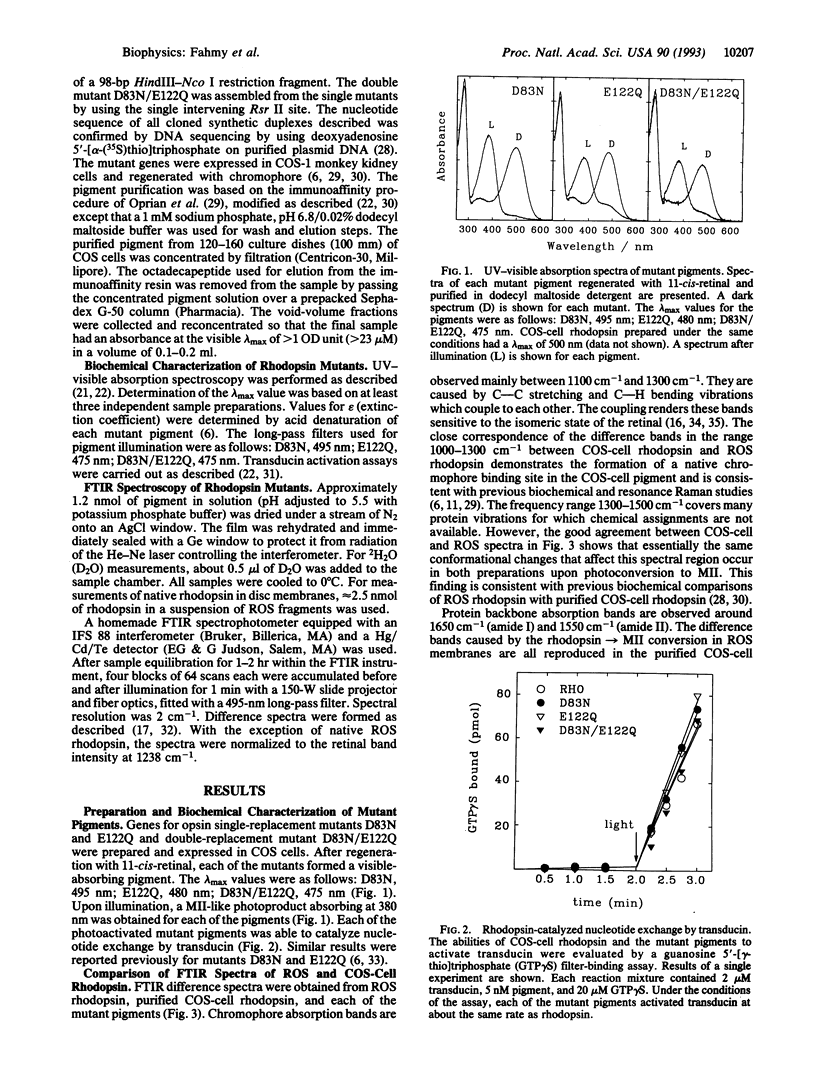
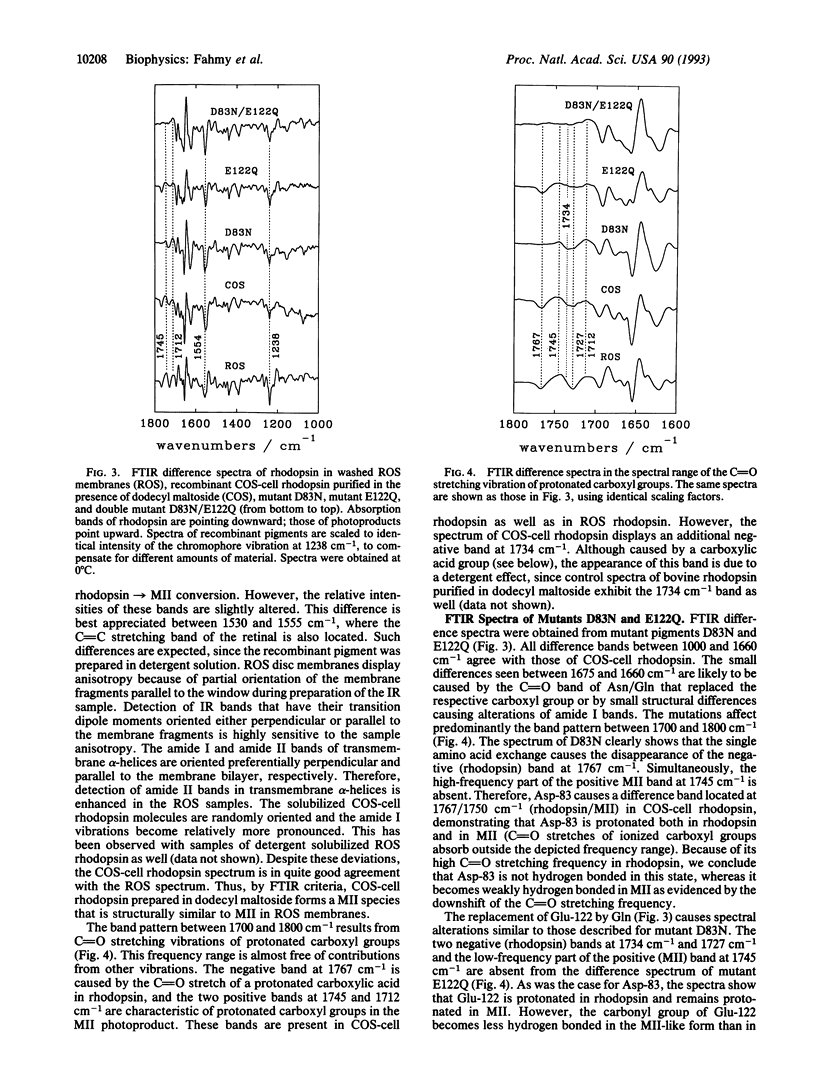
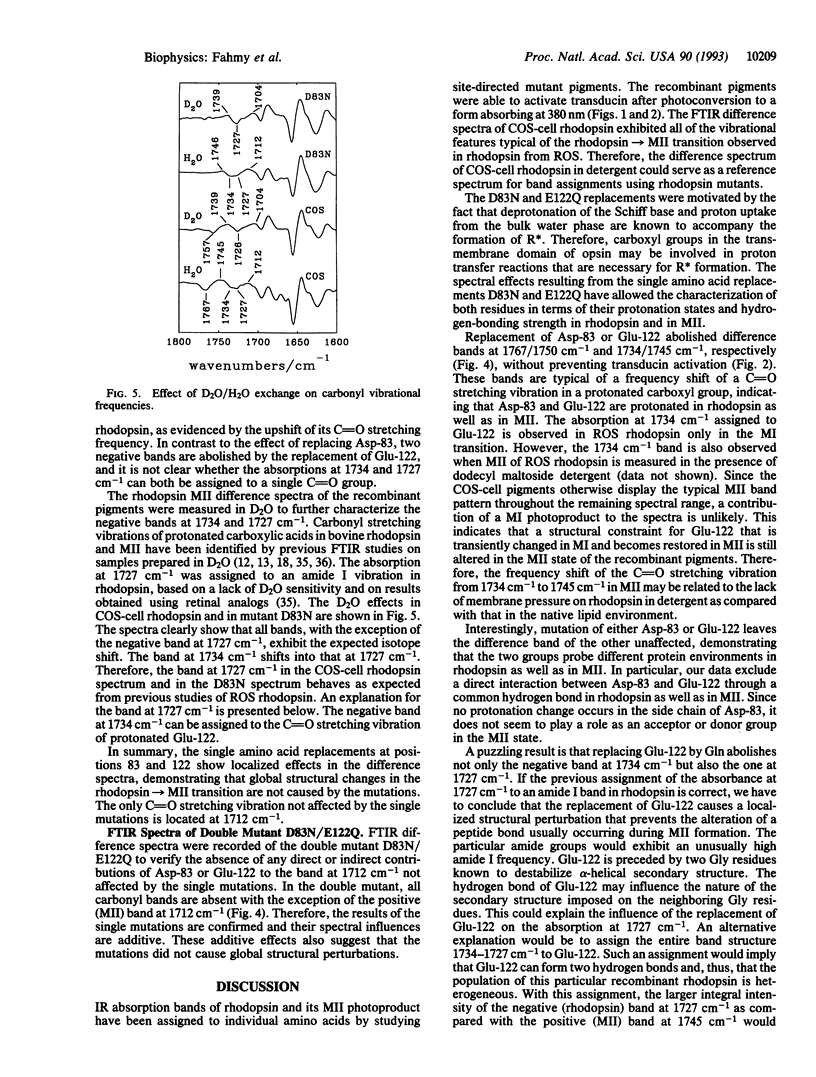
Abstract
A method was developed to measure Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) difference spectra of detergent-solubilized rhodopsin expressed in COS cells. Experiments were performed on native bovine rhodopsin, rhodopsin expressed in COS cells, and three expressed rhodopsin mutants with amino acid replacements of membrane-embedded carboxylic acid groups: Asp-83-->Asn (D83N), Glu-122-->Gln (E122Q), and the double mutant D83N/E122Q. Each of the mutant opsins bound 11-cis-retinal to yield a visible light-absorbing pigment. Upon illumination, each of the mutant pigments formed a metarhodopsin II-like species with maximal absorption at 380 nm that was able to activate guanine nucleotide exchange by transducin. Rhodopsin versus metarhodopsin II-like photoproduct FTIR-difference spectra were recorded for each sample. The COS-cell rhodopsin and mutant difference spectra showed close correspondence to that of rhodopsin from disc membranes. Difference bands (rhodopsin/metarhodopsin II) at 1767/1750 cm-1 and at 1734/1745 cm-1 were absent from the spectra of mutants D83N and E122Q, respectively. Both bands were absent from the spectrum of the double mutant D83N/E122Q. These results show that Asp-83 and Glu-122 are protonated both in rhodopsin and in metarhodopsin II, in agreement with the isotope effects observed in spectra measured in 2H2O. A photoproduct band at 1712 cm-1 was not affected by either single or double replacements at positions 83 and 122. We deduce that the 1712 cm-1 band arises from the protonation of Glu-113 in metarhodopsin II.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley K. A., Balogh-Nair V., Croteau A. A., Dollinger G., Ebrey T. G., Eisenstein L., Hong M. K., Nakanishi K., Vittitow J. Fourier-transform infrared difference spectroscopy of rhodopsin and its photoproducts at low temperature. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6055–6071. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T., Lee M., Sakmar T. P. Introduction of hydroxyl-bearing amino acids causes bathochromic spectral shifts in rhodopsin. Amino acid substitutions responsible for red-green color pigment spectral tuning. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9478–9480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. B., Oprian D. D., Robinson P. R. Mechanism of activation and inactivation of opsin: role of Glu113 and Lys296. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 22;31(50):12592–12601. doi: 10.1021/bi00165a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrip W. J., Gray D., Gillespie J., Bovee P. H., Van den Berg E. M., Lugtenburg J., Rothschild K. J. Photoexcitation of rhodopsin: conformation changes in the chromophore, protein and associated lipids as determined by FTIR difference spectroscopy. Photochem Photobiol. 1988 Oct;48(4):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1988.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy K., Sakmar T. P. Light-dependent transducin activation by an ultraviolet-absorbing rhodopsin mutant. