Abstract
Delivery of inhaled medications via an inhaler device underpins the effectiveness of treatment for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Correct inhaler technique among patients is also a predictor of achieving treatment compliance and adherence. Reporting of patient satisfaction with inhalers is therefore gaining increasing attention and is now recognized as an important patient-reported outcome in clinical trials involving patients with COPD or asthma. In this cross-sectional study, we use the validated Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire (PASAPQ) to assess the handling and satisfaction for Respimat® Soft Mist™ Inhaler (SMI) compared with the Breezhaler® dry powder inhaler (DPI) among patients with COPD in Spain. Patients were already assigned to therapy with either SPIRIVA® (tiotropium) Respimat® or with Hirobriz®/Onbrez®/Oslif® (indacaterol) Breezhaler® for at least 3 but not more than 6 months before completing the PASAPQ at a single visit to the study site. The primary endpoint of the trial was the mean total PASAPQ score. Secondary endpoints were the performance score domain of the PASAPQ, the convenience score domain of the PASAPQ, and the overall satisfaction score of the PASAPQ. For the primary endpoint, the mean PASAPQ total score in the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups was 80.7 and 79.9, respectively (difference of 0.8, 95% confidence interval [CI] −2.9 to 4.5; P=0.67). The mean total performance scores were 82.5 and 78.2 (difference of 4.3, 95% CI −0.3 to 8.9; P=0.06), and the mean total convenience scores were 78.6 and 81.9 (difference of −3.3, 95% CI −7.0 to 0.4; P=0.08) for the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups, respectively. Patients gave the Respimat® SMI and the Breezhaler® DPI overall satisfaction PASAPQ scores of 6.0 and 5.9, respectively, which shows that patients were satisfied with these inhalers.
Keywords: COPD, Respimat®, Breezhaler®, inhaler, handling
Introduction
The cornerstone of treatment delivery for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) involves administration of medications through inhaler devices.1 Inhaler choice and handling of inhalation devices are key factors for the effectiveness of treatment.2–4 Therefore, patients should receive appropriate guidance on the correct use of the inhaler with regular follow-up to ensure treatment compliance.3,5,6
Patient satisfaction with their inhaler is an acknowledged predictor of treatment adherence.7–10 In a large, multinational, cross-sectional, real-world survey reported by Chrystyn et al,10 patient satisfaction with their inhaler was closely linked to treatment compliance and loosely associated with fewer exacerbations and lower utilization of health-care resources.10 Reporting of patient satisfaction with inhalers is therefore gaining increasing attention and is now recognized as an important patient-reported outcome in clinical trials involving patients with COPD or asthma.1
Measurement of inhaler satisfaction requires the use of reliable and validated instruments such as the Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire (PASAPQ).11 Details on the development and use of the PASAPQ have been published elsewhere.11 The PASAPQ was designed to be easily understood and self-administered by patients with COPD or asthma. It also has an added advantage in that it is device- and treatment-independent, making it widely applicable to respiratory treatments. The PASAPQ has therefore been adopted as one of the principal tools for reporting patient satisfaction/preference with a variety of inhalation devices, including metered-dose inhalers (MDIs), dry powder inhalers (DPIs), and, more recently, the Respimat® Soft Mist™ Inhaler (SMI, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG, Ingelheim, Germany).12 In this study, we report on the findings from a cross-sectional study designed to assess the patient handling and satisfaction for Respimat® SMI (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG) compared with the Breezhaler® DPI13 (Novartis Pharma S.A.S., Paris, France) under everyday conditions of practical use in patients with COPD in Spain.
Methods
Study design
This was a multicenter open-label, cross-sectional, post-marketing surveillance study.
