Abstract
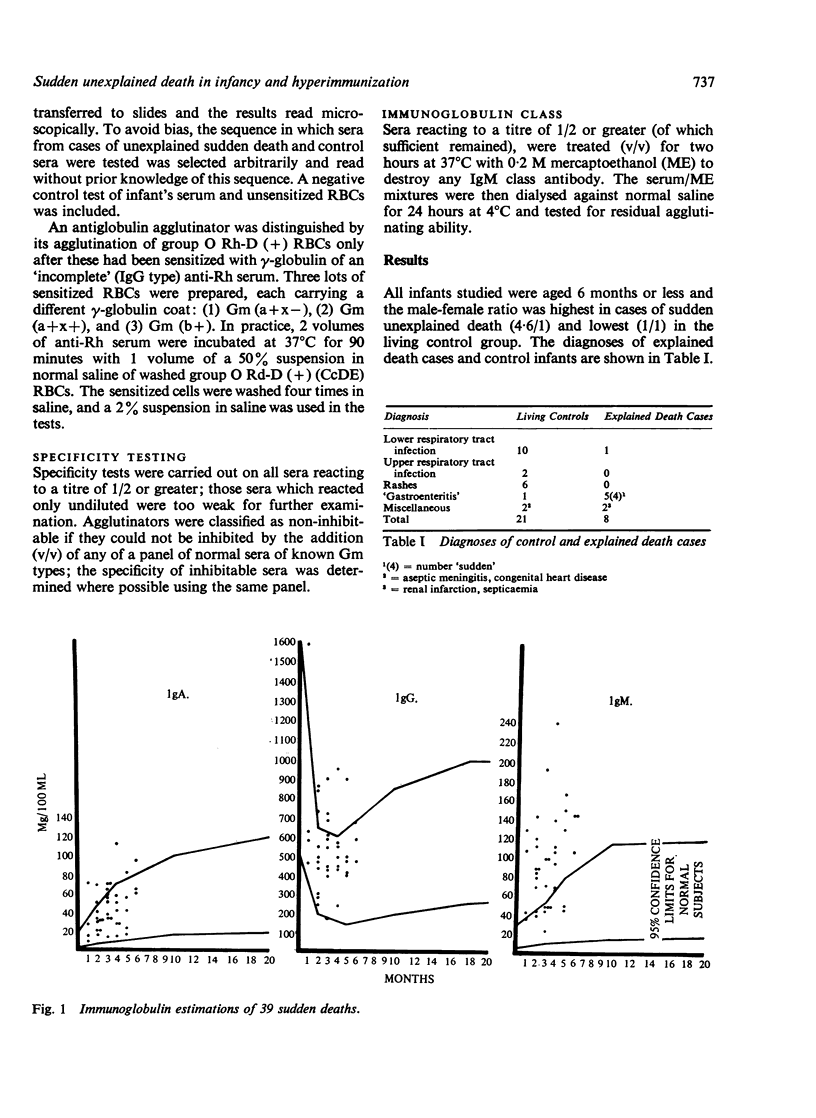
Serum immunoglobulin concentrations, predominantly IgM, were raised in 72% of 39 sudden infant death cases, consistent with a state of prolonged or repeated antigenic stimulation.
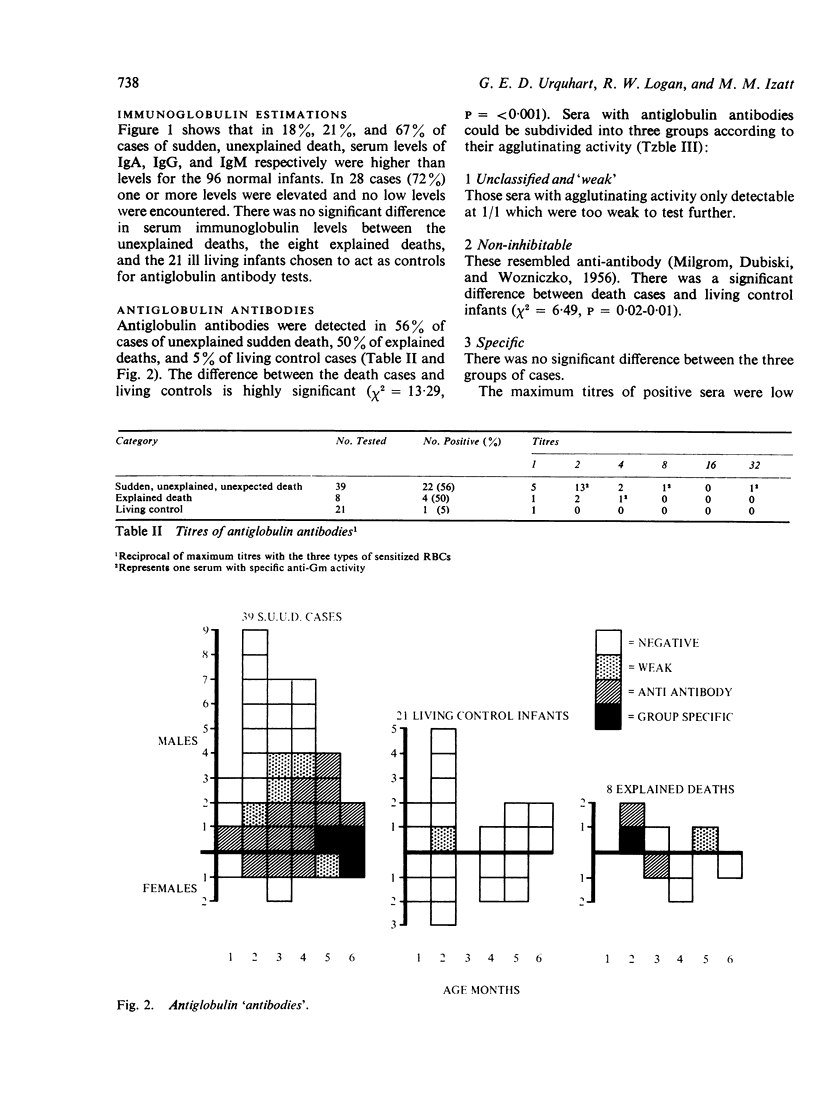
Anti-antibody was found in cases of sudden death significantly more frequently than in ill but living control infants. It is suggested that anti-antibody might participate in fatal anaphylaxis in such cases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRUZZO J. L., CHRISTIAN C. L. The induction of a rheumatoid factor-like substance in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:791–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN R. G. STATISTICS IN THE PRACTICE OF MEDICINE. JAMA. 1963 Sep 14;185:864–873. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03060110068020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEELER R. N., KADULL P. J., CLUFF L. E. INTENSIVE IMMUNIZATION OF MAN. EVALUATION OF POSSIBLE ADVERSE CONSEQUENCES. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Jul;63:44–57. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes-Dapena M. A. Sudden and unexpected death in infancy: a review of the world literature 1954-1966. Pediatrics. 1967 Jan;39(1):123–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


