Abstract
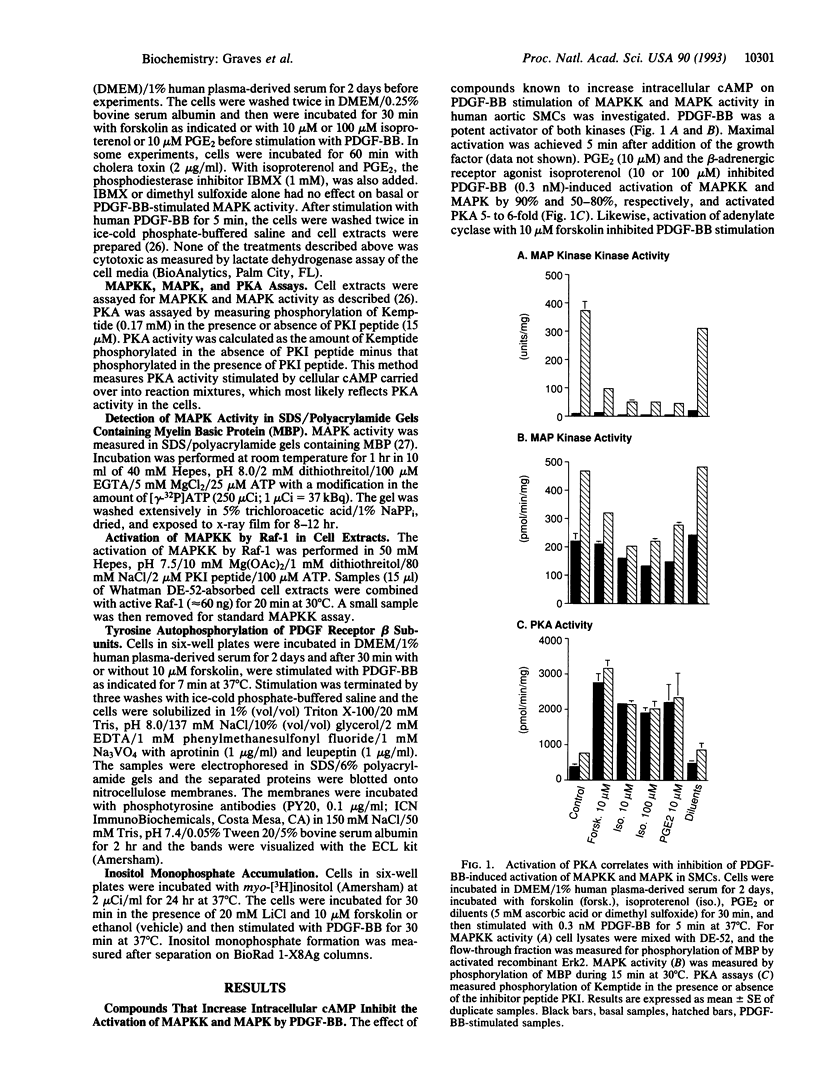
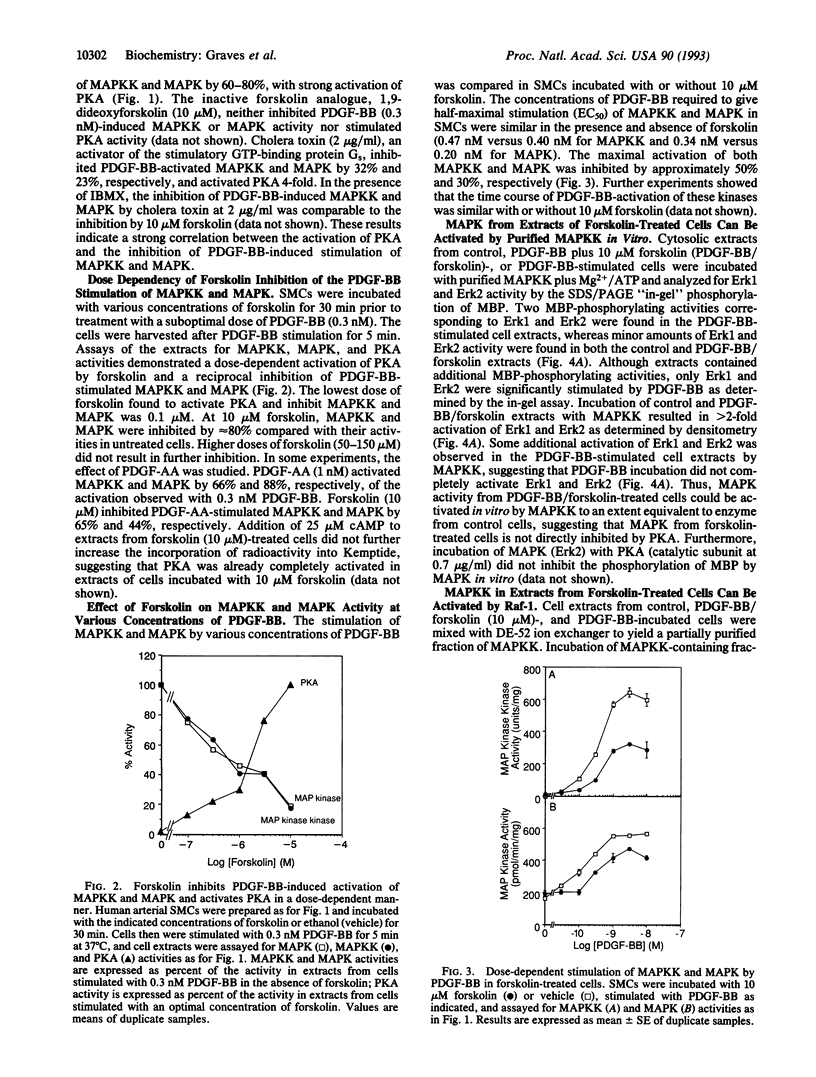
Stimulation of aortic smooth muscle cells with platelet-derived growth factor BB homodimer (PDGF-BB) leads to the rapid activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and MAPK kinase (MAPKK). Compounds that increase cAMP and activate protein kinase A (PKA)--prostaglandin E2, isoproterenol, cholera toxin, and forskolin--were found to inhibit the PDGF-BB-induced activation of MAPKK and MAPK. Forskolin, but not the inactive analogue 1,9-dideoxyforskolin, inhibited PDGF-BB-stimulated MAPKK and MAPK activation in a dose-dependent manner. PKA antagonism of MAPK signaling was observed at all doses of PDGF-BB or PDGF-AA. PKA did not inhibit MAPKK and MAPK activity in vitro, and MAPKK and MAPK from extracts of forskolin-treated cells could be activated normally with purified Raf-1 and MAPKK, respectively, suggesting that PKA blocked signaling upstream of MAPKK. Neither PDGF-BB-stimulated tyrosine autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor beta subunit nor inositol monophosphate accumulation was affected by increased PKA activity, suggesting that PKA inhibits events downstream of the PDGF receptor. This study provides an example of cross talk between two important signaling systems activated by physiological stimuli in smooth muscle cells--namely, the PKA pathway and the growth factor-activated MAPK cascade.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth A., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. The amino acid sequence of a mammalian MAP kinase kinase. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2555–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assender J. W., Southgate K. M., Hallett M. B., Newby A. C. Inhibition of proliferation, but not of Ca2+ mobilization, by cyclic AMP and GMP in rabbit aortic smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):527–532. doi: 10.1042/bj2880527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.8493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Signal integration at the level of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and their substrates. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Dastidar P., Fox C. F. cAMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3864–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E., Goldberg D., Levitzki A. Phosphorylation of the S. cerevisiae Cdc25 in response to glucose results in its dissociation from Ras. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):762–765. doi: 10.1038/360762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin N. E., Paulsson Y., Forsberg K., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Induction of cyclic AMP synthesis by forskolin is followed by a reduction in the expression of c-myc messenger RNA and inhibition of 3H-thymidine incorporation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):17–23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Sakamoto H., Tsunoda M., Aoki M., Takenawa T., Ooyama T. Evidence for involvement of phospholipase C-gamma 2 in signal transduction of platelet-derived growth factor in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):649–653. doi: 10.1042/bj2900649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kaibuchi K., Masuda T., Yamamoto T., Matsuura Y., Maeda A., Shimizu K., Takai Y. A protein