Study population
Patients with COPD were eligible for the study if they were already assigned to therapy with either SPIRIVA® (tiotropium) Respimat® (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG) or with Hirobriz®/Onbrez®/Oslif® (indacaterol) Breezhaler® (Novartis Pharma S.A.S.) for at least 3 but not more than 6 months before they were invited to complete the PASAPQ at a single visit to the study site. During this visit, data on the patients’ baseline characteristics, duration of COPD, relevant concomitant diagnoses, and concomitant medication were collected. Whether patients received training in the use of either inhaler at prescription was also documented at this visit. Inclusion criteria were men and women aged ≥40 years with a clinical diagnosis of COPD and confirmed by spirometry (a postbronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio ≤0.7). Patients followed usual clinical practice of the participant sites and were stabilized with their existing medication. Patients were excluded for the following reasons: 1) they were previously included in this study or currently participating in another interventional study; 2) had visual, cognitive, or motor impairment that, as judged by the investigator, did not allow the patient to independently read and complete the PASAPQ questionnaire; 3) they were being treated simultaneously with both inhalers: Respimat® and Breezhaler®.
All patients signed a written informed consent consistent with the International Conference on Harmonization–Good Clinical Practice (ICH–GCP) guidelines. The study was approved by the Ethics Commiittee of the Vall d’Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint of the trial was the mean total PASAPQ score. Secondary endpoints were the performance score domain of the PASAPQ, the convenience score domain of the PASAPQ, and the overall satisfaction score of the PASAPQ.
Assessments
Patient inhaler device satisfaction was analyzed using the relevant components of the PASAPQ; this comprised 14 items across three domains.11 Thirteen satisfaction questions were used to calculate the total score. Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, and 11 comprise the performance domain and questions 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, and 13 comprise the convenience domain. Question 14 examined overall patient satisfaction score (Table S1). A stand-alone item relating to device preference and willingness to continue was omitted in this study because the trial design precluded the assessment of patient preference. Patients could only use one inhaler not both; they could not compare the performance of both inhalers and therefore state a preference. All questions were answered on a 7-point scale ranging from 1 to 7 (1= very dissatisfied, 2= dissatisfied, 3= somewhat dissatisfied, 4= neither dissatisfied nor satisfied, 5= somewhat satisfied, 6= satisfied, 7= very satisfied). To calculate the domain scores, the sum of the items within each domain was transformed to a 0–100-point scale.
Statistical analyses
Descriptive statistics for N (number of nonmissing observations), mean, standard deviation (SD), minimum (min), 1st quartile, median, 3rd quartile, and maximum (max) were calculated for continuously distributed data and for ordered categorical data (ordinal data). Inferential statistics were used for the calculation of 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the difference of the means of the total score and the performance and convenience domain scores. These analyses were performed using the Student’s t-test. The statistical analysis was conducted using a two-sided test. The primary analysis was based on the full analysis set, which included all patients who provided evaluable data for the total score of the PASAPQ.
The study sample size was based on the calculation that 70 patients in each group would be required to have a 90% power to detect a minimum 10-point difference in the mean PASAPQ score between patients using Respimat® or Breezhaler®, assuming that the common standard deviation is 18.0 using a two-sample t-test with a 0.05 two-sided significance level. To account for potential patients with no evaluable data, a total number of 75 patients per group was planned.
Missing data were handled as follows: both domain scores (performance and convenience) used the standard half-scale option for scoring (eg, responses for at least half of the items in the scale). Each patient had to answer at least half of the items in the domain to calculate a score for that domain at that time point. If the patient answered at least half of the items in the domain, values for missing items were imputed using the mean of the remaining, nonmissing items in that domain. For a comparison of patient baseline demographics, P-values were based on the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test for the categorical variables, and on a two-sample t-test for the continuous variables.
Results
Patient characteristics
The study was conducted in 15 sites in Spain and enrolled 154 patients with stable COPD. All patients completed the PASAPQ. Patients in the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups were generally comparable in their baseline characteristics, prebronchodilator and postbronchodilator spirometry assessments, disease progression and duration of COPD, smoking status, and level of device training received (Table 1). Before being prescribed Respimat® or Breezhaler® by their treating physician, 73 patients received training on using Respimat® compared with 76 patients who received training on the use of Breezhaler® (Table 1).
