Abstract
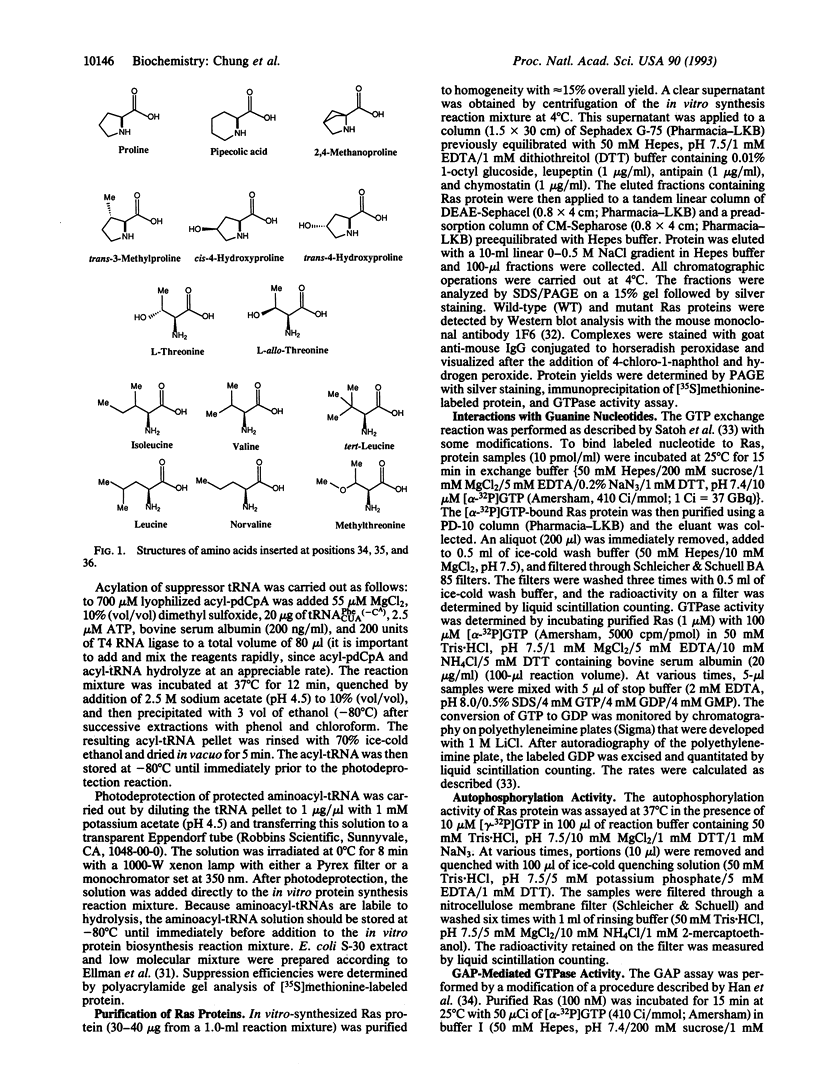
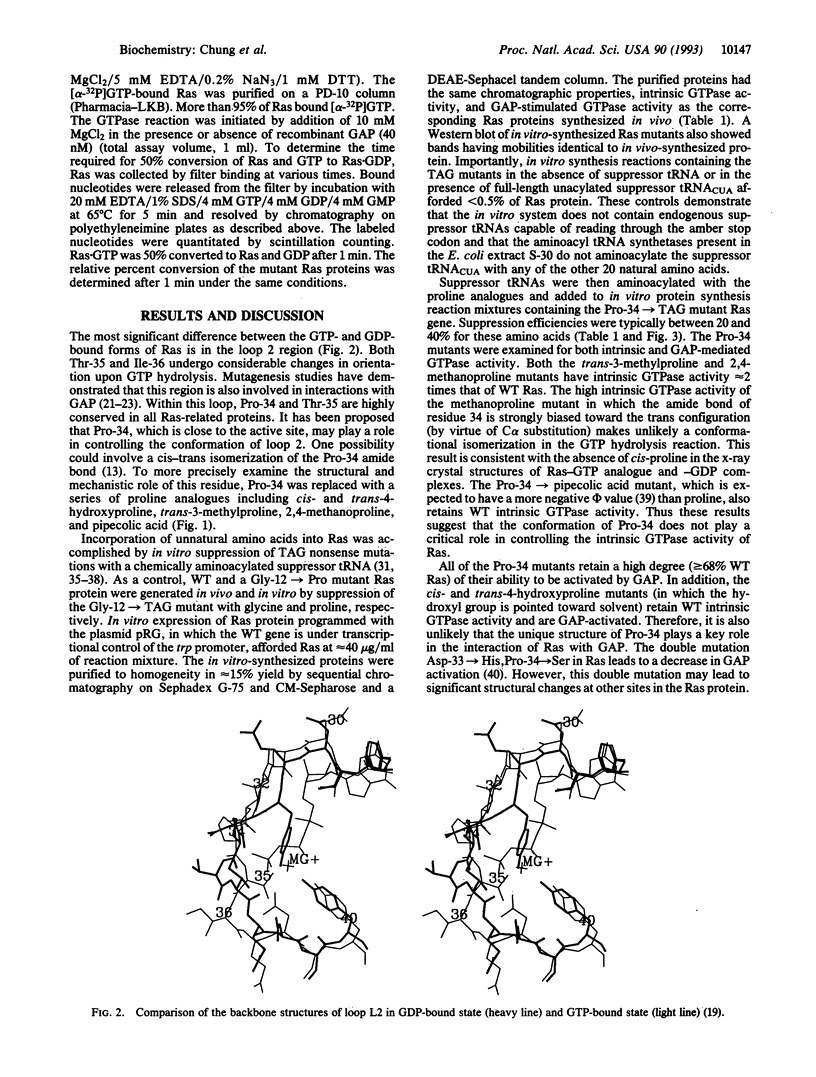
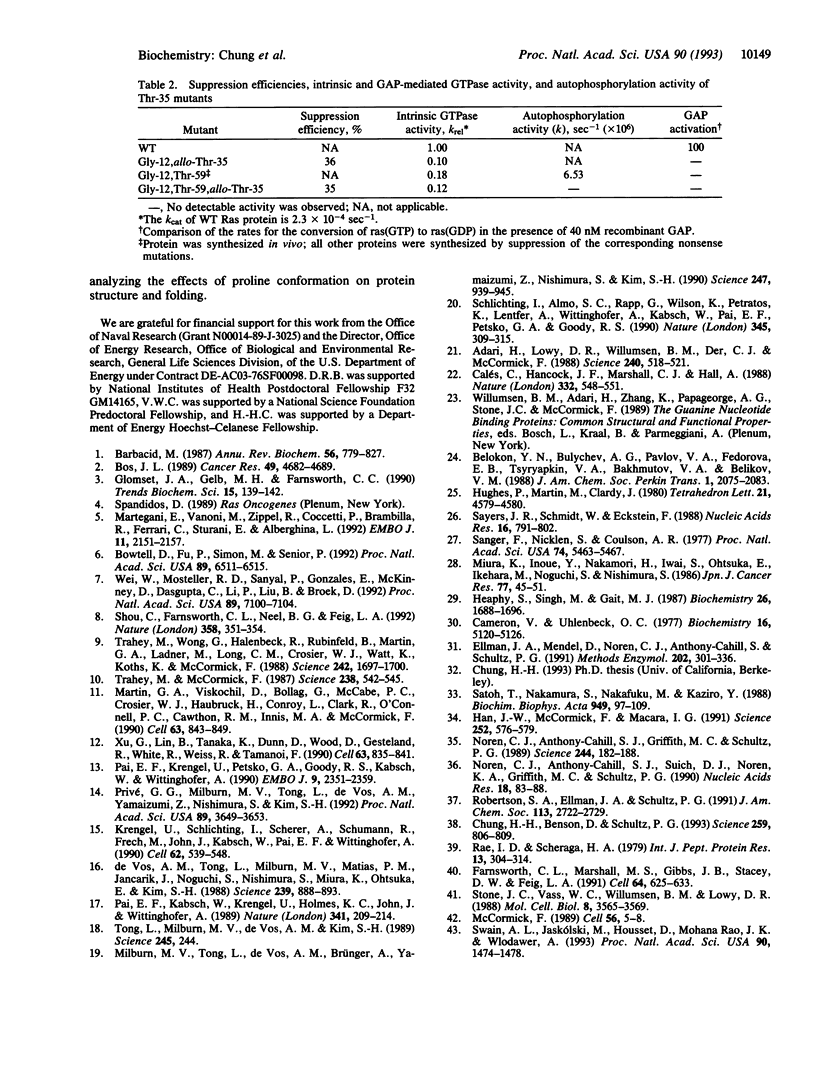
The YDPT sequence motif (residues 32-35) in loop 2 (residues 32-40) of Ha-Ras p21 protein is conserved in the Ras protein family. X-ray crystal structures have revealed significant conformational differences in this region between the GTP- and GDP-bound forms. Moreover, mutations in this region block neoplastic transformation and prevent interaction with GTPase-activating protein (GAP), suggesting that this region may contribute to the effector function of Ras. To better understand the structural features required for GAP interaction and GTPase activity, the expanded repertoire of unnatural amino acid mutagenesis has been used to investigate the roles of the key residues, Pro-34, Thr-35, and Ile-36. A Pro-34-->methanoproline mutant, in which residue 34 is locked in the trans conformation, was found to retain high levels of intrinsic and GAP-activated GTPase activity, making unlikely conformational isomerization at this position. Deletion of a single methyl group from Ile (Ile-36-->norvaline) abolished GAP activation of Ras, revealing a remarkable specificity in this protein-protein interaction. Finally, replacement of Thr-35 with diastereomeric allo-threonine led to inactivation of Ras, demonstrating the importance of the orientation of this critical residue in Ras function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D., Fu P., Simon M., Senior P. Identification of murine homologues of the Drosophila son of sevenless gene: potential activators of ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron V., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-Phosphatase activity in T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5120–5126. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. H., Benson D. R., Schultz P. G. Probing the structure and mechanism of Ras protein with an expanded genetic code. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):806–809. doi: 10.1126/science.8430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman J., Mendel D., Anthony-Cahill S., Noren C. J., Schultz P. G. Biosynthetic method for introducing unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:301–336. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Stacey D. W., Feig L. A. Preferential inhibition of the oncogenic form of RasH by mutations in the GAP binding/"effector" domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90246-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Gelb M. H., Farnsworth C. C. Prenyl proteins in eukaryotic cells: a new type of membrane anchor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90213-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. W., McCormick F., Macara I. G. Regulation of Ras-GAP and the neurofibromatosis-1 gene product by eicosanoids. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):576–579. doi: 10.1126/science.1902323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Singh M., Gait M. J. Effect of single amino acid changes in the region of the adenylylation site of T4 RNA ligase. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1688–1696. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krengel U., Schlichting I., Scherer A., Schumann R., Frech M., John J., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Wittinghofer A. Three-dimensional structures of H-ras p21 mutants: molecular basis for their inability to function as signal switch molecules. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90018-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martegani E., Vanoni M., Zippel R., Coccetti P., Brambilla R., Ferrari C., Sturani E., Alberghina L. Cloning by functional complementation of a mouse cDNA encoding a homologue of CDC25, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS activator. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Inoue Y., Nakamori H., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Noguchi S., Nishimura S. Synthesis and expression of a synthetic gene for the activated human c-Ha-ras protein. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;77(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noren C. J., Anthony-Cahill S. J., Griffith M. C., Schultz P. G. A general method for site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):182–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2649980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noren C. J., Anthony-Cahill S. J., Suich D. J., Noren K. A., Griffith M. C., Schultz P. G. In vitro suppression of an amber mutation by a chemically aminoacylated transfer RNA prepared by runoff transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privé G. G., Milburn M. V., Tong L., de Vos A. M., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. X-ray