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):9165–9171. doi: 10.1021/bi00086a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Graham R. M., Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin. Studies of the interaction between the rhodopsin cytoplasmic domain and transducin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14767–14774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Oprian D. D., Khorana H. G. A single amino acid substitution in rhodopsin (lysine 248----leucine) prevents activation of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2119–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U. M., Gärtner W., Siebert F. Rhodopsin-lumirhodopsin phototransition of bovine rhodopsin investigated by Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7480–7488. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U. M., Longstaff C., Pajares M. A., Rando R. R., Siebert F. Fourier transform infrared studies of active-site-methylated rhodopsin. Implications for chromophore-protein interaction, transducin activation, and the reaction pathway. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):640–644. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82279-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U. M., Schmid E. D., Perez-Sala D., Rando R. R., Siebert F. Removal of the 9-methyl group of retinal inhibits signal transduction in the visual process. A Fourier transform infrared and biochemical investigation. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5954–5962. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., McDowell J. H., Curtis D. R., Wang J. K., Juszczak E., Fong S. L., Rao J. K., Argos P. The structure of bovine rhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1983;9(4):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00535659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlert M., König B., Hofmann K. P. Displacement of rhodopsin by GDP from three-loop interaction with transducin depends critically on the diphosphate beta-position. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18928–18932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger A. L., Braiman M. S. Structural comparison of metarhodopsin II, metarhodopsin III, and opsin based on kinetic analysis of Fourier transform infrared difference spectra. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1244–1255. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81700-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. W., Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G., Mathies R. A. Resonance Raman microprobe spectroscopy of rhodopsin mutants: effect of substitutions in the third transmembrane helix. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 9;31(22):5105–5111. doi: 10.1021/bi00137a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff C., Calhoon R. D., Rando R. R. Deprotonation of the Schiff base of rhodopsin is obligate in the activation of the G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. C., Zvyaga T. A., Cypess A. M., Sakmar T. P. Characterization of mutant rhodopsins responsible for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Mutations on the cytoplasmic surface affect transducin activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9400–9404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T. A., Khorana H. G. Mapping of the amino acids in membrane-embedded helices that interact with the retinal chromophore in bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4269–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J. Determinants of visual pigment absorbance: identification of the retinylidene Schiff's base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9746–9752. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A. R., Callender R. H. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of rhodopsin in retinal disk membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4243–4248. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palings I., Pardoen J. A., van den Berg E., Winkel C., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Assignment of fingerprint vibrations in the resonance Raman spectra of rhodopsin, isorhodopsin, and bathorhodopsin: implications for chromophore structure and environment. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2544–2556. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. R., Cohen G. B., Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Constitutively active mutants of rhodopsin. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90034-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. Glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8309–8313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. The role of the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in rhodopsin in determining wavelength absorbance and Schiff base pKa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3079–3083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Khorana H. G. Total synthesis and expression of a gene for the alpha-subunit of bovine rod outer segment guanine nucleotide-binding protein (transducin). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6361–6372. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert F., Mäntele W., Gerwert K. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy applied to rhodopsin. The problem of the protonation state of the retinylidene Schiff base re-investigated. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Effect of carboxylic acid side chains on the absorption maximum of visual pigments. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):928–930. doi: 10.1126/science.2573154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvyaga T. A., Min K. C., Beck M., Sakmar T. P. Movement of the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in rhodopsin by one helix turn reverses the pH dependence of the metarhodopsin I to metarhodopsin II transition. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4661–4667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Grip W. J., Gillespie J., Rothschild K. J. Carboxyl group involvement in the meta I and meta II stages in rhodopsin bleaching. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 28;809(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