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
| Respimat® (n=77) | Breezhaler® (n=77) | Total (N=154) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age – mean (SD) | 69.7 (10.0) | 67.0 (9.9) | 68.4 (10.0) | 0.102 |
| Male – n (%) | 69 (89.6) | 70 (90.9) | 139 (90.3) | 0.786 |
| BMI – n (%) | 0.063 | |||
| <18 kg/m2 | 1 (1.3) | 1 (1.3) | 2 (1.3) | |
| 18 to ≤30 kg/m2 | 48 (62.3) | 51 (66.2) | 99 (64.3) | |
| >30 kg/m2 | 27 (35.1) | 25 (32.5) | 52 (33.8) | |
| Smoking status – n (%) | 0.496 | |||
| Current smoker | 18 (23.4) | 15 (19.5) | 33 (21.4) | |
| Ex-smokers | 55 (71.4) | 60 (77.9) | 115 (74.7) | |
| Pack-years of smoking – mean (SD) | 57.9 (26.2) | 55.7 (24.7) | 56.8 (25.4) | 0.605 |
| Time since COPD diagnosis, years – (SD) | 6.3 (6.0) | 5.9 (5.4) | 6.1 (5.7) | 0.643 |
| Postbronchodilation spirometry – mean (SD) | ||||
| FEV1 – liters | 1.5 (0.6) | 1.6 (0.7) | 1.6 (0.6) | 0.214 |
| FEV1 – % of predicted value | 55.1 (16.5) | 56.5 (21.5) | 55.8 (19.1) | 0.652 |
| FVC – liters | 2.8 (0.8) | 3.1 (0.9) | 3.0 (0.9) | 0.035 |
| FVC – % of predicted value | 76.2 (16.7) | 81.7 (23.4) | 78.9 (20.4) | 0.098 |
| FEV1/FVC | 53.9 (12.9) | 51.8 (12.2) | 52.9 (12.5) | 0.304 |
| Respiratory medication – n (%) | ||||
| Inhaled anticholinergics | ||||
| Long-acting | ||||
| SPIRIVA® Respimat® | 77 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 77 (50.0) | |
| Short-acting | 8 (10.4) | 13 (16.9) | 21 (13.6) | 0.240 |
| Inhaled β-agonists | ||||
| Long-acting | ||||
| Hirobriz® Breezhaler® | 0 (0.0) | 16 (20.8) | 16 (10.4) | |
| Onbrez® Breezhaler® | 0 (0.0) | 51 (66.2) | 51 (33.1) | |
| Oslif® Breezhaler® | 0 (0.0) | 10 (13.0) | 10 (6.5) | |
| Short-acting | 46 (59.7) | 43 (55.8) | 89 (57.8) | 0.624 |
| Corticosteroids | ||||
| Inhaled | 52 (67.5) | 22 (28.6) | 74 (48.1) | <0.001 |
| Systemic | 3 (3.9) | 3 (3.9) | 6 (3.9) | 1.000 |
| Theophylline | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.6) | 2 (1.3) | 0.497 |
| Received training on inhalation technique at initial prescription – n (%) | 73 (94.8) | 76 (98.7) | 149 (96.8) | 0.367 |
| Instructions given by – n (%) | ||||
| Doctor | 51 (69.9) | 42 (55.3) | 93 (62.4) | |
| Nurse | 18 (24.7) | 34 (44.7) | 52 (34.9) | |
| Pharmacist | 2 (2.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.3) | |
| Other | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.7) | |
| Missing | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.7) | |
Note: P-values are based on chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test for the categorical variables, and on a two-sample t-test for the continuous variables.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC1, forced vital capacity; SD, standard deviation.
