan T. D., Keegstra K. Information for targeting to the chloroplastic inner envelope membrane is contained in the mature region of the maize Bt1-encoded protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18999–19004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E. MgtA and MgtB: prokaryotic P-type ATPases that mediate Mg2+ influx. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Jun;24(3):319–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00768852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H. K., Antebi A., Fink G. R., Buckley C. M., Dorman T. E., LeVitre J., Davidow L. S., Mao J. I., Moir D. T. The yeast secretory pathway is perturbed by mutations in PMR1, a member of a Ca2+ ATPase family. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saghai-Maroof M. A., Soliman K. M., Jorgensen R. A., Allard R. W. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):8014–8018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.8014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmers L. E., Ewing N. N., Bennett A. B. Higher plant Ca(2+)-ATPase: primary structure and regulation of mRNA abundance by salt. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9205–9209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L. The Ca(2+)-transport ATPases from the plasma membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Jun;24(3):285–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00768849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]