factor for ras p21-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase through MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Kikuchi A., Hoshijima M., Yamamoto K., Hashimoto E., Yamamura H., Takai Y. Phosphorylation of smg p21, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in a cell-free system and in response to prostaglandin E1 in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15688–15695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamy F., Wilkin F., Baptist M., Posada J., Roger P. P., Dumont J. E. Phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases is involved in the epidermal growth factor and phorbol ester, but not in the thyrotropin/cAMP, thyroid mitogenic pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8398–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesberg C., van Wijk R., Zandbergen J., van Aken W. G., van Mourik J. A., de Groot P. G. Cell cycle-dependent inhibition of human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by prostaglandin E1. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Sep;160(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Phosphorylation of Xenopus mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase by MAP kinase kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3277–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakielny S., Cohen P., Wu J., Sturgill T. MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2123–2129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., Olsson A. G. Prostaglandin E1 inhibits DNA synthesis in arterial smooth muscle cells stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. Atherosclerosis. 1984 Oct;53(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Gotoh Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90019-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. Inhibition of CD3-linked phospholipase C by phorbol ester and by cAMP is associated with decreased phosphotyrosine and increased phosphoserine contents of PLC-gamma 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1496–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Johnson G. S., Anderson W. B. Role of cyclic nucleotides in growth control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:491–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Posada J., Munar E. S., Jensen A. M., Cooper J. A., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14373–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Lozeman F. J., Ahn N. G., Graves L. M., Campbell J. S., Ericsson L., Harrylock M., Jensen A. M., Krebs E. G. Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25628–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevetson B. R., Kong X., Lawrence J. C., Jr Increasing cAMP attenuates activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10305–10309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L., Rosen O. M. Increasing the cAMP content of IM-9 cells alters the phosphorylation state and protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3402–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Rochet N., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effect of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase on insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):19–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2450019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]