Patient satisfaction with inhaler performance and convenience
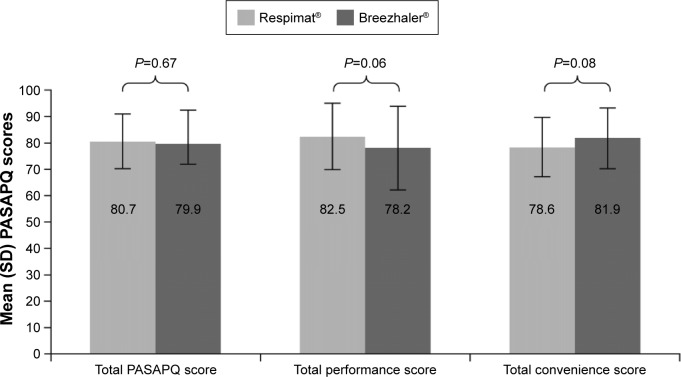
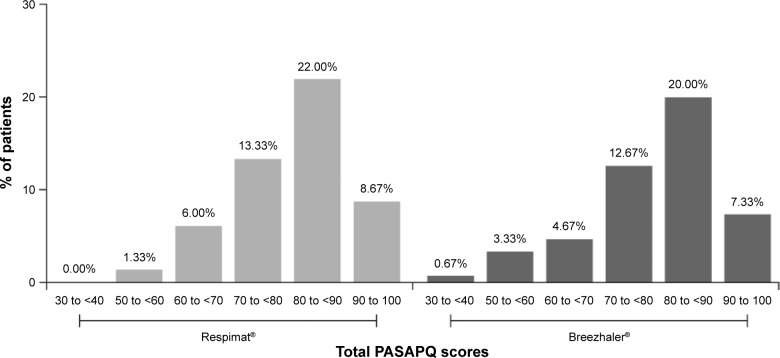
For the primary endpoint, there was not a statistically significant difference in the mean PASAPQ total score between the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups (80.7 and 79.9, respectively, difference of 0.8, 95% CI −2.9 to 4.5; P=0.67) (Figure 1; Table 2). For the secondary endpoints of mean total performance and convenience domain scores, there were no differences in scores between the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups (mean performance score: 82.5 and 78.2, respectively, difference of 4.3, 95% CI −0.3 to 8.9; P=0.06; and mean convenience score: 78.6 and 81.9, respectively, difference of −3.3, 95% CI −7.0 to 0.4; P=0.08) (Figure 1; Table 2). This was also true for the secondary endpoint of overall patient satisfaction score (difference of 0.1, 95% CI −0.3 to 0.4; P=0.70). For both the Respimat® and Breezhaler® groups, the distributions in patient total PASAPQ scores were comparable. This distribution was mirrored in the performance and convenience domain scores, which showed that >95% of patients were satisfied with the performance and convenience of using their assigned inhaler (scores >60 show that patients are satisfied) (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Mean PASAPQ scores by treatment.
Abbreviations: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire; SD, standard deviation.
Table 2.
PASAPQ scores by treatment
| PASAPQ scores | Respimat® (n=77) | Breezhaler® (n=77) | Mean difference (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total score | 80.7 (10.5) | 79.9 (12.7) | 0.8 (−2.9 to 4.5) | 0.67 |
| Total performance | 82.5 (12.6) | 78.2 (15.8) | 4.3 (−0.3 to 8.9) | 0.06 |
| Total convenience | 78.6 (11.3) | 81.9 (11.7) | −3.3 (−7.0 to 0.4) | 0.08 |
| Overall satisfaction | 6.0 (0.8) | 5.9 (1.2) | 0.1 (−0.3 to 0.4) | 0.70 |
Note: Data are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified.
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire; SD, standard deviation.
Figure 2.
Distribution of total PASAPQ scores.
Abbreviation: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire.
Subgroup analyses
Stratification of the PASAPQ scores for performance, convenience, and overall satisfaction according to age (Table 3), smoking status (Table 4), and duration of COPD (Table 5) did not reveal statistically significant differences between the Respimat® and Breezhaler® patient groups.
Table 3.
PASAPQ scores stratified by age groups
| PASAPQ scores | Age groups
|
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤70 years | >70 years | ||
| Total score | |||
| Respimat® | 80.1 (12.4) | 81.3 (8.2) | 0.62 |
| Breezhaler® | 81.8 (11.2) | 77.1 (14.4) | 0.11 |
| Total performance | |||
| Respimat® | 81.0 (15.4) | 84.0 (8.7) | 0.30 |
| Breezhaler® | 80.7 (13.4) | 74.5 (18.5) | 0.09 |
| Total convenience | |||
| Respimat® | 79.1 (12.7) | 78.1 (9.8) | 0.72 |
| Breezhaler® | 83.1 (10.8) | 80.2 (13.1) | 0.29 |
| Overall satisfaction | |||
| Respimat® | 6.0 (1.0) | 6.0 (0.6) | 0.88 |
| Breezhaler® | 6.1 (1.2) | 5.6 (1.2) | 0.04 |
Note: Data are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified.
