Abstract
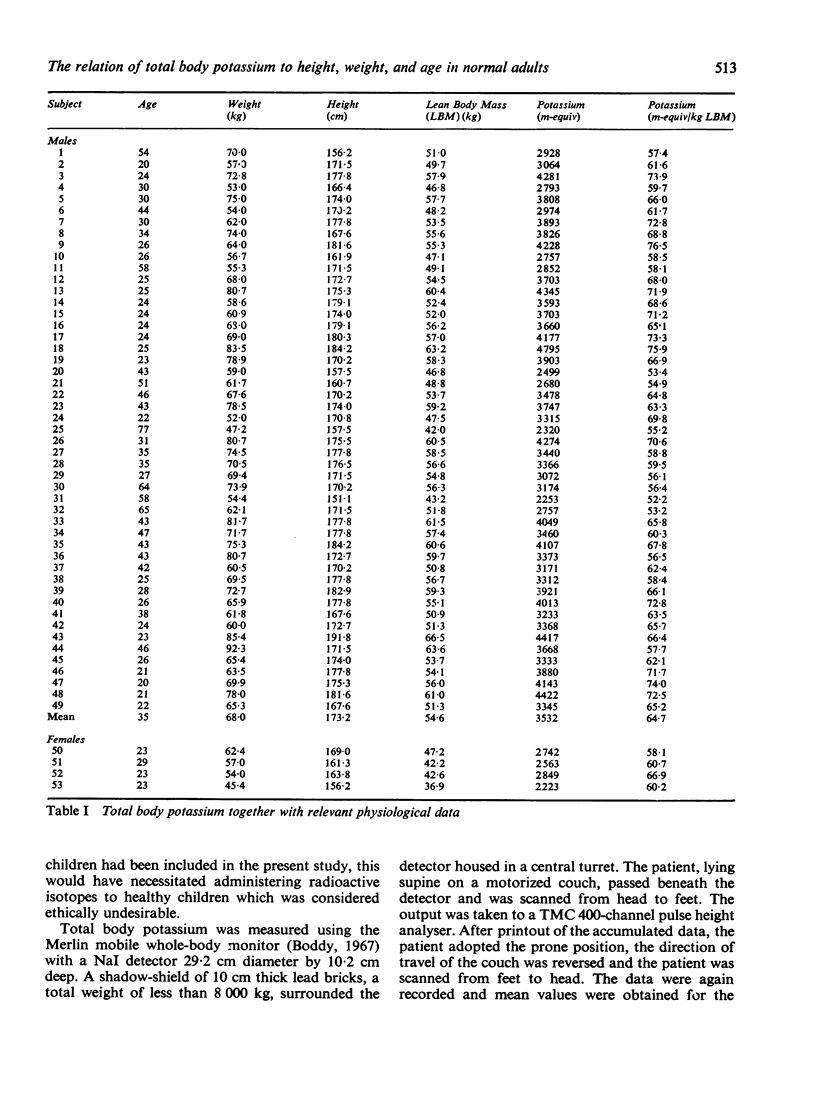
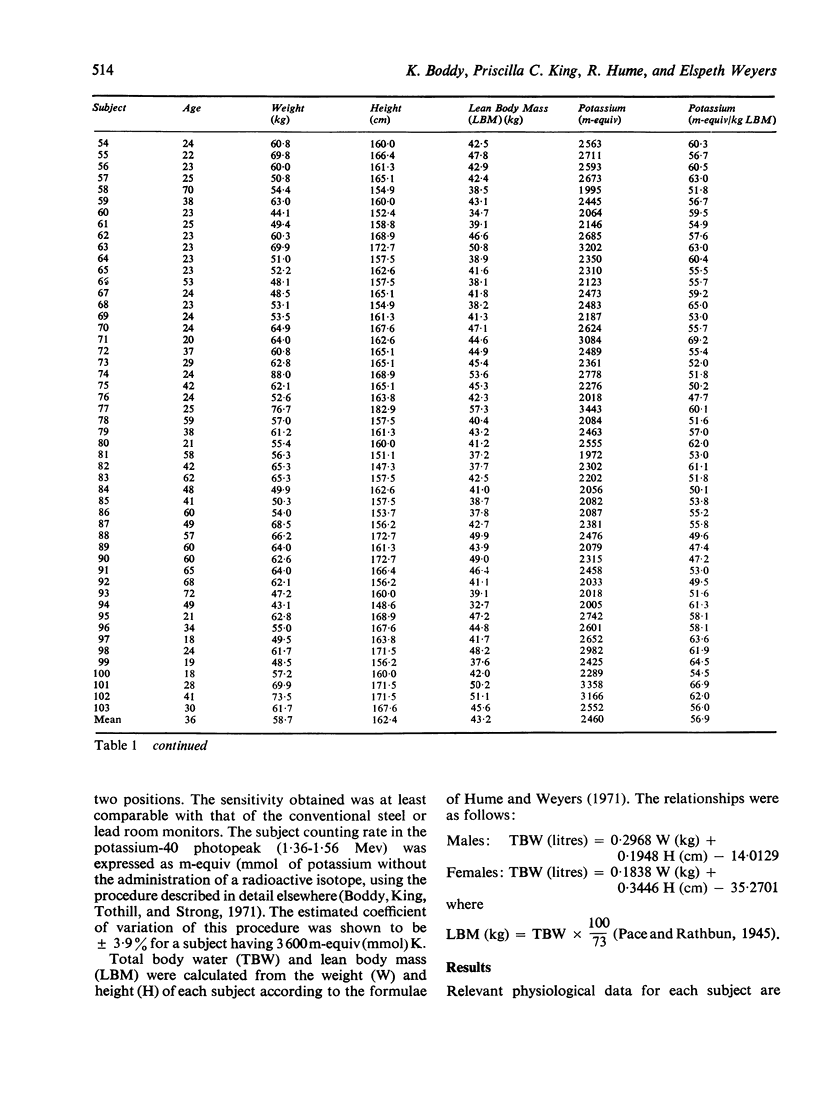
Total body potassium was measured in 103 healthy adults using a shadow-shield whole-body monitor of high sensitivity. The range of height was 147 to 192 cm, of weight 43 to 92 kg, and of age 18 to 77 years.
