Abstract
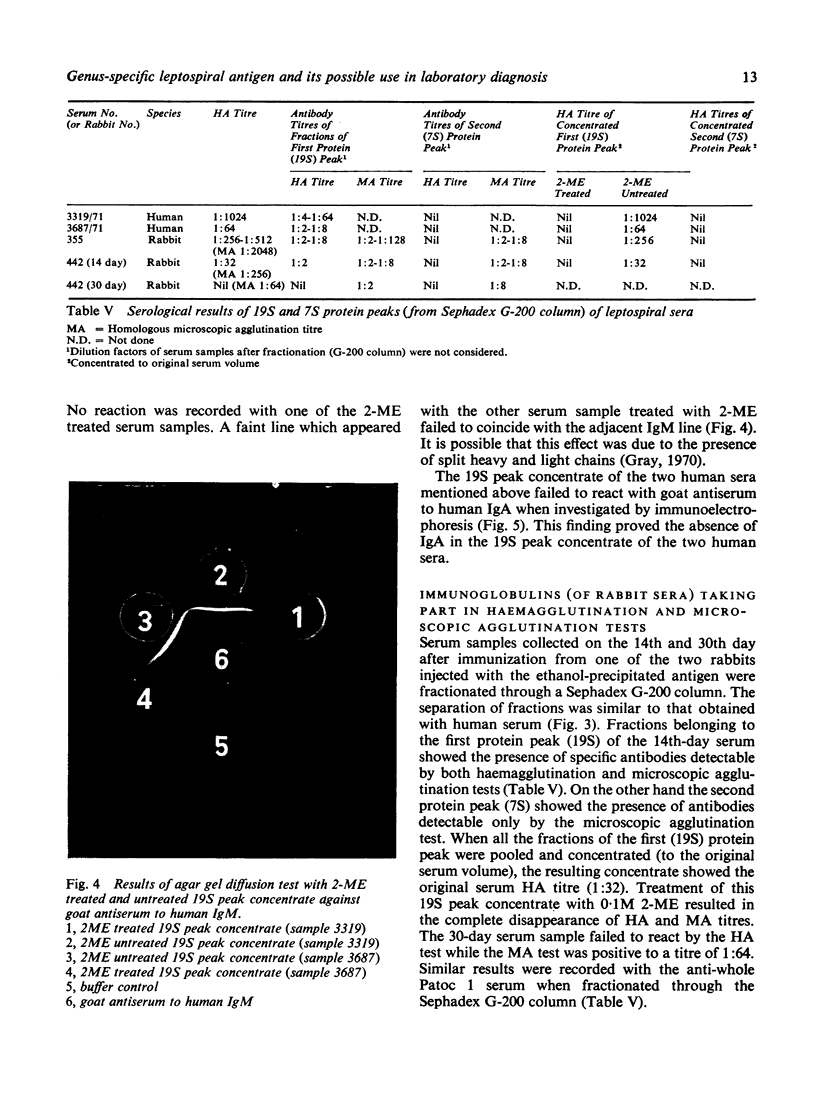
Sheep red cells, sensitized with a genus-specific leptospiral substance extracted from a water leptospira, were preserved by freeze drying. The serological reactivity of the preparation was tested against a total of 41 sera from proven cases of human leptospirosis and 27 from proven cases of animal leptospirosis. The sensitized, freeze-dried red cells appeared to be a sensitive reagent for the detection of leptospiral antibodies by haemagglutination. The use of this reagent as a screening test for leptospiral diagnosis is discussed. In the reported haemagglutination test on human and rabbit antisera the findings suggested that only IgM (19S) antibodies took part in the reaction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L. STUDIES ON MOUSE ANTIBODIES. II. MERCAPTOETHANOL-SENSITIVE 7 S ANTIBODIES IN MOUSE ANTISERA TO PROTEIN ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG R. S. M., McCOMB D. E. Erythrocyte sensitizing substance from five strains of Leptospirae. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 May;3(3):481–489. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1954.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D., ALEXANDER A. D., MURPHY L. C. Evaluation of the hemolytic test in the serodiagnosis of human leptospirosis. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):210–218. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D. Hemolysis of sheep erythrocytes sensitized with leptospiral extracts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):610–615. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A., Faine S. Electron-microscopic evidence for reactions of axial filaments of Leptospira with IgM and IgG antibodies. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(4):571–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL T. M., STAVITSKY A. B. PASSIVE HEMAGGLUTINATION IN STUDY OF ANTIGENS AND ANTIBODIES. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: FRACTIONATION OF OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX AND A MEDIUM OF BOVINE ALBUMIN AND POLYSORBATE 80. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faine S. Acid-treated, heated serum derivative for culture media for Leptospira. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):185–185. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.185-.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJEWSKI M., GREENWALT T. J. THE CENTRAL FILE FOR RARE DONORS AND FROZEN BLOOD PROGRAM OF THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF BLOOD BANKS. Am J Med Technol. 1965 May-Jun;31:175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves S., Faine S. Antileptospiral agglutinins produced in rabbits. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(4):579–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMANN L., FILITTI WURMSER S., JACQUOT ARMAN Y., MAILLOUX M., HUREZ D., FAUVERT R. NATURE MACROMOL'ECULAIRE D'UN ANTICORPS DE LA LEPTOSPIROSE AUSTRALIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:249–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyselová M., Libich M., Srbová H. Titration of tetanus and diphtheria antibodies by means of hemagglutination test, using freeze-dried sensitized sheep erythrocytes. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1970 Apr;139(3):228–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATASTE-DOROLLE C., EYQUEM A., BURI J. F. ANALYSE IMMUNO-'ELECTROPHOR'ETIQUE, EN MILIEU G'ELOS'E, DES PROT'EINES S'ERIQUES DANS LES LEPTOSPIROSES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Apr;106:646–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E. Bacterial hemagglutination and hemolysis. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Sep;20(3):166–188. doi: 10.1128/br.20.3.166-188.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palit A., Sharma G. L. Comparison of microscopic agglutination, indirect haemagglutination and complement-fixation tests in rabbit and buffalo-calf hyperimmune sera for detection of leptospiral antibodies. Br Vet J. 1971 Apr;127(4):154–162. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M., McBrayer H. L., Schulze M. L., Chandler C. H. Chromatographic analysis and sulfhydryl sensitivity of antileptospira agglutinins in rabbit and human sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):786–789. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner L. H. Leptospirosis. II. Serology. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(6):880–899. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dalen A., Seijen H. G., Gruber M. Structural homologies in immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):615–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





