Abstract
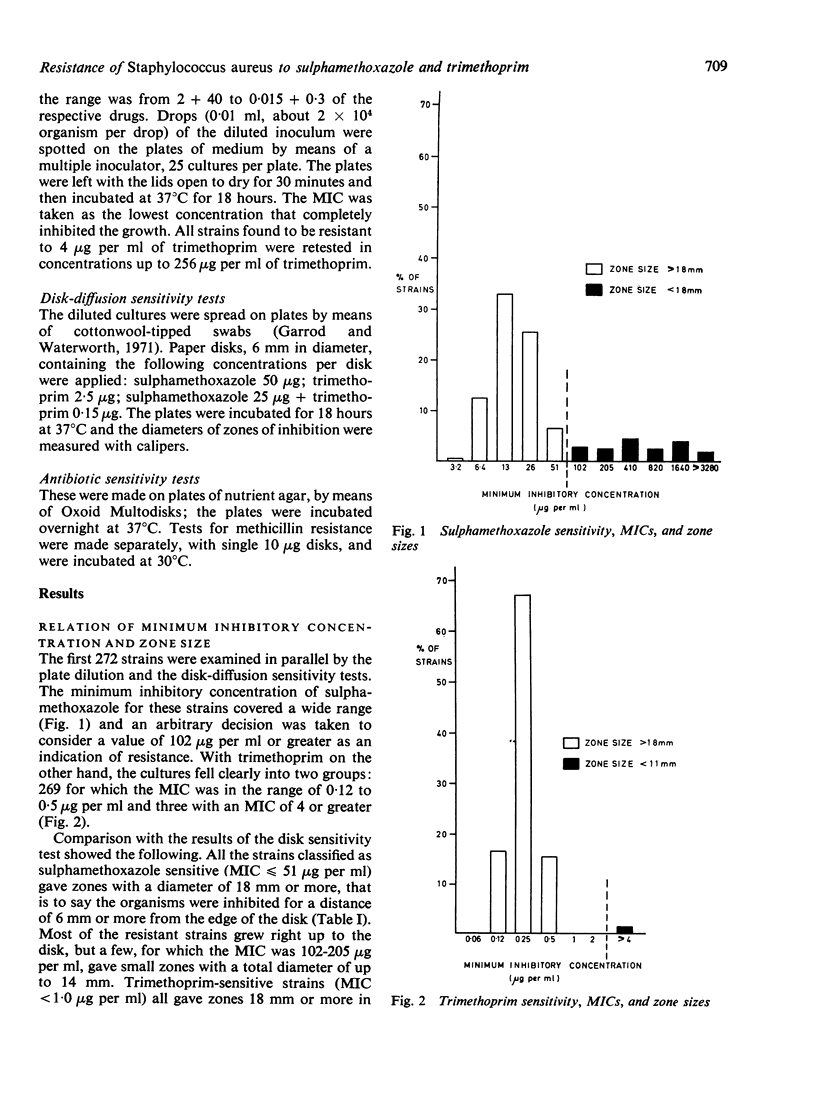
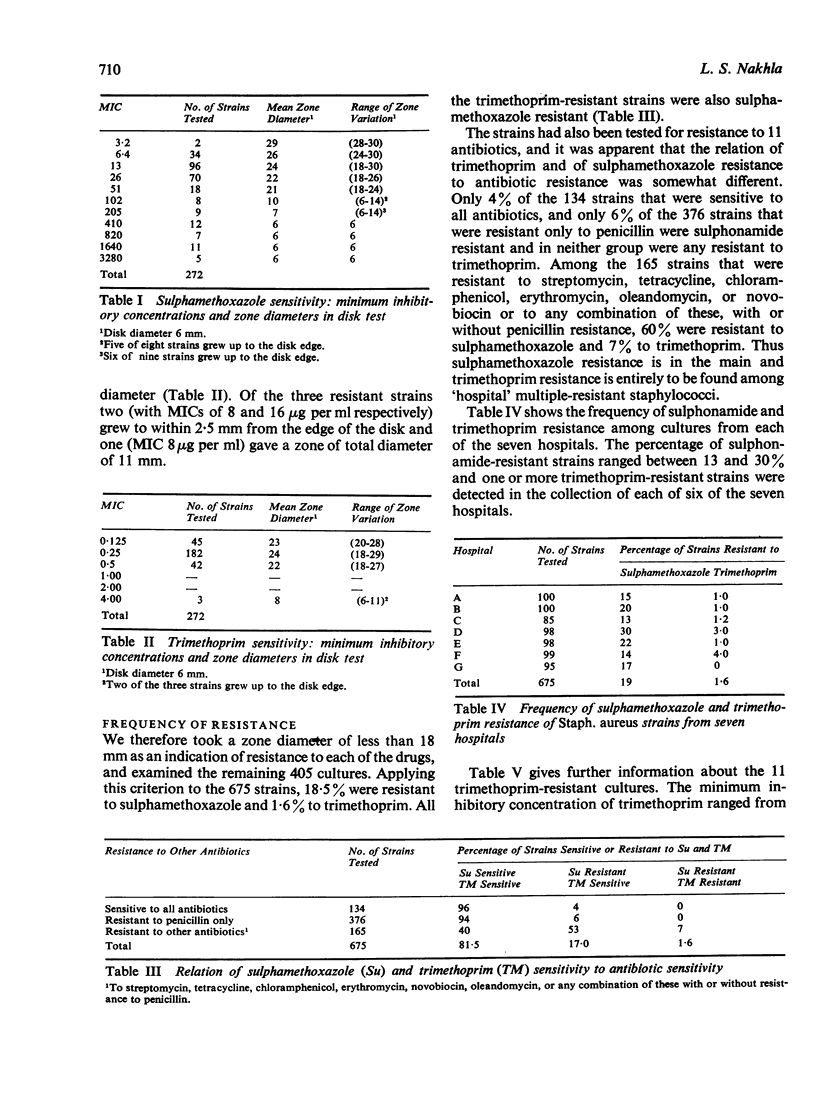
Strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from the lesions of hospital patients were surveyed for resistance to sulphamethoxazole and to trimethoprim. Of 675 strains tested, 18·5% were resistant to sulphamethoxazole and 1·6% to trimethoprim. All the trimethoprim-resistant strains were resistant to sulphamethoxazole and to a 1:20 mixture of the two drugs. Trimethoprim-resistant strains were on average more resistant to sulphamethoxazole than were trimethoprim-sensitive strains. They were all resistant to several other antimicrobial agents. Most of them had the phage-typing pattern 84/85, 84, or 85.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumfitt W., Faiers M. C., Pursell R. E., Reeves D. S., Turnbull A. R. Bacteriological, pharmacological and clinical studies with trimethoprim-sulphonamide combinations with particular reference to the treatment of urinary infections. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven J. L., Pugsley D. J., Blowers R. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in acute osteomyelitis due to penicillin-resistant staphylococci in Uganda. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 25;3(5716):201–203. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5716.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Trimethoprim: laboratory and clinical studies. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):202–209. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P. The possible scope of trimethoprim-sulphonamide treatment. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Tests of bacterial sensitivity to drugs. Dis Mon. 1971 Jul;:1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie D. J., Alder V. G., Gillespie W. A. Changes in the drug resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in a non-hospital population during a 20-year period. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Feb;24(1):44–47. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. T. Treatment of exacerbations of chronic chest infections with combinations of sulphamethoxazole4trimethoprim (including comparison with ampicillin). Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):86–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEVONS M. P., PARKER M. T. THE EVOLUTION OF NEW HOSPITAL STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:243–250. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevons M. P., John M., Parker M. T. Cultural characters of a newly recognized group of hospital staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):305–312. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Bruten D. M., Gillespie W. A., Lewis E. L. Trimethoprim-resistant coliforms. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady F., Chamberlain D. A., Stark J. E., Cattell W. R., Sardeson J. M., Fry I. F., Spiro F. I., Waters A. H. Long-term, low-dosage, trimethoprim-sulphonamide in the control of chronic bacteriuria. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