The values obtained for total body potassium were correlated with height, with weight, and with height and weight. Age was then included as an additional variable.
The standard deviation from regression was smaller when total body potassium was correlated with height than with weight and was further reduced, to about 9%, in a multiple regression using height and age. The advantages of this relationship over indices involving weight are discussed.
The smallest standard deviation from regression, 7·5%, was obtained when total body potassium was correlated with height, weight, and age. The usefulness of this relationship is discussed with comment on its limitations.
A regression equation was derived between lean body mass (derived from height and weight) and total body potassium with a standard deviation from regression of 5·5% in males and 7·3% in females.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN T. H., ANDERSON E. C., LANGHAM W. H. Total body potassium and gross body composition in relation to age. J Gerontol. 1960 Oct;15:348–357. doi: 10.1093/geronj/15.4.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. C., LANGHAM W. H. Average potassium concentration of the human body as a function of age. Science. 1959 Sep 18;130(3377):713–714. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3377.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAARLI J., MADSHUS K., LIDEN K., McCALL R. C. Radiocaesium and potassium in Norwegians. Nature. 1961 Jul 29;191:436–438. doi: 10.1038/191436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTER J., FORBES G. B. CORRELATION OF POTASSIUM-40 DATA WITH ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:264–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K. A high sensitivity shadow-shield whole body monitor with scanning-bed and tilting chair geometries, incorporated in a mobile laboratory. Br J Radiol. 1967 Aug;40(476):631–637. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-40-476-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., King P. C., Lindsay R. M., Briggs J. D., Winchester J. F., Kennedy A. C. Total body potassium in non-dialysed and dialysed patients with chronic renal failure. Br Med J. 1972 Mar 25;1(5803):771–775. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5803.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., King P. C., Tothill P., Strong J. A. Measurement of total body potassium with a shadow shield whole-body counter: calibration and errors. Phys Med Biol. 1971 Apr;16(2):275–282. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/16/2/310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnin J. V., Rahaman M. M. The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness. Br J Nutr. 1967 Aug;21(3):681–689. doi: 10.1079/bjn19670070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES G. B., GALLUP J., HURSH J. B. Estimation of total body fat from potassium-40 content. Science. 1961 Jan 13;133(3446):101–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES G. B., LEWIS A. M. Total sodium, potassium and chloride in adult man. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jun;35(6):596–600. doi: 10.1172/JCI103313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Williams R. E., Smith A. H. Clinical studies on whole-body potassium content measured by gamma-ray spectrometry in health and disease. Clin Sci. 1967 Jun;32(3):503–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R. Prediction of lean body mass from height and weight. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):389–391. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R., Weyers E. Relationship between total body water and surface area in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Apr;24(3):234–238. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.3.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENEELY G. R., BALL C. O., FERGUSON J. L., PAYNE D. D., LORIMER A. R., WEILAND R. L., ROLF H. L., HEYSSEL R. M. Use of computers in measuring body electrolytes by gamma spectrometry. Circ Res. 1962 Sep;11:539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLSON J. P., ZILVA J. F. BODY CONSTITUENTS AND FUNCTIONS IN RELATION TO HEIGHT AND WEIGHT. Clin Sci. 1964 Aug;27:97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp R. C., Cohen N. L., Gaffey W. R., McKey T., Bron G., Siri W. E., Sargent T. W., Isaacs E. Measures of body fat and related factors in normal adults. II. A simple clinical method to estimate body fat and lean body mass. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Dec;18(12):1291–1307. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODWARD K. T., TRUJILLO T. T., SCHUCH R. L., ANDERSON E. C. Correlation of total body potassium with body-water. Nature. 1956 Jul 14;178(4524):97–98. doi: 10.1038/178097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