Abbreviations: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire; SD, standard deviation.
Table 4.
PASAPQ scores stratified by smoking status
| PASAPQ scores | Smoking status
|
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current smoker | Ex-smoker | ||
| Total score | |||
| Respimat® | 82.8 (11.5) | 79.8 (10.4) | 0.30 |
| Breezhaler® | 76.1 (10.7) | 80.8 (13.1) | 0.20 |
| Total performance | |||
| Respimat® | 82.7 (14.1) | 82.2 (12.5) | 0.89 |
| Breezhaler® | 73.8 (13.7) | 79.3 (16.2) | 0.23 |
| Total convenience | |||
| Respimat® | 83.0 (10.7) | 77.1 (11.5) | 0.06 |
| Breezhaler® | 78.7 (11.5) | 82.5 (11.9) | 0.27 |
| Overall satisfaction | |||
| Respimat® | 6.2 (0.9) | 5.9 (0.8) | 0.19 |
| Breezhaler® | 5.3 (1.7) | 6.1 (1.0) | 0.02 |
Note: Data are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified.
Abbreviations: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire; SD, standard deviation.
Table 5.
PASAPQ scores stratified by time since diagnosis of COPD
| PASAPQ scores | Time since COPD diagnosis
|
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤6 years | >6 years | ||
| Total score | |||
| Respimat® | 79.6 (12.3) | 82.3 (6.9) | 0.28 |
| Breezhaler® | 80.0 (12.8) | 79.9 (12.7) | 0.98 |
| Total performance | |||
| Respimat® | 80.5 (14.8) | 85.5 (7.6) | 0.09 |
| Breezhaler® | 78.2 (15.4) | 78.2 (16.8) | 0.99 |
| Total convenience | |||
| Respimat® | 78.7 (13.0) | 78.6 (8.4) | 0.98 |
| Breezhaler® | 82.0 (12.3) | 81.9 (11.1) | 0.96 |
| Overall satisfaction | |||
| Respimat® | 5.9 (1.0) | 6.0 (0.5) | 0.73 |
| Breezhaler® | 5.8 (1.3) | 6.0 (1.0) | 0.43 |
Note: Data are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified.
Abbreviations: COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire; SD, standard deviation.
Discussion
This cross-sectional study had three important findings. First, it was shown that patient overall satisfaction, including with the performance and convenience of the Respimat® SMI12 compared with the Breezhaler® DPI,13 was similar in patients with stable COPD, as measured by the validated PASAPQ. Second, this analysis showed that patient satisfaction with the handling and performance of Respimat® compared with the Breezhaler® inhaler was independent of age, smoking history, and duration of COPD. Third, patients gave Respimat® and Breezhaler® overall satisfaction PASAPQ scores of 6.0 and 5.9, respectively, which shows that both sets of patients were satisfied with the inhaler they were assigned.
A modified version of the PASAPQ questionnaire was used in this trial, excluding the questions on inhaler preference and willingness to continue after the end of the assessment period. The trial did not employ a crossover design, and patients used only one device during the study. Inhaler preference should be assessed using a randomized, crossover design, with the same medication in different devices, and for a longer assessment period.14
We explored possible sources of bias including site recruitment differences, patient recruitment rates, and the quality of device training received by patients enrolled in the trial. The majority of patients in both groups were instructed by the physician, followed by the nurse (62.4% and 34.9% of total number of patients receiving training, respectively). In addition, no statistical differences in PASAPQ scores by site or by patient recruitment rates were found (data not shown).
