Abstract
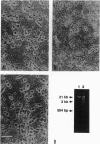
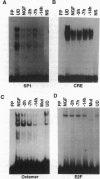
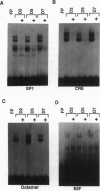
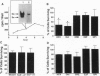
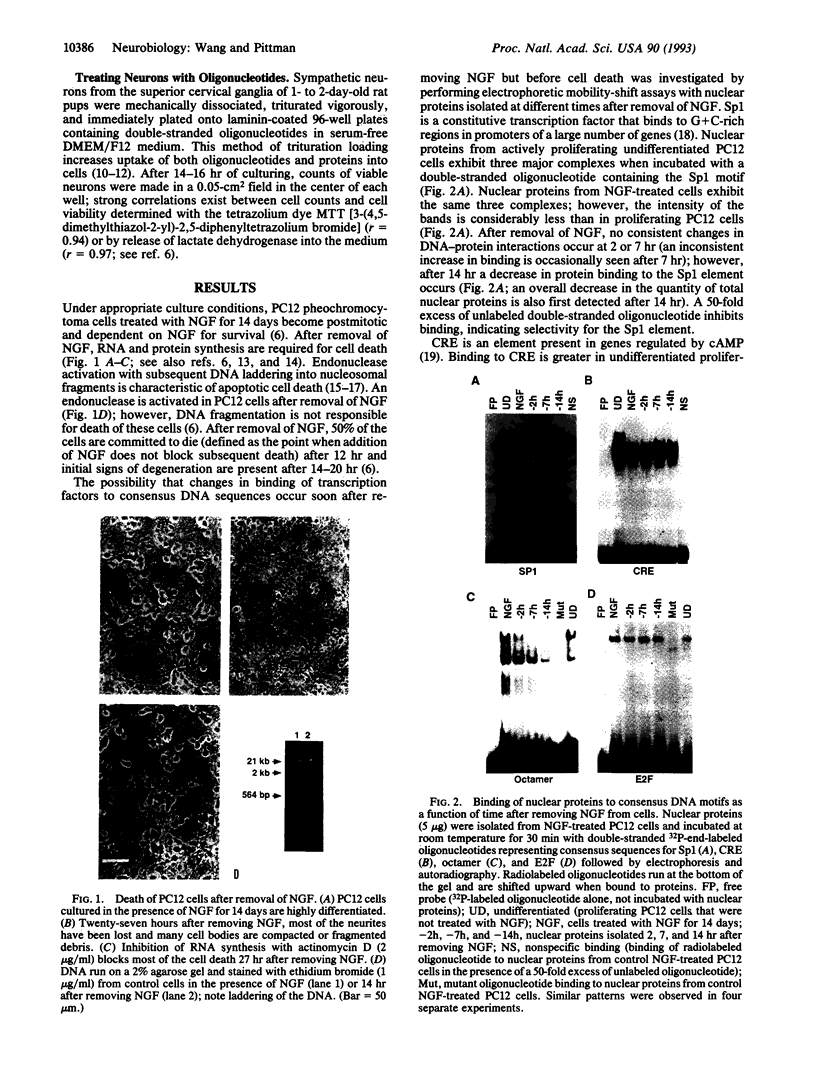
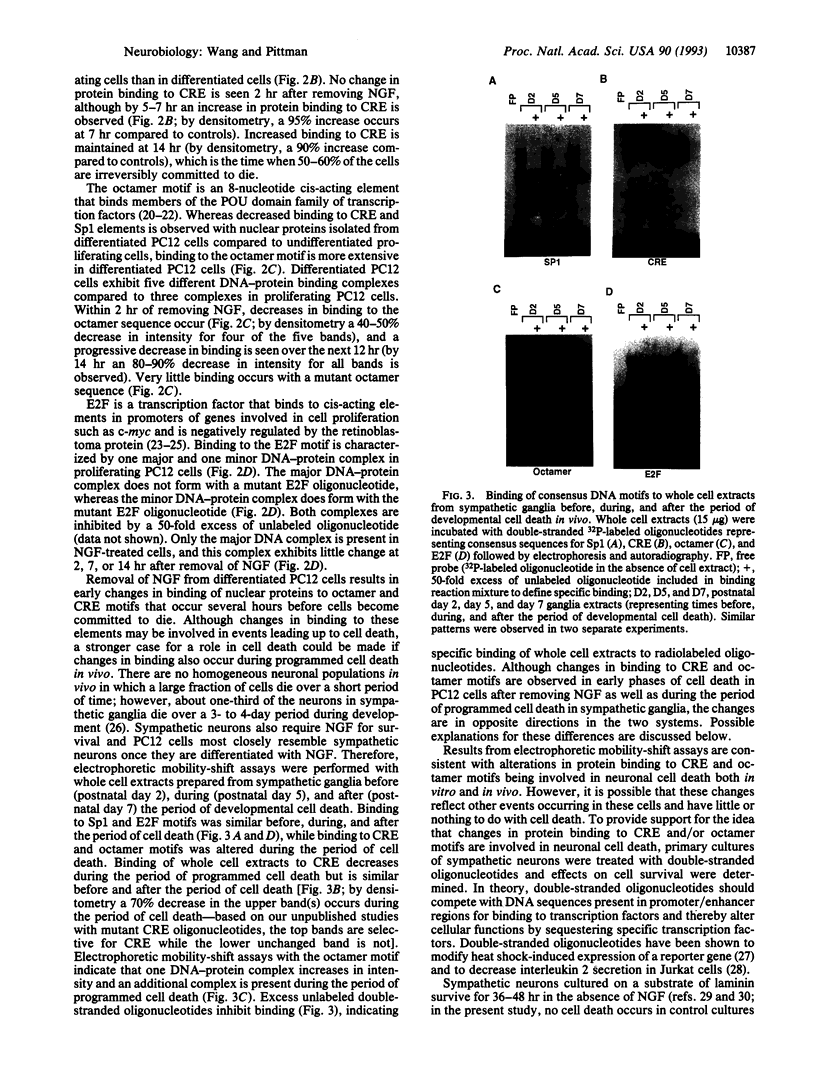
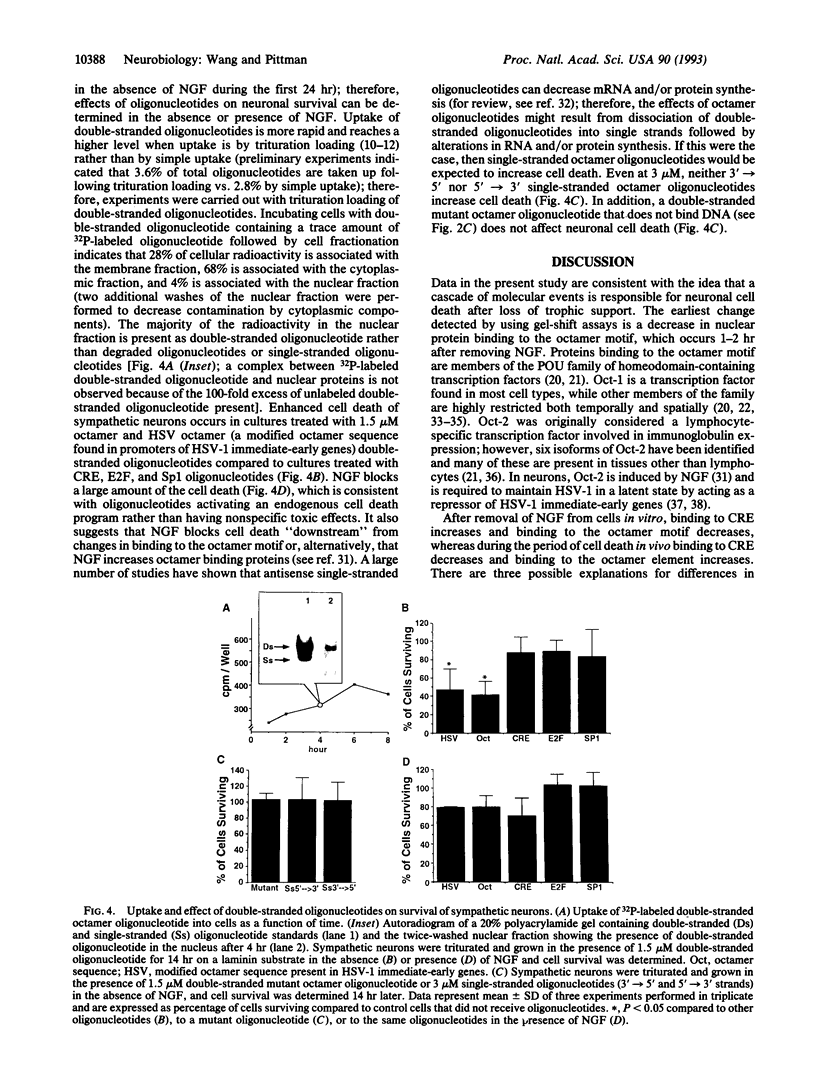
Electrophoretic mobility-shift assays were used to characterize binding of nuclear proteins to consensus sequences for Sp1, E2F, octamer, and cAMP responsive enhancer element (CRE) during neuronal death in vitro after removal of nerve growth factor (NGF). Molecular events occurring prior to cell death in terminally differentiated PC12 cells could be divided into three phases: (i) within 2 hr of removing NGF, binding to the octamer sequence decreased, (ii) after 5-7 hr an increase in binding to CRE occurred; and (iii) after 14 hr (the point at which 50% of the cells are committed to die) a decrease in binding to the Sp1 sequence occurred. Assays performed with extracts from sympathetic ganglia indicated that changes in binding to CRE and octamer motifs also occurred during the period of developmental cell death in vivo. Double-stranded oligonucleotides were delivered to neurons to act as dominant negative "promoters" unable to couple to transcriptional events but capable of binding and sequestering transcription factors. Double-stranded but not single-stranded octamer oligonucleotides increased cell death of primary cultures of sympathetic neurons. Most of the induced neuronal cell death could be blocked with NGF, which is consistent with oligonucleotides activating an endogenous death program rather than having a nonspecific toxic effect. Other double-stranded oligonucleotides as well as a mutant octamer oligonucleotide had little or no effect on cell death. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that cell death results from a cascade of cellular and molecular events and that an early event in programmed neuronal cell death is a decrease in binding of transcription factor(s) to octamer motif sequences.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bielinska A., Shivdasani R. A., Zhang L. Q., Nabel G. J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.2237444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borasio G. D., John J., Wittinghofer A., Barde Y. A., Sendtner M., Heumann R. ras p21 protein promotes survival and fiber outgrowth of cultured embryonic neurons. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1087–1096. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Skaper S. D., Varon S. S., Sato G. H. Selective survival of neurons from chick embryo sensory ganglionic dissociates utilizing serum-free supplemented medium. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. Neurite outgrowth induced by the substrate associated material from nonneuronal cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Sep;79(1):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Boylan J. F., Parker S., Sisken J. E., Patel G. L., Zimmer S. G. Transfection of mammalian cells with plasmid DNA by scrape loading and sonication loading. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8463–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G. The unc-86 gene product couples cell lineage and cell identity in C. elegans. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):895–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Brini A. T., Ferris D. K., Robin P., Farrar W. L. In situ detection of a heat-shock regulatory element binding protein using a soluble synthetic enhancer sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzopoulos A. K., Stoykova A. S., Erselius J. R., Goulding M., Neuman T., Gruss P. Structure and expression of the mouse Oct2a and Oct2b, two differentially spliced products of the same gene. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T. Molecular and cellular mechanism of neuronal degeneration caused by nerve growth factor deprivation approached through PC12 cell culture. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1992 Jan;16(1):95–106. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(92)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander A. D., Fujii D. K., Gospodarowicz D., Reichardt L. F. Characterization of a factor that promotes neurite outgrowth: evidence linking activity to a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):574–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Dent C. L., Wheatley S. C., Beech M. N., Ninkina N. N., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. The octamer-binding protein Oct-2 represses HSV immediate-early genes in cell lines derived from latently infectable sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90290-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. P., Schmidt R. E., DiStefano P. S., Lowry O. H., Carter J. G., Johnson E. M., Jr Inhibitors of protein synthesis and RNA synthesis prevent neuronal death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):829–844. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation kills immature thymocytes. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1843–1849. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2497041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Murphy R. F., Lanni F., Taylor D. L. A method for incorporating macromolecules into adherent cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1556–1564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesner P. W., Winters T. R., Green S. H. Nerve growth factor withdrawal-induced cell death in neuronal PC12 cells resembles that in sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1669–1680. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Prevette D., Tytell M., Homma S. Naturally occurring and induced neuronal death in the chick embryo in vivo requires protein and RNA synthesis: evidence for the role of cell death genes. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):104–113. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90180-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M. M., Chen J., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. Complexes containing the retinoblastoma gene product recognize different DNA motifs related to the E2F binding site. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Wang S., DiBenedetto A. J., Mills J. C. A system for characterizing cellular and molecular events in programmed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3669–3680. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03669.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G., Finney M. Regulation of transcription and cell identity by POU domain proteins. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90227-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ciesiolka T., Gruss P. A nexus between Oct-4 and E1A: implications for gene regulation in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90619-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S. A., Davies A. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis prevents cell death in sensory and parasympathetic neurons deprived of neurotrophic factor in vitro. J Neurobiol. 1990 Jun;21(4):630–638. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treacy M. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a family of POU-domain protein regulatory genes during development of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:139–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley S. C., Dent C. L., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. A cellular factor binding to the TAATGARAT DNA sequence prevents the expression of the HSV immediate-early genes following infection of nonpermissive cell lines derived from dorsal root ganglion neurons. Exp Cell Res. 1991 May;194(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90132-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. L., Smith R. L., Freed C. R., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor-dependence of herpes simplex virus latency in peripheral sympathetic and sensory neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1268–1275. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Lillycrop K. A., Dent C. L., Ninkina N. N., Beech M. M., Willoughby J. J., Winter J., Latchman D. S. Regulation of expression of the neuronal POU protein Oct-2 by nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17787–17791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright L. L., Cunningham T. J., Smolen A. J. Developmental neuron death in the rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglion: cell counts and ultrastructure. J Neurocytol. 1983 Oct;12(5):727–738. doi: 10.1007/BF01258147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Morris R. G., Smith A. L., Dunlop D. Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. J Pathol. 1984 Jan;142(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]