Abstract
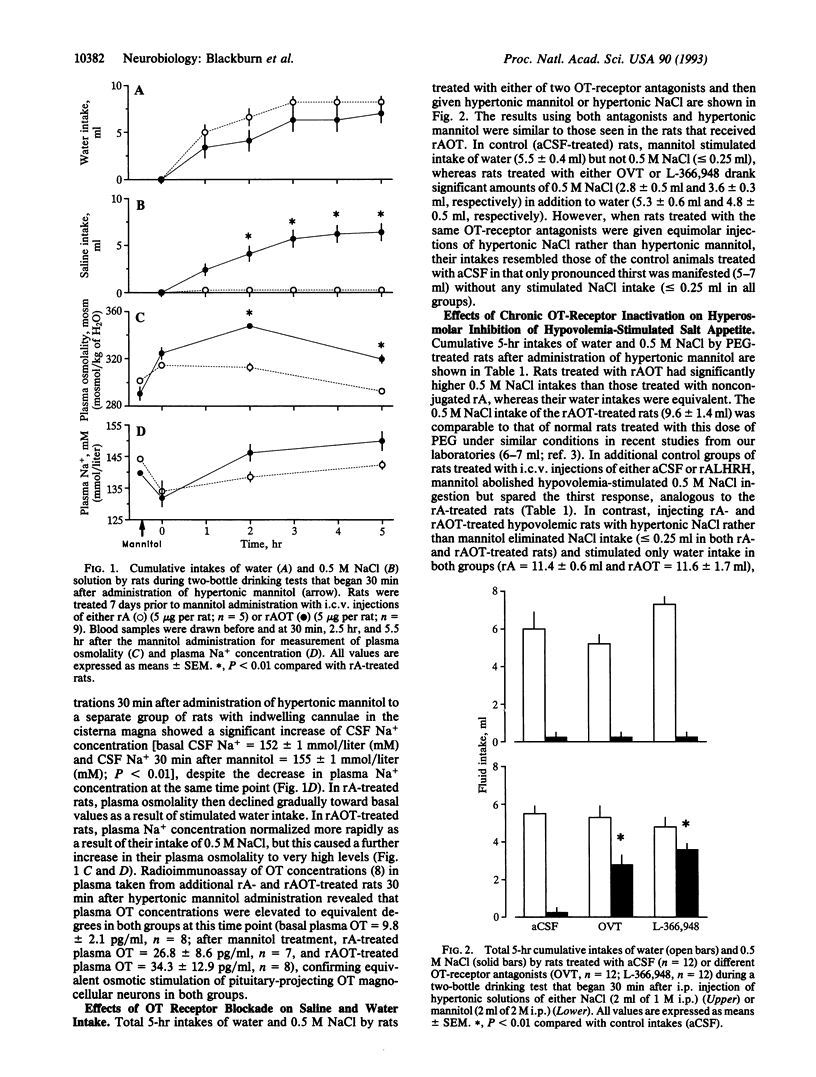
Sodium chloride ingestion is stimulated during conditions of sodium deficiency to maintain body fluid and electrolyte balance. Recent studies have indicated that salt appetite in rats is often inversely related to peripheral and central secretion of the hormone oxytocin (OT). We studied the potential role of central OT on salt and water ingestion by treating rats intracerebroventricularly with OT conjugated to the A chain of the plant cytotoxin ricin (rAOT) to produce a chronic selective inactivation of brain cells containing OT-receptive elements. The rats treated with rAOT and control rats treated with the ricin A chain alone were given 5-hr two-bottle (water and 0.5 M NaCl) drinking tests 30 min after they were made hyperosmolar by injections of hypertonic (2M) mannitol solution, which elevated plasma osmolality but reduced plasma Na+ concentration. In the control rats only water intake was stimulated in response to the induced hyperosmolality, but in the rAOT-treated rats hypertonic mannitol caused a robust salt appetite as well as thirst. Analogous results were obtained in rats treated with two different OT-receptor antagonists prior to induction of hyperosmolality with mannitol. In contrast to these results, when hyperosmolality was induced by administration of equivalently hypertonic (1M) NaCl, which elevated both plasma osmolality and plasma Na+ concentration, only water intake but not salt intake was stimulated in both control and OT-receptor antagonist-treated rats. When salt appetite was stimulated by the physiological stimulus of polyethylene glycol-induced hypovolemia, hypertonic mannitol similarly inhibited salt ingestion in control animals but not in rAOT-treated rats, whereas hypertonic NaCl inhibited subsequent salt ingestion in both groups. These results suggest that salt appetite is regulated by both Na(+)- and osmolality-sensing mechanisms in rats. In addition, they indicate that central OT likely mediates a significant component of osmolality-related inhibition of salt appetite but does not appear to be essential for Na(+)-related inhibition of this important homeostatic behavior.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B. Regulation of body fluids. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:185–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B. Thirst--and brain control of water balance. Am Sci. 1971 Jul-Aug;59(4):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn R. E., Demko A. D., Hoffman G. E., Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Central oxytocin inhibition of angiotensin-induced salt appetite in rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 2):R1347–R1353. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.6.R1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn R. E., Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Central oxytocin mediates inhibition of sodium appetite by naloxone in hypovolemic rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 Aug;56(2):255–263. doi: 10.1159/000126236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. D., Barakat A. S., Smith D. D., Hruby V. J., Pedersen C. A. A uterotonic antagonist blocks the oxytocin-induced facilitation of female sexual receptivity. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 2;512(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90639-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton D. A., McKinley M. J., Nelson J. F., Osborne P., Simpson J., Tarjan E., Weisinger R. S. Species differences in the effect of decreased CSF sodium concentration on salt appetite. J Physiol (Paris) 1984;79(6):499–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan L. M., Olson B. R., Sved A. F., Verbalis J. G., Stricker E. M. Gastric motility in conscious rats given oxytocin and an oxytocin antagonist centrally. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 24;578(1-2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf R., Neumann I., Schwarzberg H. Central and peripheral release of vasopressin and oxytocin in the conscious rat after osmotic stimulation. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 9;457(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90689-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. J., Denton D. A., Weisinger R. S. Sensors for antidiuresis and thirst--osmoreceptors or CSF sodium detectors? Brain Res. 1978 Feb 3;141(1):89–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90619-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson B. R., Drutarosky M. D., Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Brain oxytocin receptors mediate corticotropin-releasing hormone-induced anorexia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):R448–R452. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.2.R448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson W. K., Alexander B. D., Skala K. D., Huang F. L., Fulton R. J. Central peptidergic mechanisms controlling reproductive hormone secretion: novel methodology reveals a role for the natriuretic peptides. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 May;70(5):773–778. doi: 10.1139/y92-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson W. K., Martin L., Mogg R. J., Fulton R. J. A nonoxytocinergic prolactin releasing factor and a nondopaminergic prolactin inhibiting factor in bovine neurointermediate lobe extracts: in vitro and in vivo studies. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1610–1617. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stivers J. A., Kaltwasser M. T., Hill P. S., Hruby V. J., Crawley J. N. Ventral tegmental oxytocin induces grooming. Peptides. 1988;9 (Suppl 1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker E. M. Thirst and sodium appetite after colloid treatment in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1981 Feb;95(1):1–25. doi: 10.1037/h0077764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Central inhibitory control of sodium appetite in rats: correlation with pituitary oxytocin secretion. Behav Neurosci. 1987 Aug;101(4):560–567. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.101.4.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Interaction of osmotic and volume stimuli in regulation of neurohypophyseal secretion in rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):R267–R275. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.2.R267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker E. M., Wolf G. Blood volume and tonicity in relation to sodium appetite. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1966 Oct;62(2):275–279. doi: 10.1037/h0023665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbalis J. G., Blackburn R. E., Olson B. R., Stricker E. M. Central oxytocin inhibition of food and salt ingestion: a mechanism for intake regulation of solute homeostasis. Regul Pept. 1993 Apr 29;45(1-2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90198-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbalis J. G., Mangione M. P., Stricker E. M. Oxytocin produces natriuresis in rats at physiological plasma concentrations. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1317–1322. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Fulton R. J., May R. D., Till M., Uhr J. W. Redesigning nature's poisons to create anti-tumor reagents. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1098–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.3317828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