Although there were no major differences in demographic variables between the Breezhaler® and Respimat® arms, such as, for example, age, sex, time since COPD diagnosis, and smoking history, a higher proportion of patients in the Respimat® group was previously using inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) compared with those in the Breezhaler® arm. However, to minimize a positive selection bias, the decision to treat patients with Respimat® or Breezhaler® was taken before patients were recruited into the study, and this had to be in compliance with usual clinical practice at the study sites, ie, only patients who already used either device for a period of 3–6 months were recruited into the study. Although patients on higher ICS use prior to the study observation period could have presented a more symptomatic disease state than those patients with less use of corticosteroids, this was not thought to have a major influence on the results of the study. Patients in either group showed similar baseline lung function obstruction, as shown by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)% predicted. In this trial, no additional data on symptoms scoring (COPD Assessment Test, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire) or exacerbation data has been collected. Nevertheless, it cannot be completely ruled out that for some patients, the efficacy provided by their prescribed treatment, either before or concomitant with the observation period, may have influenced their perception of the inhaler device.
Patient satisfaction with their inhalers is now acknowledged as an important patient-reported outcome in respiratory medicine8 owing to its impact on patients’ adherence to their prescribed treatments.15 Patient satisfaction is dependent on physical attributes of the inhaler device such as ease of use, convenience, robustness, portability, and whether the instructions were simple and easy to follow.1,10 The ability to be used easily and having multiple doses to reduce the need for device preparation are also desirable.1 A reason for patient dissatisfaction with their inhalation device might be drug deposition to the back of the throat. With prolonged use, this causes inflammation in the back of the throat. Therefore, improved delivery to the lung of the active compound is important for improved patient satisfaction and treatment adherence. This can be achieved by having the following attributes: formulation of aerosol cloud <5.8 μm in size, low cloud velocity, and cloud generation that is independent of patient inspiration rate.1
The decision to compare the Respimat® SMI with the Breezhaler® DPI in our study was based on their design features; more than other competing devices, they closely adhere to key features identified as being important in the design of an ideal inhaler device. The Respimat® SMI was designed to overcome problems such as limited drug deposition in the lung and the reliance on adequate patient coordination for effective inhalation. It is a multiple-dose device that generates a fine aerosol cloud that is emitted more slowly and lasts 1.5 seconds compared with <0.2 to >0.3 seconds for chlorofluorocarbon MDIs and hydrofluoroalkane pressurized MDIs (HFA pMDIs), respectively.1 In vitro data showed a reduced throat deposition using Respimat® SMI versus Breezhaler® in patients with moderate/very severe COPD. In addition, its delivery mechanism has been optimized to maximize the proportion of the inhaled dose that reaches the patient’s lung.16 The consequence of this is that drug exposure and clinical efficacy is achieved at a much lower tiotropium dose, compared with the HandiHaler® DPI (18 μg for SPIRIVA® HandiHaler®). Using the Breezhaler® DPI, the dose of indacaterol is either 150 or 300 μg. In the current study, these advantages of the Respimat® SMI were not assessed directly and therefore not detected by patients in the Respimat® SMI group.
The Breezhaler® is a low airflow resistance, single-dose DPI. It is designed in such a way that the drug/carrier mixture is partly dispersed into inhalable drug particles by the inspiratory airflow of the patient. The extent of device emptying and dispersion, which determines the fine-particle dose of drug emitted, depends strongly on the inspiratory airflow and absolute lung capacity, both of which differ from patient to patient.1
Other studies have previously investigated patient satisfaction and preference for inhalers, but these have differed in their assessment of this outcome measure.14,17 This has been due to differences in the instruments that have been used to gauge patient satisfaction and preference for a given inhaler.1,17 Instruments have included simple preference questionnaires and nonvalidated proprietary questionnaires with poorly defined response scales, developed without psychometric testing. To date, only two instruments, the PASAPQ and the Patient Device Experience Assessment, have incorporated input from experts in psychometric testing and have been subjected to field testing. Of these two, only the PASAPQ has a published validation.11 Based on the validation reported by Kozma et al,11 which assessed validity, reliability, and responsiveness, and explored the between-group difference in PASAPQ scores across asthma, COPD, and mixed respiratory diseases, the PASAPQ is a practical, reliable, valid, and responsive instrument for measuring device satisfaction in respiratory diseases.