crystal structures of transforming p21 ras mutants suggest a transition-state stabilization mechanism for GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae I. D., Scheraga H. A. H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of some peptides with fibrinogen-like reactivity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979 Mar;13(3):304–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakamura S., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. Studies on ras proteins. Catalytic properties of normal and activated ras proteins purified in the absence of protein denaturants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting I., Almo S. C., Rapp G., Wilson K., Petratos K., Lentfer A., Wittinghofer A., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Petsko G. A. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):309–315. doi: 10.1038/345309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou C., Farnsworth C. L., Neel B. G., Feig L. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor for Ras p21. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):351–354. doi: 10.1038/358351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Vass W. C., Willumsen B. M., Lowy D. R. p21-ras effector domain mutants constructed by "cassette" mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3565–3569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain A. L., Jaskólski M., Housset D., Rao J. K., Wlodawer A. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase, an enzyme used in cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1474–1478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L., Milburn M. V., de Vos A. M., Kim S. H. Structure of ras proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):244–244. doi: 10.1126/science.2665078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei W., Mosteller R. D., Sanyal P., Gonzales E., McKinney D., Dasgupta C., Li P., Liu B. X., Broek D. Identification of a mammalian gene structurally and functionally related to the CDC25 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7100–7104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Lin B., Tanaka K., Dunn D., Wood D., Gesteland R., White R., Weiss R., Tamanoi F. The catalytic domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product stimulates ras GTPase and complements ira mutants of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]