Our scores for the overall patient satisfaction, performance, and convenience domains for the Respimat® SMI are consistent with those from previous trials that utilized the PASAPQ to assess patient satisfaction.18–21 In these studies, which were conducted in patients with asthma, COPD, or both, patient satisfaction for the Respimat® SMI was compared with that of the HFA pMDI, and the DPIs Turbuhaler® and Diskus®, using the PASAPQ. The durations of these studies ranged from 4 to 48 weeks.18–21 In Schurmann et al’s study,18 a crossover study that compared the Respimat® SMI to the HFA pMDI, patients were trained in inhaler use at the beginning of each treatment period and given ≤5 attempts to demonstrate satisfactory technique; however, use of the inhalers prior to randomization was not permitted. Similarly, Hodder et al’s study,19 which had a parallel-group, double-dummy design, did not enroll patients with prior use of the inhalers under evaluation. Patient performance and convenience domain scores for the Respimat® SMI ranged from 81.6 to 88.2 and from 78.6 to 83.6, respectively, compared with 82.5 and 78.6 for the performance and convenience domains, respectively, in our current study.
When comparing DPIs with the Respimat® SMI, the main difference between the current study and other trials that used PASAPQ to assess patient satisfaction for a given inhaler was the relatively higher scores for the Breezhaler® DPI compared with other DPIs. In previous comparator studies with Respimat® SMI, DPIs (Turbuhaler® and Diskus®) received mean total, performance domain, and convenience domain PASAPQ scores ranging from 75.5 to 76.9, 72 to 75.5, and 75.4 to 82.7, respectively.19,20 This compares with 79.9, 78.2, and 81.9 for mean total, performance domain, and convenience domain PASAPQ scores, respectively, for Breezhaler®.
In conclusion, patients with COPD in Spain who used either the Respimat® SMI or the Breezhaler® DPI reported being similarly satisfied with the performance and convenience of each inhaler. Furthermore, these results suggest that the use of either of these inhalers would encourage treatment adherence in patients with COPD.
Supplementary material
Table S1.
Validated questions included in the modified PASAPQ
| Domain | Question | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total score | ||
| Performance domain | Q1 | Overall feeling of inhaling |
| Q2 | Inhaled dose goes to lungs | |
| Q3 | Amount of medication left | |
| Q4 | Works reliably | |
| Q5 | Ease of inhaling a dose | |
| Q10 | Using the inhaler | |
| Q11 | Speed medicine comes out | |
| Convenience domain | Q6 | Instructions for use |
| Q7 | Size of inhaler | |
| Q8 | Durability of inhaler | |
| Q9 | Ease of cleaning inhaler | |
| Q12 | Ease of holding during use | |
| Q13 | Convenience of carrying | |
| Q14 | Overall satisfaction | |
Notes: All items scored on a 7-point Likert scale: 1= very dissatisfied, 2= dissatisfied, 3= somewhat dissatisfied, 4= neither satisfied nor dissatisfied, 5= somewhat satisfied, 6= satisfied, 7= very satisfied.
Abbreviation: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire.
Acknowledgments
Writing assistance was provided by Godfrey Lisk, of PAREXEL, funded by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Footnotes
Author contributions
All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
Marc Miravitlles has received speaker fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Esteve, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, Grifols, and Novartis, and consulting fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Gebro Pharma, CLS Behring, MedImmune, Takeda, Novartis, and Grifols.
Juan Luis Garcia-Rivero has received speaker fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, Takeda, Teva, Ferrer, and Novartis, and consulting fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim and Menarini. Salud Santos has received speaker fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, Novartis, and Teva Pharma, and consulting fees from Almirall, Gebro Pharma, Novartis, Faes, and Menarini.
Jéssica Montero-Caballero, Frank Richard, and Xavier Ribera are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Moroni-Zentgraf P. Impact of patient needs on design and usage of an inhalation device in respiratory medicine. Respir Drug Deliv Eur. 2013;1:141–152. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Virchow JC, Crompton GK, Dal NR, et al. Importance of inhaler devices in the management of airway disease. Respir Med. 2008;102(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lavorini F, Magnan A, Dubus JC, et al. Effect of incorrect use of dry powder inhalers on management of patients with asthma and COPD. Respir Med. 2008;102(4):593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(5):487–497. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra050100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Molimard M. How to achieve good compliance and adherence with inhalation therapy. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005;21(Suppl 4):S33–S37. doi: 10.1185/030079905X61776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roy A, Battle K, Lurslurchachai L, Halm EA, Wisnivesky JP. Inhaler device, administration technique, and adherence to inhaled corticosteroids in patients with asthma. Prim Care Respir J. 2011;20(2):148–154. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2011.00022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Atkinson MJ, Sinha A, Hass SL, et al. Validation of a general measure of treatment satisfaction, the Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM), using a national panel study of chronic disease. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2004;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-2-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shikiar R, Rentz AM. Satisfaction with medication: an overview of conceptual, methodologic, and regulatory issues. Value Health. 2004;7(2):204–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2004.72252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Small M, Anderson P, Vickers A, Kay S, Fermer S. Importance of inhaler-device satisfaction in asthma treatment: real-world observations of physician-observed compliance and clinical/patient-reported outcomes. Adv Ther. 2011;28(3):202–212. doi: 10.1007/s12325-010-0108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chrystyn H, Small M, Milligan G, Higgins V, Gil EG, Estruch J. Impact of patients’ satisfaction with their inhalers on treatment compliance and health status in COPD. Respir Med. 2014;108(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kozma CM, Slaton TL, Monz BU, Hodder R, Reese PR. Development and validation of a patient satisfaction and preference questionnaire for inhalation devices. Treat Respir Med. 2005;4(1):41–52. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200504010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spiriva Respimat 25 microgram, inhalation solution (summary of product characteristics) Ingelheim, Germany: Boehringer Ingelheim; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hirobriz®/Onbrez®/Oslif® Breezhaler® (summary of product characteristics) Basel, Switzerland: Novartis; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Anderson PJ. Patient preferences for and satisfaction with inhaler devices. Eur Respir Rev. 2005;14(96):109–116. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Blasi F, Raddi F, Miravitlles M. Interactive Monitoring Service and COPD: is it possible to reduce nonadherence? COPD. 2015;12(3):227–232. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2014.933796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ciciliani AM, Langguth P, Bickman D, Wachtel H, Voshaar T. In vitro dose comparison of Respimat® Soft Mist™ inhaler with dry powder inhalers for COPD maintenance therapy; Abstract presented at: International Society of Addiction Medicine Annual Congress; April 6–10, 2013; Chapel Hill, NC. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hodder R. Design and interpretation of device preference trials: marketing tools or scientific instruments? Respir Drug Deliv. 2006;1:19–36. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schurmann W, Schmidtmann S, Moroni P, Massey D, Qidan M. Respimat Soft Mist inhaler versus hydrofluoroalkane metered dose inhaler: patient preference and satisfaction. Treat Respir Med. 2005;4(1):53–61. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200504010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hodder R, Reese PR, Slaton T. Asthma patients prefer Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler to Turbuhaler. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2009;4:225–232. doi: 10.2147/copd.s3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Freytag F, Rau-Berger H, Glaab T. Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler preferred to Diskus by patients with COPD and/or asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:A639. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ferguson GT, Ghafouri M, Dai L, Dunn LJ. COPD patient satisfaction with ipratropium bromide/albuterol delivered via Respimat: a randomized, controlled study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013;8:139–150. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S38577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Validated questions included in the modified PASAPQ
| Domain | Question | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total score | ||
| Performance domain | Q1 | Overall feeling of inhaling |
| Q2 | Inhaled dose goes to lungs | |
| Q3 | Amount of medication left | |
| Q4 | Works reliably | |
| Q5 | Ease of inhaling a dose | |
| Q10 | Using the inhaler | |
| Q11 | Speed medicine comes out | |
| Convenience domain | Q6 | Instructions for use |
| Q7 | Size of inhaler | |
| Q8 | Durability of inhaler | |
| Q9 | Ease of cleaning inhaler | |
| Q12 | Ease of holding during use | |
| Q13 | Convenience of carrying | |
| Q14 | Overall satisfaction | |
Notes: All items scored on a 7-point Likert scale: 1= very dissatisfied, 2= dissatisfied, 3= somewhat dissatisfied, 4= neither satisfied nor dissatisfied, 5= somewhat satisfied, 6= satisfied, 7= very satisfied.
Abbreviation: PASAPQ, Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire.