Thiophenes substituted in position 2 and 5 by chiral imine groups display non-crystallographic or crystallographic twofold symmetry.
Keywords: crystal structure, Schiff base, bis-imine, thiophene
Abstract
A series of thiophenes substituted in positions 2 and 5 by imine groups have been synthesized using a solvent-free approach, and their crystal structures determined. The substituents are chiral groups, and the expected absolute configuration for each molecule was confirmed by refinement of the Flack parameter. The compounds are 2,5-bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)imino]thiophene, C26H26N2S, (I), 2,5-bis{[(R)-(−)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene, C24H26N2O2S, (II), 2,5-bis{[(R)-(−)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene, C22H20F2N2S, (III), and 2,5-bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene, C22H20Cl2N2S, (IV). A common feature of all four molecules is the presence of twofold symmetry. For (I), which crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1, this symmetry is non-crystallographic, but for (II) in C2 and the isomorphous structures (III) and (IV) that crystallize in P21212, the twofold symmetry is crystallographically imposed with one half of each molecule in the asymmetric unit. The comparable molecular symmetry in the four structures is also reflected in similar packing, with molecules aggregated to form chains through weak C—H⋯S interactions.
Chemical context
Thiophenedicarbaldehydes have a variety of applications (Dean, 1982a
▸,b
▸), for instance in the synthesis of annulenones and polyenyl-substituted thiophenes (Sargent & Cresp, 1975 ▸), in the preparation of macrocyclic ligands for bimetallic complexes that are able to mimic enzymes (Nelson et al., 1983 ▸), in crown ether chemistry (Cram & Trueblood, 1981 ▸) and, more recently, in the preparation of azomethines for photovoltaic applications (Bolduc et al., 2013a
▸,b
▸; Petrus et al., 2014 ▸). In regard to this latter application, most of the conjugated materials used in organic electronics are synthesized using time-consuming Suzuki-, Wittig-, or Heck-type coupling reactions that require expensive catalysts, stringent reaction conditions, and tedious purification processes. In order to afford a more economic route towards organic photovoltaic materials, Schiff bases derived from 2,5-thiophenedicarbaldehyde as the conjugated linker unit have recently been used. The azomethine bond, which is isoelectronic with the vinyl bond and possesses similar optoelectronic and thermal properties, is easily accessible through the Schiff condensation under near ambient reaction conditions (Morgan et al., 1987 ▸; Pérez Guarìn et al., 2007 ▸; Sicard et al., 2013 ▸).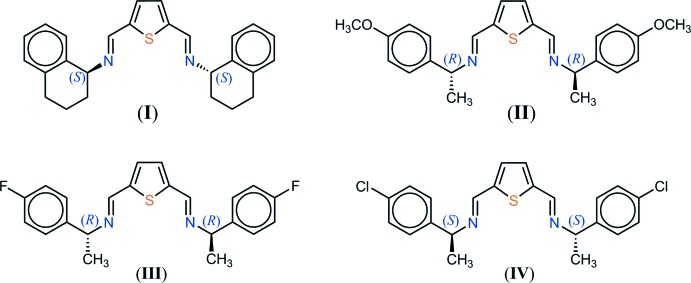
We report here the synthesis and X-ray characterization of such thiophene derivatives, as a continuation of a partially published record (Bernès et al., 2013 ▸; Mendoza et al., 2014 ▸). We are improving a general solvent-free approach for these syntheses, recognising that ecological aspects in organic chemistry have become a priority, in order to minimize the quantity of toxic waste and by-products, and to decrease the amount of solvent in the reaction media or during work-up (Tanaka & Toda, 2000 ▸; Noyori, 2005 ▸).
In the synthesis of the thiophenes reported here, the Schiff condensation generates a single by-product, water, and a one-step recrystallization affords the pure substituted thiophene in nearly quantitative yields. Our protocol may be readily extended to any low molecular weight 2,5-susbtituted thiophene, providing that a liquid amine is used for the condensation. In the present work, the starting material is 2,5-thiophenedicarbaldehyde, a low melting-point compound (m.p. = 388–390 K), and four chiral amines were used. We took advantage of the anomalous dispersion of the sulfur sites to confirm that the configuration of the chiral amine is retained during the condensation.
Structural commentary
The first compound was synthesized using (S)-(+)-1-aminotetraline. The Schiff base (I), C26H26N2S, crystallizes in the space group P1, with the expected absolute configuration (Fig. 1 ▸). The general shape of the molecule displays a pseudo-twofold axis, passing through the S atom and the midpoint of the thiophene C—C σ-bond. As a consequence, the independent benzene rings are placed above and below the thiophene ring, and are inclined to one another at a dihedral angle of 73.76 (15)°. The central core containing the thiophene ring and the imine bonds is virtually planar, and the imine bonds are substituted by the tetralin ring systems, which present the same conformation. The aliphatic rings C9–C13/C18 and C19–C23/C28 each have a half-chair conformation.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms at the 30% probability level.
Compound (II), C24H26N2O2S, was obtained using (R)-(+)-(4-methoxy)phenylethylamine as the chiral component in the Schiff condensation. The twofold molecular axis, which was a latent symmetry in the case of (I), is a true crystallographic symmetry in (II), and this compound crystallizes in the space group C2 (Fig. 2 ▸). The asymmetric unit thus contains half a molecule, and the molecular conformation for the complete molecule is similar to that of (I). The benzene rings have a free relative orientation, since these rings are not fused in a bicyclic system, as in (I); the dihedral angle between symmetry-related rings is 61.30 (7)°.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of (II), with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms at the 30% probability level. Non-labeled atoms are generated by symmetry code (1 − x, y, 1 − z).
Compounds (III) and (IV), synthesized with enantiomerically pure (4-halogen)phenylethylamines (halogen = F, Cl) are isomorphous and crystallize with orthorhombic unit cells. The latent twofold symmetry of (I) is again observed, since both molecules lie on the crystallographic twofold axes of the space group P21212 (Fig. 3 ▸). The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is close to that observed for (II): 64.18 (8)° for (III) and 62.03 (9)° for (IV). The same Schiff base but with Br as the halogen substituent has been published previously (Mendoza et al., 2014 ▸), but is not isomorphous with (III) and (IV). Instead, this molecule was found to crystallize in the space group C2, with unit-cell parameters and a crystal structure very similar to those of (II). A systematic trend is thus emerging for these 2,5-substituted thiophenes, related to the potential twofold molecular symmetry: they have a strong tendency to crystallize in space groups that include at least one C 2 axis, such as C2 and P21212 for the chiral crystals. This trend extends to achiral molecules, which also have twofold crystallographic symmetry in the space group C2/c (Kudyakova et al., 2011 ▸; Suganya et al., 2014 ▸; Boyle et al., 2015 ▸; Moussallem et al., 2015 ▸). The features shared by these related compounds could also be a signature of a propensity towards polymorphism between monoclinic and orthorhombic systems.
Figure 3.
The molecular structures of isomorphous compounds (III) and (IV), with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms at the 30% probability level. Notice the different configuration for chiral center C5 in (III) and (IV). Non-labeled atoms are generated by symmetry codes (1 − x, −y, z) and (1 − x, 2 − y, z) for (III) and (IV), respectively.
The difference between non-crystallographic symmetry in (I) and exact C 2 molecular symmetry in (II)–(IV) is also reflected in the degree of conjugation between thiophene rings and imine bonds. For (I), dihedral angles between the thiophene and C=N—C* mean planes (C* is the chiral C atom bonded to the imine functionality) are 6.9 (7) and 1.9 (6)°. Other crystals have a symmetry restriction, inducing a small deconjugation of the imine bonds. The corresponding dihedral angles with the thiophene rings are 8.5 (4), 10.1 (3), and 9.8 (3)°, for (II), (III) and (IV), respectively.
Supramolecular features
Although all compounds have benzene rings, neither π–π nor C—H⋯π contacts stabilize the crystal structures. However, these compounds share a common supramolecular feature. Lone pairs of S atoms interact with thiophenic CH groups of a neighboring molecule in the crystal, forming chains along the short cell axes: [100] for (I), [010] for (II) and [001] for (III) and (IV). An example is presented in Fig. 4 ▸, for compound (II). These bifurcated S⋯C—H contacts have a significant strength for (I), perhaps as a consequence of the relaxed molecular symmetry in space group P1. The contacts are weaker for (II), (III) and (IV), which have a geometry restrained by the crystallographic symmetry (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 4.
Part of the crystal structure of (II), showing C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) linking molecules along [010]. [Symmetry codes: (i) 1 − x, y, 1 − z; (ii) x, 1 + y, z.]
Table 1. Comparison of C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds (Å, °) in compounds (I)–(IV).
| Compound | Contact | C—H | H⋯S | C⋯S | C—H⋯S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | C4—H4A⋯S1i | 0.93 | 3.00 | 3.562 (5) | 121 |
| (I) | C5—H5A⋯S1i | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.547 (5) | 122 |
| (II) | C4—H4A⋯S1ii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.572 (3) | 122 |
| (III) | C4—H4A⋯S1iii | 0.93 | 3.15 | 3.743 (3) | 124 |
| (IV) | C4—H4A⋯S1iv | 0.93 | 3.23 | 3.828 (4) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x + 1, y, z; (ii) x, y + 1, z; (iii) x, y, z + 1; (iv) x, y, z − 1.
Database survey
Many thiophenes substituted in the 2 and 5 positions by imine groups have been characterized; however, almost all were achiral compounds. X-ray structures have been reported mostly in space group C2/c (Suganya et al., 2014 ▸; Kudyakova et al., 2011 ▸, 2012 ▸; Bolduc et al., 2013b ▸). Other represented space groups for achiral molecules are P21 (Skene & Dufresne, 2006 ▸) and P21/c (Wiedermann et al., 2005 ▸). Finally, a single case of a molecule presenting mirror symmetry has been described (Fridman & Kaftory, 2007 ▸), in space group Pnma.
The group of chiral molecules belonging to this family is much less populated, with two examples reported by our group in this journal. Both are molecules with the C 2 point group and crystallize in space groups C2 (Mendoza et al., 2014 ▸) and P22121 (Bernès et al., 2013 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
Synthesis. The chiral amines used for the Schiff condensation were obtained directly from suppliers: (S)-(+)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthylamine for (I), (R)-(+)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamine for (II), (R)-(+)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethylamine for (III) and (S)-(−)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylamine for (IV). 2,5-Thiophenedicarbaldehyde (100 mg, 0.71 mmol) and the chiral amine (1.4 mmol) in a 1:2 molar ratio were mixed at room temperature under solvent-free conditions, giving light-yellow (II and IV), colorless (III) or light-brown (IV) solids, in 95-97% yields. The crude solids were recrystallized from CH2Cl2, affording colorless crystals of (I)–(IV).
Spectroscopy. (I): m.p. 437–438 K. [α]20 D = +655.4 (c = 1, CHCl3). FTIR: 1616 cm−1 (C=N). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CHCl3/TMS): δ = 1.76–1.86 (m, 2H; H-al), 1.96–2.06 (m, 6H; H-al), 2.74–2.90 (m, 4H; H-al), 4.51 (t, 2H; H-al), 6.98–7.02 (m, 2H; H-ar), 7.09–7.15 (m, 6H; H-ar), 7.28 (s, 2H; H-ar), 8.36 (s, 2H; HC=N). 13C NMR: δ = 19.7, 29.3, 31.1, 67.7 (C-al), 125.7, 126.9, 128.7, 129.1, 129.6, 136.8, 137.1, 145.1 (C-ar), 153.1 (HC=N). MS–EI: m/z = 398 (M +).
(II): m.p. 405–406 K. [α]20 D = −626.8 (c = 1, CHCl3). FTIR: 1631 cm−1 (C=N). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CHCl3/TMS): δ = 1.53 (d, 6H; CHCH 3), 3.78 (s, 6H; OCH 3), 4.47 (q, 2H; CHCH3), 6.85–6.88 (m, 4H; H-ar), 7.19 (s, 2H; H-ar), 7.29–7.32 (m, 4H; H-ar), 8.33 (s, 2H; HC=N). 13C NMR: δ = 24.8 (CHCH3), 55.2 (OCH3), 68.1 (CHCH3), 113.7, 127.6, 129.6, 137.1, 145.2, 152.1 (C-ar), 158.5 (HC=N). MS–EI: m/z = 406 (M +).
(III): m.p. 420–421 K. [α]20 D = −542.5 (c = 1, CHCl3). FTIR: 1621 cm−1 (C=N). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CHCl3/TMS): δ = 1.53 (d, 6H; CHCH 3), 4.49 (q, 2H; CHCH3), 7.00–7.38 (m, 10H; H-ar), 8.37 (s, 2H; HC=N). 13C NMR: δ = 25.2 (CHCH3), 68.7 (CHCH3), 115.2 (d, J F-C = 21.2 Hz; C-ar), 128.1 (d, J F-C = 8.7 Hz; C-ar), 130.1 (C-ar), 140.7 (d, J F-C = 2.5 Hz; C-ar), 145.1 (C-ar), 161.1 (d, J F-C = 242.5 Hz; C-ar), 152.5 (HC=N). MS–EI: m/z = 382 (M +).
(IV): m.p. 434–435 K. [α]20 D = +726.5 (c = 1, CHCl3). FTIR: 1623 cm−1 (C=N). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CHCl3/TMS): δ = 1.53 (d, 6H; CHCH 3), 4.48 (q, 2H; CHCH3), 7.23–7.35 (m, 10H; H-ar), 8.37 (s, 2H; HC=N). 13C NMR: δ = 25.2 (CHCH3), 68.7 (CHCH3), 128.0, 128.6, 130.2, 132.5, 143.5, 145.1 (C-ar), 152.7 (HC=N).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. No unusual issues appeared, and refinements were carried out on non-restricted models. All H atoms were placed in calculated positions, and refined as riding on their carrier C atoms, with C—H bond lengths fixed to 0.93 (aromatic CH), 0.96 (methyl CH3), 0.97 (methylene CH2), or 0.98 Å (methine CH). Isotropic displacement parameters were calculated as U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms. For all compounds, the absolute configuration was based on the refinement of the Flack parameter (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸), confirming that the configuration of the chiral amine used as the starting material was retained during the Schiff condensation.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C26H26N2S | C24H26N2O2S | C22H20F2N2S | C22H20Cl2N2S |
| M r | 398.55 | 406.53 | 382.46 | 415.36 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P1 | Monoclinic, C2 | Orthorhombic, P21212 | Orthorhombic, P21212 |
| Temperature (K) | 298 | 298 | 298 | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 5.9093 (4), 7.6258 (5), 12.6570 (8) | 25.3917 (13), 5.9488 (3), 7.5623 (4) | 21.1153 (16), 7.7846 (6), 6.1343 (5) | 21.893 (2), 7.9212 (6), 6.2315 (4) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 87.802 (5), 78.329 (5), 87.427 (5) | 90, 97.174 (4), 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 |
| V (Å3) | 557.76 (6) | 1133.34 (10) | 1008.32 (14) | 1080.66 (15) |
| Z | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.41 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.34 × 0.12 × 0.06 | 0.45 × 0.33 × 0.12 | 0.89 × 0.47 × 0.33 | 0.52 × 0.40 × 0.07 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) | Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) | Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) | Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) |
| Absorption correction | Analytical CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013 ▸) | Analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▸) | Analytical CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013 ▸) | Multi-scan CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.969, 0.992 | 0.973, 0.993 | 0.904, 0.958 | 0.692, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 6689, 4036, 2958 | 6341, 2221, 1892 | 12336, 2067, 1591 | 14195, 2743, 1534 |
| R int | 0.040 | 0.027 | 0.058 | 0.058 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.618 | 0.618 | 0.625 | 0.692 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.058, 0.127, 1.02 | 0.036, 0.085, 1.02 | 0.044, 0.092, 1.06 | 0.052, 0.117, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 4036 | 2221 | 2067 | 2743 |
| No. of parameters | 262 | 134 | 124 | 124 |
| No. of restraints | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.31, −0.19 | 0.11, −0.17 | 0.15, −0.25 | 0.13, −0.17 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 962 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | Flack x determined using 708 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | Flack x determined using 518 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | Flack x determined using 465 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.12 (7) | −0.02 (4) | 0.07 (6) | 0.10 (6) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, IV, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Support from VIEP–UAP is acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Crystal data
| C26H26N2S | F(000) = 212 |
| Mr = 398.55 | Dx = 1.187 Mg m−3 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Melting point: 437 K |
| a = 5.9093 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 7.6258 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 2148 reflections |
| c = 12.6570 (8) Å | θ = 3.3–22.6° |
| α = 87.802 (5)° | µ = 0.16 mm−1 |
| β = 78.329 (5)° | T = 298 K |
| γ = 87.427 (5)° | Plate, colorless |
| V = 557.76 (6) Å3 | 0.34 × 0.12 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 1 |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) diffractometer | 4036 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2958 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5564 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: analytical CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.969, Tmax = 0.992 | l = −15→15 |
| 6689 measured reflections |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.127 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0525P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4036 reflections | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 262 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 962 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 0 constraints | Absolute structure parameter: −0.12 (7) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.66581 (19) | 0.49640 (17) | 0.11819 (12) | 0.0488 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.5097 (7) | 0.7980 (6) | 0.2625 (3) | 0.0507 (12) | |
| C2 | 0.7239 (10) | 0.7657 (7) | 0.2474 (4) | 0.0490 (13) | |
| H2A | 0.8132 | 0.8300 | 0.2834 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.8355 (8) | 0.6297 (7) | 0.1747 (4) | 0.0469 (13) | |
| C4 | 1.0622 (9) | 0.5892 (7) | 0.1402 (5) | 0.0575 (15) | |
| H4A | 1.1792 | 0.6461 | 0.1628 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 1.1042 (8) | 0.4510 (7) | 0.0658 (5) | 0.0595 (15) | |
| H5A | 1.2513 | 0.4075 | 0.0348 | 0.071* | |
| C6 | 0.9068 (8) | 0.3894 (6) | 0.0450 (4) | 0.0425 (12) | |
| C7 | 0.8786 (9) | 0.2528 (7) | −0.0268 (4) | 0.0503 (14) | |
| H7A | 1.0094 | 0.1943 | −0.0651 | 0.060* | |
| N8 | 0.6816 (8) | 0.2106 (6) | −0.0390 (3) | 0.0518 (12) | |
| C9 | 0.4190 (9) | 0.9453 (7) | 0.3325 (4) | 0.0518 (13) | |
| H9A | 0.5365 | 0.9745 | 0.3730 | 0.062* | |
| C10 | 0.3728 (12) | 1.1032 (8) | 0.2631 (5) | 0.0772 (18) | |
| H10A | 0.2751 | 1.0713 | 0.2143 | 0.093* | |
| H10B | 0.5174 | 1.1431 | 0.2201 | 0.093* | |
| C11 | 0.2537 (13) | 1.2501 (8) | 0.3345 (5) | 0.0802 (19) | |
| H11A | 0.3449 | 1.2749 | 0.3875 | 0.096* | |
| H11B | 0.2407 | 1.3560 | 0.2909 | 0.096* | |
| C12 | 0.0161 (11) | 1.1958 (8) | 0.3911 (5) | 0.0682 (18) | |
| H12A | −0.0468 | 1.2796 | 0.4462 | 0.082* | |
| H12B | −0.0847 | 1.1991 | 0.3393 | 0.082* | |
| C13 | 0.0174 (9) | 1.0143 (7) | 0.4429 (4) | 0.0486 (14) | |
| C14 | −0.1721 (10) | 0.9610 (9) | 0.5196 (5) | 0.0620 (16) | |
| H14A | −0.2950 | 1.0410 | 0.5406 | 0.074* | |
| C15 | −0.1846 (11) | 0.7955 (9) | 0.5651 (5) | 0.0749 (18) | |
| H15A | −0.3143 | 0.7635 | 0.6159 | 0.090* | |
| C16 | −0.0009 (13) | 0.6756 (9) | 0.5347 (6) | 0.080 (2) | |
| H16A | −0.0068 | 0.5621 | 0.5644 | 0.095* | |
| C17 | 0.1892 (11) | 0.7268 (8) | 0.4602 (5) | 0.0665 (16) | |
| H17A | 0.3134 | 0.6471 | 0.4414 | 0.080* | |
| C18 | 0.2020 (8) | 0.8935 (7) | 0.4123 (4) | 0.0465 (12) | |
| C19 | 0.6721 (9) | 0.0655 (6) | −0.1121 (4) | 0.0498 (13) | |
| H19A | 0.8294 | 0.0400 | −0.1523 | 0.060* | |
| C20 | 0.5911 (13) | −0.0955 (8) | −0.0465 (5) | 0.0728 (17) | |
| H20A | 0.4515 | −0.0668 | 0.0058 | 0.087* | |
| H20B | 0.7086 | −0.1390 | −0.0075 | 0.087* | |
| C21 | 0.5425 (13) | −0.2380 (8) | −0.1206 (5) | 0.0755 (19) | |
| H21A | 0.6802 | −0.2628 | −0.1750 | 0.091* | |
| H21B | 0.5024 | −0.3453 | −0.0786 | 0.091* | |
| C22 | 0.3465 (11) | −0.1769 (9) | −0.1746 (5) | 0.0688 (18) | |
| H22A | 0.3350 | −0.2584 | −0.2300 | 0.083* | |
| H22B | 0.2028 | −0.1782 | −0.1216 | 0.083* | |
| C23 | 0.3768 (9) | 0.0051 (8) | −0.2248 (4) | 0.0503 (14) | |
| C24 | 0.2515 (10) | 0.0601 (9) | −0.3022 (4) | 0.0624 (15) | |
| H24A | 0.1532 | −0.0175 | −0.3233 | 0.075* | |
| C25 | 0.2684 (12) | 0.2252 (10) | −0.3484 (5) | 0.079 (2) | |
| H25A | 0.1830 | 0.2591 | −0.4004 | 0.095* | |
| C26 | 0.4143 (14) | 0.3418 (9) | −0.3167 (6) | 0.086 (2) | |
| H26A | 0.4269 | 0.4550 | −0.3469 | 0.103* | |
| C27 | 0.5398 (11) | 0.2877 (8) | −0.2403 (5) | 0.0671 (17) | |
| H27A | 0.6391 | 0.3653 | −0.2199 | 0.080* | |
| C28 | 0.5226 (8) | 0.1213 (7) | −0.1928 (4) | 0.0484 (13) |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0574 (8) | 0.0551 (7) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0088 (5) | −0.0201 (6) |
| N1 | 0.045 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.026 (2) |
| C2 | 0.049 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.047 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.013 (2) | −0.016 (3) |
| C3 | 0.039 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.002 (2) | −0.016 (2) | −0.014 (3) |
| C4 | 0.036 (3) | 0.071 (4) | 0.070 (4) | 0.000 (3) | −0.017 (3) | −0.027 (3) |
| C5 | 0.033 (3) | 0.075 (4) | 0.072 (4) | 0.005 (3) | −0.010 (2) | −0.031 (3) |
| C6 | 0.031 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C7 | 0.046 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.010 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.018 (3) |
| N8 | 0.048 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.050 (3) | −0.003 (2) | −0.008 (2) | −0.023 (2) |
| C9 | 0.049 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.054 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| C10 | 0.102 (5) | 0.061 (4) | 0.060 (4) | −0.002 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.015 (3) |
| C11 | 0.109 (5) | 0.050 (4) | 0.070 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.010 (4) | −0.007 (3) |
| C12 | 0.082 (5) | 0.062 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.024 (3) | −0.015 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| C13 | 0.048 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.002 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.016 (3) |
| C14 | 0.056 (3) | 0.075 (4) | 0.056 (3) | 0.009 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.027 (3) |
| C15 | 0.075 (4) | 0.082 (5) | 0.062 (4) | −0.011 (4) | 0.006 (3) | −0.022 (4) |
| C16 | 0.104 (5) | 0.061 (4) | 0.066 (4) | −0.012 (4) | 0.001 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C17 | 0.072 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.064 (4) | 0.007 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C18 | 0.045 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.012 (2) | −0.019 (3) |
| C19 | 0.052 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.017 (3) |
| C20 | 0.114 (5) | 0.060 (4) | 0.051 (3) | −0.010 (4) | −0.030 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C21 | 0.119 (5) | 0.055 (4) | 0.056 (4) | −0.012 (4) | −0.021 (4) | −0.009 (3) |
| C22 | 0.074 (4) | 0.078 (5) | 0.056 (4) | −0.028 (4) | −0.008 (3) | −0.017 (3) |
| C23 | 0.048 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.019 (3) |
| C24 | 0.056 (3) | 0.079 (4) | 0.054 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.013 (3) | −0.028 (3) |
| C25 | 0.096 (5) | 0.084 (5) | 0.066 (4) | 0.026 (4) | −0.037 (4) | −0.028 (4) |
| C26 | 0.129 (6) | 0.057 (4) | 0.080 (5) | 0.016 (4) | −0.044 (5) | −0.010 (4) |
| C27 | 0.084 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.064 (4) | −0.003 (3) | −0.022 (4) | −0.019 (3) |
| C28 | 0.050 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.006 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.018 (3) |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C6 | 1.724 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| S1—C3 | 1.728 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.390 (9) |
| N1—C2 | 1.255 (6) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C9 | 1.471 (6) | C16—C17 | 1.373 (9) |
| C2—C3 | 1.458 (7) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.386 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.348 (7) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.420 (7) | C19—C20 | 1.496 (7) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C19—C28 | 1.518 (7) |
| C5—C6 | 1.355 (6) | C19—H19A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.536 (8) |
| C6—C7 | 1.445 (7) | C20—H20A | 0.9700 |
| C7—N8 | 1.263 (6) | C20—H20B | 0.9700 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9300 | C21—C22 | 1.508 (9) |
| N8—C19 | 1.479 (6) | C21—H21A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.512 (8) | C21—H21B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C18 | 1.520 (7) | C22—C23 | 1.507 (9) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9800 | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C10—C11 | 1.522 (8) | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C23—C24 | 1.384 (8) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C23—C28 | 1.389 (7) |
| C11—C12 | 1.510 (9) | C24—C25 | 1.367 (9) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C24—H24A | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C25—C26 | 1.390 (10) |
| C12—C13 | 1.509 (8) | C25—H25A | 0.9300 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9700 | C26—C27 | 1.374 (8) |
| C12—H12B | 0.9700 | C26—H26A | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.390 (8) | C27—C28 | 1.382 (7) |
| C13—C18 | 1.398 (7) | C27—H27A | 0.9300 |
| C14—C15 | 1.366 (9) | ||
| C6—S1—C3 | 91.5 (2) | C16—C15—H15A | 120.4 |
| C2—N1—C9 | 116.5 (4) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.2 (7) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.5 (5) | C17—C16—H16A | 120.4 |
| N1—C2—H2A | 119.3 | C15—C16—H16A | 120.4 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.3 | C16—C17—C18 | 122.1 (6) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 129.7 (5) | C16—C17—H17A | 119.0 |
| C4—C3—S1 | 111.3 (4) | C18—C17—H17A | 119.0 |
| C2—C3—S1 | 119.1 (4) | C17—C18—C13 | 118.7 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 113.2 (5) | C17—C18—C9 | 120.0 (5) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 123.4 | C13—C18—C9 | 121.2 (5) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 123.4 | N8—C19—C20 | 109.4 (4) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 112.6 (5) | N8—C19—C28 | 110.1 (4) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 123.7 | C20—C19—C28 | 113.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 123.7 | N8—C19—H19A | 108.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 129.0 (5) | C20—C19—H19A | 108.0 |
| C5—C6—S1 | 111.4 (4) | C28—C19—H19A | 108.0 |
| C7—C6—S1 | 119.6 (4) | C19—C20—C21 | 109.9 (4) |
| N8—C7—C6 | 121.9 (5) | C19—C20—H20A | 109.7 |
| N8—C7—H7A | 119.1 | C21—C20—H20A | 109.7 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 119.1 | C19—C20—H20B | 109.7 |
| C7—N8—C19 | 117.5 (4) | C21—C20—H20B | 109.7 |
| N1—C9—C10 | 109.1 (4) | H20A—C20—H20B | 108.2 |
| N1—C9—C18 | 110.3 (4) | C22—C21—C20 | 109.9 (5) |
| C10—C9—C18 | 111.6 (5) | C22—C21—H21A | 109.7 |
| N1—C9—H9A | 108.6 | C20—C21—H21A | 109.7 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 108.6 | C22—C21—H21B | 109.7 |
| C18—C9—H9A | 108.6 | C20—C21—H21B | 109.7 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 109.6 (5) | H21A—C21—H21B | 108.2 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.7 | C23—C22—C21 | 112.9 (5) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.7 | C23—C22—H22A | 109.0 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.7 | C21—C22—H22A | 109.0 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.7 | C23—C22—H22B | 109.0 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.2 | C21—C22—H22B | 109.0 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 109.6 (5) | H22A—C22—H22B | 107.8 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.7 | C24—C23—C28 | 119.1 (5) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.7 | C24—C23—C22 | 119.5 (5) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.7 | C28—C23—C22 | 121.4 (5) |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.7 | C25—C24—C23 | 121.8 (6) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 108.2 | C25—C24—H24A | 119.1 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 112.9 (5) | C23—C24—H24A | 119.1 |
| C13—C12—H12A | 109.0 | C24—C25—C26 | 119.3 (6) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.0 | C24—C25—H25A | 120.4 |
| C13—C12—H12B | 109.0 | C26—C25—H25A | 120.4 |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.0 | C27—C26—C25 | 119.1 (6) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 107.8 | C27—C26—H26A | 120.4 |
| C14—C13—C18 | 118.4 (5) | C25—C26—H26A | 120.4 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.1 (5) | C26—C27—C28 | 121.9 (6) |
| C18—C13—C12 | 121.5 (5) | C26—C27—H27A | 119.1 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 122.5 (6) | C28—C27—H27A | 119.1 |
| C15—C14—H14A | 118.8 | C27—C28—C23 | 118.8 (5) |
| C13—C14—H14A | 118.8 | C27—C28—C19 | 119.8 (5) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 119.1 (6) | C23—C28—C19 | 121.3 (5) |
| C14—C15—H15A | 120.4 | ||
| C9—N1—C2—C3 | −176.4 (5) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | −177.8 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 172.4 (6) | C14—C13—C18—C9 | −177.3 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—S1 | −6.2 (7) | C12—C13—C18—C9 | 5.4 (7) |
| C6—S1—C3—C4 | −1.4 (5) | N1—C9—C18—C17 | 39.8 (6) |
| C6—S1—C3—C2 | 177.5 (4) | C10—C9—C18—C17 | 161.1 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.8 (5) | N1—C9—C18—C13 | −143.5 (4) |
| S1—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (6) | C10—C9—C18—C13 | −22.1 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (7) | C7—N8—C19—C20 | 105.5 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 178.9 (5) | C7—N8—C19—C28 | −129.5 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—S1 | −1.3 (6) | N8—C19—C20—C21 | 170.8 (5) |
| C3—S1—C6—C5 | 1.5 (4) | C28—C19—C20—C21 | 47.7 (7) |
| C3—S1—C6—C7 | −178.7 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −64.0 (7) |
| C5—C6—C7—N8 | −179.1 (6) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 49.0 (7) |
| S1—C6—C7—N8 | 1.1 (7) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 161.6 (5) |
| C6—C7—N8—C19 | −178.2 (5) | C21—C22—C23—C28 | −20.5 (8) |
| C2—N1—C9—C10 | 102.3 (6) | C28—C23—C24—C25 | 0.4 (8) |
| C2—N1—C9—C18 | −134.9 (5) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 178.4 (6) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | 173.7 (5) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −0.3 (9) |
| C18—C9—C10—C11 | 51.6 (7) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 0.5 (10) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −66.2 (7) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | −0.9 (10) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 48.1 (7) | C26—C27—C28—C23 | 1.0 (8) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 164.1 (5) | C26—C27—C28—C19 | 177.5 (6) |
| C11—C12—C13—C18 | −18.7 (8) | C24—C23—C28—C27 | −0.7 (7) |
| C18—C13—C14—C15 | −0.5 (8) | C22—C23—C28—C27 | −178.7 (6) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 176.8 (5) | C24—C23—C28—C19 | −177.2 (5) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.5 (9) | C22—C23—C28—C19 | 4.9 (8) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.5 (10) | N8—C19—C28—C27 | 41.7 (6) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.6 (10) | C20—C19—C28—C27 | 164.5 (5) |
| C16—C17—C18—C13 | 1.6 (9) | N8—C19—C28—C23 | −141.9 (5) |
| C16—C17—C18—C9 | 178.4 (6) | C20—C19—C28—C23 | −19.1 (7) |
| C14—C13—C18—C17 | −0.5 (7) |
(I) 2,5-Bis[(S)-(+)-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)imino]thiophene . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4A···S1i | 0.93 | 3.00 | 3.562 (5) | 121 |
| C5—H5A···S1i | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.547 (5) | 122 |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y, z.
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Crystal data
| C24H26N2O2S | Dx = 1.191 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 406.53 | Melting point: 405 K |
| Monoclinic, C2 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 25.3917 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 2504 reflections |
| b = 5.9488 (3) Å | θ = 3.0–24.2° |
| c = 7.5623 (4) Å | µ = 0.16 mm−1 |
| β = 97.174 (4)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1133.34 (10) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.45 × 0.33 × 0.12 mm |
| F(000) = 432 |
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) diffractometer | 2221 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1892 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.027 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | h = −31→31 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.993 | k = −7→7 |
| 6341 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0393P)2 + 0.1801P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.085 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.02 | Δρmax = 0.11 e Å−3 |
| 2221 reflections | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
| 134 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 708 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: −0.02 (4) |
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.5000 | 0.37429 (14) | 0.5000 | 0.0490 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.56565 (9) | 0.3213 (4) | 0.1855 (3) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.55195 (11) | 0.5176 (5) | 0.2189 (4) | 0.0469 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.5608 | 0.6324 | 0.1445 | 0.056* | |
| C3 | 0.52314 (10) | 0.5774 (5) | 0.3665 (4) | 0.0449 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.51313 (13) | 0.7856 (5) | 0.4229 (4) | 0.0596 (8) | |
| H4A | 0.5225 | 0.9159 | 0.3665 | 0.072* | |
| C5 | 0.59848 (11) | 0.2933 (4) | 0.0386 (4) | 0.0484 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.5949 | 0.4291 | −0.0354 | 0.058* | |
| C6 | 0.57863 (13) | 0.0963 (6) | −0.0754 (4) | 0.0658 (8) | |
| H6A | 0.5416 | 0.1162 | −0.1164 | 0.099* | |
| H6B | 0.5835 | −0.0394 | −0.0065 | 0.099* | |
| H6C | 0.5981 | 0.0861 | −0.1759 | 0.099* | |
| C7 | 0.65613 (11) | 0.2719 (4) | 0.1189 (3) | 0.0441 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.69277 (11) | 0.4349 (4) | 0.0871 (4) | 0.0494 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.6817 | 0.5585 | 0.0168 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.74515 (11) | 0.4171 (5) | 0.1576 (4) | 0.0571 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.7692 | 0.5278 | 0.1343 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.76215 (11) | 0.2354 (6) | 0.2628 (4) | 0.0546 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.72642 (12) | 0.0745 (6) | 0.2994 (4) | 0.0593 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.7375 | −0.0469 | 0.3722 | 0.071* | |
| C12 | 0.67374 (12) | 0.0936 (6) | 0.2275 (4) | 0.0551 (8) | |
| H12A | 0.6497 | −0.0161 | 0.2528 | 0.066* | |
| O1 | 0.81556 (9) | 0.2307 (5) | 0.3227 (3) | 0.0781 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.83539 (15) | 0.0345 (9) | 0.4189 (5) | 0.1010 (15) | |
| H13A | 0.8734 | 0.0434 | 0.4432 | 0.152* | |
| H13B | 0.8257 | −0.0970 | 0.3487 | 0.152* | |
| H13C | 0.8204 | 0.0258 | 0.5292 | 0.152* |
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0540 (6) | 0.0354 (5) | 0.0603 (6) | 0.000 | 0.0183 (4) | 0.000 |
| N1 | 0.0442 (13) | 0.0512 (16) | 0.0477 (13) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0129 (10) | 0.0058 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0460 (15) | 0.0443 (18) | 0.0507 (16) | −0.0021 (13) | 0.0071 (13) | 0.0121 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0421 (14) | 0.0392 (14) | 0.0534 (17) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0062 (13) | 0.0052 (12) |
| C4 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0365 (16) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0193 (16) | 0.0074 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0497 (16) | 0.0537 (18) | 0.0434 (15) | 0.0015 (12) | 0.0120 (12) | 0.0097 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0626 (19) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0551 (19) | −0.0010 (18) | 0.0058 (15) | −0.0036 (17) |
| C7 | 0.0468 (15) | 0.0492 (15) | 0.0387 (14) | 0.0022 (13) | 0.0147 (12) | 0.0018 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0559 (17) | 0.0500 (17) | 0.0451 (14) | −0.0025 (13) | 0.0169 (13) | 0.0045 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0528 (17) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0548 (17) | −0.0139 (16) | 0.0177 (14) | −0.0004 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0455 (16) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0414 (16) | 0.0001 (15) | 0.0080 (13) | −0.0080 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0575 (18) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0524 (18) | 0.0087 (17) | 0.0086 (14) | 0.0150 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0527 (17) | 0.0569 (17) | 0.0574 (19) | −0.0031 (14) | 0.0138 (14) | 0.0147 (15) |
| O1 | 0.0478 (13) | 0.121 (2) | 0.0642 (14) | −0.0021 (14) | 0.0011 (10) | −0.0011 (14) |
| C13 | 0.063 (2) | 0.161 (4) | 0.075 (3) | 0.022 (3) | −0.0086 (19) | 0.022 (3) |
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C3i | 1.724 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.381 (4) |
| S1—C3 | 1.724 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.253 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.374 (4) |
| N1—C5 | 1.480 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.453 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.379 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.345 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.371 (4) |
| C4—C4i | 1.413 (6) | C10—O1 | 1.375 (3) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.384 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.504 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C7 | 1.519 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | O1—C13 | 1.433 (5) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9600 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9600 | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6C | 0.9600 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C3i—S1—C3 | 91.01 (19) | C12—C7—C5 | 121.8 (2) |
| C2—N1—C5 | 116.9 (2) | C8—C7—C5 | 120.4 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 124.2 (3) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.2 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 117.9 | C9—C8—H8A | 119.4 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 117.9 | C7—C8—H8A | 119.4 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 127.1 (3) | C8—C9—C10 | 120.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—S1 | 111.6 (2) | C8—C9—H9A | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—S1 | 121.3 (2) | C10—C9—H9A | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—C4i | 112.91 (17) | C11—C10—O1 | 124.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 123.5 | C11—C10—C9 | 119.8 (3) |
| C4i—C4—H4A | 123.5 | O1—C10—C9 | 115.5 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 109.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.7 (3) |
| N1—C5—C7 | 108.3 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—C7 | 113.7 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 120.2 |
| N1—C5—H5A | 108.3 | C7—C12—C11 | 121.5 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.3 | C7—C12—H12A | 119.3 |
| C7—C5—H5A | 108.3 | C11—C12—H12A | 119.3 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C10—O1—C13 | 117.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 | O1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | O1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | O1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 117.8 (3) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C2—C3 | −175.3 (2) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 1.5 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 171.0 (3) | C5—C7—C8—C9 | −179.4 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—S1 | −5.7 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.3 (4) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C4 | −0.22 (17) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.1 (4) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C2 | 176.9 (3) | C8—C9—C10—O1 | 178.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4i | −176.3 (3) | O1—C10—C11—C12 | −178.1 (3) |
| S1—C3—C4—C4i | 0.6 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.2 (4) |
| C2—N1—C5—C6 | −136.4 (3) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.4 (4) |
| C2—N1—C5—C7 | 99.0 (3) | C5—C7—C12—C11 | 179.6 (3) |
| N1—C5—C7—C12 | 63.9 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.0 (5) |
| C6—C5—C7—C12 | −58.3 (3) | C11—C10—O1—C13 | 4.8 (4) |
| N1—C5—C7—C8 | −115.0 (3) | C9—C10—O1—C13 | −174.6 (3) |
| C6—C5—C7—C8 | 122.7 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, y, −z+1.
(II) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4A···S1ii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.572 (3) | 122 |
Symmetry code: (ii) x, y+1, z.
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Crystal data
| C22H20F2N2S | Dx = 1.260 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 382.46 | Melting point: 420 K |
| Orthorhombic, P21212 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 21.1153 (16) Å | Cell parameters from 2744 reflections |
| b = 7.7846 (6) Å | θ = 3.8–23.2° |
| c = 6.1343 (5) Å | µ = 0.19 mm−1 |
| V = 1008.32 (14) Å3 | T = 298 K |
| Z = 2 | Prism, colourless |
| F(000) = 400 | 0.89 × 0.47 × 0.33 mm |
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) diffractometer | 2067 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1591 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.058 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5564 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 3.8° |
| ω scans | h = −26→26 |
| Absorption correction: analytical CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.904, Tmax = 0.958 | l = −7→7 |
| 12336 measured reflections |
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0384P)2 + 0.0613P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2067 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 124 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 518 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.07 (6) |
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 1.06817 (15) | 0.0479 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.85802 (10) | 0.3203 (3) | 0.5731 (5) | 0.1163 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.58698 (11) | 0.3119 (3) | 1.0120 (4) | 0.0498 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.56853 (13) | 0.2830 (4) | 1.2046 (5) | 0.0479 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.5795 | 0.3610 | 1.3130 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | 0.53102 (13) | 0.1344 (4) | 1.2646 (4) | 0.0461 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.51751 (14) | 0.0774 (4) | 1.4690 (4) | 0.0556 (8) | |
| H4A | 0.5300 | 0.1342 | 1.5953 | 0.067* | |
| C5 | 0.62513 (14) | 0.4679 (4) | 0.9770 (5) | 0.0568 (8) | |
| H5A | 0.6336 | 0.5216 | 1.1185 | 0.068* | |
| C6 | 0.58661 (16) | 0.5931 (5) | 0.8368 (7) | 0.0829 (12) | |
| H6A | 0.5476 | 0.6200 | 0.9094 | 0.124* | |
| H6B | 0.5777 | 0.5412 | 0.6983 | 0.124* | |
| H6C | 0.6105 | 0.6967 | 0.8149 | 0.124* | |
| C7 | 0.68777 (14) | 0.4223 (3) | 0.8702 (5) | 0.0462 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.74419 (15) | 0.4799 (4) | 0.9563 (5) | 0.0577 (8) | |
| H8A | 0.7436 | 0.5427 | 1.0852 | 0.069* | |
| C9 | 0.80144 (15) | 0.4470 (4) | 0.8567 (7) | 0.0697 (10) | |
| H9A | 0.8391 | 0.4873 | 0.9163 | 0.084* | |
| C10 | 0.80134 (17) | 0.3551 (5) | 0.6707 (7) | 0.0689 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.74733 (18) | 0.2932 (4) | 0.5777 (5) | 0.0654 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.7489 | 0.2301 | 0.4491 | 0.078* | |
| C12 | 0.69042 (15) | 0.3265 (4) | 0.6789 (5) | 0.0543 (8) | |
| H12A | 0.6532 | 0.2843 | 0.6184 | 0.065* |
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0499 (6) | 0.0559 (6) | 0.0379 (5) | −0.0056 (6) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| F1 | 0.0687 (14) | 0.1167 (19) | 0.164 (2) | −0.0047 (14) | 0.0485 (15) | −0.030 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0452 (14) | 0.0502 (15) | 0.0540 (16) | −0.0082 (12) | 0.0032 (11) | −0.0028 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0405 (16) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0489 (18) | −0.0028 (15) | −0.0043 (14) | −0.0073 (16) |
| C3 | 0.0388 (15) | 0.0544 (19) | 0.0452 (17) | −0.0011 (15) | −0.0013 (13) | −0.0024 (14) |
| C4 | 0.056 (2) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0396 (15) | −0.0115 (15) | −0.0020 (13) | −0.0040 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0545 (18) | 0.0513 (19) | 0.0647 (18) | −0.0104 (16) | 0.0112 (15) | −0.0111 (16) |
| C6 | 0.065 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.123 (3) | 0.0111 (19) | 0.023 (2) | 0.016 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0468 (17) | 0.0403 (15) | 0.0514 (17) | −0.0063 (14) | 0.0002 (14) | 0.0001 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0576 (19) | 0.0492 (17) | 0.0662 (19) | −0.0090 (17) | 0.0002 (16) | −0.0104 (18) |
| C9 | 0.047 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.099 (3) | −0.0114 (17) | −0.0023 (19) | −0.007 (2) |
| C10 | 0.054 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.095 (3) | −0.0009 (18) | 0.021 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C11 | 0.075 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.0577 (19) | 0.000 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.0053 (18) |
| C12 | 0.0499 (18) | 0.0573 (19) | 0.0557 (18) | −0.0058 (17) | −0.0063 (16) | −0.0020 (16) |
(III) 2,5-Bis{[(R)-(-)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C3i | 1.725 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| S1—C3 | 1.725 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| F1—C10 | 1.365 (4) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.264 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.378 (4) |
| N1—C5 | 1.473 (4) | C7—C12 | 1.392 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.450 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.378 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.360 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.347 (5) |
| C4—C4i | 1.414 (6) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.363 (5) |
| C5—C7 | 1.518 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.377 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.533 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C3i—S1—C3 | 91.4 (2) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C5 | 116.8 (3) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 123.2 (3) | C8—C7—C12 | 117.6 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 118.4 | C8—C7—C5 | 120.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 118.4 | C12—C7—C5 | 121.6 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 127.5 (3) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.9 (3) |
| C4—C3—S1 | 111.5 (2) | C7—C8—H8A | 119.1 |
| C2—C3—S1 | 120.9 (2) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.1 |
| C3—C4—C4i | 112.81 (18) | C10—C9—C8 | 118.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 123.6 | C10—C9—H9A | 120.9 |
| C4i—C4—H4A | 123.6 | C8—C9—H9A | 120.9 |
| N1—C5—C7 | 110.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 122.9 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 108.4 (2) | C9—C10—F1 | 118.4 (3) |
| C7—C5—C6 | 111.6 (2) | C11—C10—F1 | 118.7 (3) |
| N1—C5—H5A | 108.8 | C10—C11—C12 | 118.4 (3) |
| C7—C5—H5A | 108.8 | C10—C11—H11A | 120.8 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.8 | C12—C11—H11A | 120.8 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C11—C12—C7 | 121.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C7—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 | ||
| C5—N1—C2—C3 | −179.6 (2) | C6—C5—C7—C12 | −67.4 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 168.6 (3) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 1.0 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—S1 | −8.7 (4) | C5—C7—C8—C9 | −176.9 (3) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C4 | −0.29 (16) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.4 (5) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C2 | 177.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4i | −176.7 (3) | C8—C9—C10—F1 | −179.1 (3) |
| S1—C3—C4—C4i | 0.8 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.0 (6) |
| C2—N1—C5—C7 | 124.5 (3) | F1—C10—C11—C12 | 179.0 (3) |
| C2—N1—C5—C6 | −113.0 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.6 (5) |
| N1—C5—C7—C8 | −129.0 (3) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.1 (4) |
| C6—C5—C7—C8 | 110.4 (3) | C5—C7—C12—C11 | 176.7 (3) |
| N1—C5—C7—C12 | 53.2 (4) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y, z.
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Crystal data
| C22H20Cl2N2S | Dx = 1.276 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 415.36 | Melting point: 434 K |
| Orthorhombic, P21212 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 21.893 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 2744 reflections |
| b = 7.9212 (6) Å | θ = 3.7–21.5° |
| c = 6.2315 (4) Å | µ = 0.41 mm−1 |
| V = 1080.66 (15) Å3 | T = 298 K |
| Z = 2 | Prism, colorless |
| F(000) = 432 | 0.52 × 0.40 × 0.07 mm |
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Atlas, Gemini) diffractometer | 2743 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1534 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.058 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5564 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| ω scans | h = −28→27 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan CrysAlis PRO, (Agilent, 2013) | k = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.692, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −8→8 |
| 14195 measured reflections |
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0483P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2743 reflections | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 124 parameters | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 465 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.10 (6) |
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.5000 | 1.0000 | −0.13764 (18) | 0.0590 (4) | |
| Cl1 | 0.15354 (6) | 0.67176 (16) | 0.4970 (2) | 0.1059 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.41391 (14) | 0.6958 (3) | −0.0839 (5) | 0.0612 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.43185 (16) | 0.7244 (4) | −0.2735 (6) | 0.0589 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.4204 | 0.6496 | −0.3812 | 0.071* | |
| C3 | 0.46969 (15) | 0.8689 (4) | −0.3311 (5) | 0.0544 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.48309 (16) | 0.9247 (4) | −0.5338 (5) | 0.0640 (10) | |
| H4A | 0.4711 | 0.8688 | −0.6581 | 0.077* | |
| C5 | 0.37559 (18) | 0.5438 (4) | −0.0520 (7) | 0.0677 (11) | |
| H5A | 0.3625 | 0.5021 | −0.1927 | 0.081* | |
| C6 | 0.4148 (2) | 0.4087 (5) | 0.0553 (9) | 0.0986 (17) | |
| H6A | 0.4484 | 0.3803 | −0.0369 | 0.148* | |
| H6B | 0.3905 | 0.3098 | 0.0810 | 0.148* | |
| H6C | 0.4302 | 0.4509 | 0.1892 | 0.148* | |
| C7 | 0.31964 (17) | 0.5839 (4) | 0.0796 (5) | 0.0555 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.26313 (19) | 0.5202 (5) | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0701 (10) | |
| H8A | 0.2593 | 0.4575 | −0.0999 | 0.084* | |
| C9 | 0.21198 (19) | 0.5464 (5) | 0.1512 (7) | 0.0735 (11) | |
| H9A | 0.1744 | 0.5020 | 0.1109 | 0.088* | |
| C10 | 0.21746 (18) | 0.6384 (5) | 0.3351 (6) | 0.0640 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.2728 (2) | 0.7062 (5) | 0.3945 (6) | 0.0691 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.2761 | 0.7692 | 0.5199 | 0.083* | |
| C12 | 0.32346 (18) | 0.6802 (4) | 0.2665 (5) | 0.0623 (9) | |
| H12A | 0.3607 | 0.7276 | 0.3056 | 0.075* |
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0694 (9) | 0.0596 (7) | 0.0482 (6) | −0.0040 (7) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Cl1 | 0.0878 (9) | 0.1061 (9) | 0.1238 (10) | 0.0069 (7) | 0.0384 (8) | 0.0026 (9) |
| N1 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0569 (18) | 0.0643 (19) | −0.0089 (15) | 0.0064 (15) | 0.0009 (14) |
| C2 | 0.055 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0015 (17) | −0.0031 (19) | −0.0056 (18) |
| C3 | 0.050 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0523 (19) | 0.0004 (17) | −0.0008 (16) | −0.0008 (17) |
| C4 | 0.063 (3) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0487 (18) | −0.0130 (18) | −0.0011 (17) | −0.0059 (17) |
| C5 | 0.071 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.075 (2) | −0.0098 (18) | 0.015 (2) | −0.0050 (18) |
| C6 | 0.085 (3) | 0.064 (2) | 0.147 (4) | 0.011 (2) | 0.040 (3) | 0.019 (3) |
| C7 | 0.061 (2) | 0.0442 (17) | 0.061 (2) | −0.0052 (17) | −0.0039 (18) | 0.0020 (16) |
| C8 | 0.073 (3) | 0.061 (2) | 0.076 (2) | −0.017 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C9 | 0.063 (3) | 0.067 (3) | 0.091 (3) | −0.0168 (19) | −0.003 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C10 | 0.065 (3) | 0.056 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0010 (19) | 0.007 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C11 | 0.081 (3) | 0.068 (2) | 0.059 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.0067 (18) |
| C12 | 0.059 (2) | 0.065 (2) | 0.063 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.010 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
(IV) 2,5-Bis{[(S)-(+)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]iminomethyl}thiophene . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C3 | 1.724 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| S1—C3i | 1.724 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| Cl1—C10 | 1.746 (4) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.265 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.378 (5) |
| N1—C5 | 1.481 (4) | C7—C12 | 1.394 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.458 (5) | C8—C9 | 1.382 (5) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.370 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.363 (5) |
| C4—C4i | 1.404 (7) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.376 (5) |
| C5—C7 | 1.508 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.382 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.527 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C3—S1—C3i | 91.3 (2) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C5 | 116.6 (3) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 123.2 (3) | C8—C7—C12 | 117.3 (4) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 118.4 | C8—C7—C5 | 121.3 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 118.4 | C12—C7—C5 | 121.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 127.0 (3) | C7—C8—C9 | 122.2 (4) |
| C4—C3—S1 | 111.6 (3) | C7—C8—H8A | 118.9 |
| C2—C3—S1 | 121.3 (2) | C9—C8—H8A | 118.9 |
| C3—C4—C4i | 112.8 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.0 (4) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 123.6 | C10—C9—H9A | 120.5 |
| C4i—C4—H4A | 123.6 | C8—C9—H9A | 120.5 |
| N1—C5—C7 | 111.2 (3) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.8 (4) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 108.1 (3) | C9—C10—Cl1 | 119.8 (3) |
| C7—C5—C6 | 111.5 (3) | C11—C10—Cl1 | 119.4 (3) |
| N1—C5—H5A | 108.7 | C10—C11—C12 | 119.5 (3) |
| C7—C5—H5A | 108.7 | C10—C11—H11A | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.7 | C12—C11—H11A | 120.2 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C11—C12—C7 | 121.0 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C7—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 | ||
| C5—N1—C2—C3 | 179.8 (3) | C6—C5—C7—C12 | 74.9 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −168.8 (4) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −1.2 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—S1 | 7.3 (5) | C5—C7—C8—C9 | 175.8 (3) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C4 | 0.42 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (6) |
| C3i—S1—C3—C2 | −176.3 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.8 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4i | 175.3 (4) | C8—C9—C10—Cl1 | −179.6 (3) |
| S1—C3—C4—C4i | −1.1 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.3 (6) |
| C2—N1—C5—C7 | −132.2 (3) | Cl1—C10—C11—C12 | −179.9 (3) |
| C2—N1—C5—C6 | 105.1 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −1.0 (6) |
| N1—C5—C7—C8 | 137.3 (4) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.7 (5) |
| C6—C5—C7—C8 | −102.0 (4) | C5—C7—C12—C11 | −175.3 (3) |
| N1—C5—C7—C12 | −45.8 (4) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+2, z.
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA.
- Bernès, S., Hernández-Téllez, G., Sharma, M., Portillo-Moreno, O. & Gutiérrez, R. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bolduc, A., Al Ouahabi, A., Mallet, C. & Skene, W. G. (2013a). J. Org. Chem. 78, 9258–9269. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bolduc, A., Dufresne, S. & Skene, W. G. (2013b). Acta Cryst. C69, 1196–1199. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Boyle, R., Crundwell, G. & Glagovich, N. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cram, D. J. & Trueblood, K. N. (1981). Top. Curr. Chem. 98, 43–106.
- Dean, F. M. (1982a). Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 30, 167–238.
- Dean, F. M. (1982b). Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 31, 237–344.
- Fridman, N. & Kaftory, M. (2007). Pol. J. Chem. 81, 825–832.
- Kudyakova, Yu. S., Burgart, Ya. V. & Saloutin, V. I. (2011). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 47, 558–563.
- Kudyakova, Y. S., Burgart, Y. V., Slepukhin, P. A. & Saloutin, V. I. (2012). Mendeleev Commun. 22, 284–286.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mendoza, A., Bernès, S., Hernández-Téllez, G., Portillo-Moreno, O. & Gutiérrez, R. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P. W., Kwolek, S. L. & Pletcher, T. C. (1987). Macromolecules, 20, 729–739.
- Moussallem, C., Allain, M., Mallet, C., Gohier, F. & Frère, P. (2015). J. Fluor. Chem. 178, 34–39.
- Nelson, S. M., Esho, F., Lavery, A. & Drew, M. G. B. (1983). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 5693–5695.
- Noyori, R. (2005). Chem. Commun. pp. 1807–1811. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Pérez Guarìn, S. A., Bourgeaux, M., Dufresne, S. & Skene, W. G. (2007). J. Org. Chem. 72, 2631–2643. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Petrus, M. L., Bouwer, R. K. M., Lafont, U., Athanasopoulos, S., Greenham, N. C. & Dingemans, T. J. (2014). J. Mater. Chem. A, 2, 9474–9477.
- Sargent, M. V. & Cresp, T. M. (1975). Fortschritte Chem. Forschung, 57, 111–143.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Sicard, L., Navarathne, D., Skalski, T. & Skene, W. G. (2013). Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 3549–3559.
- Skene, W. G. & Dufresne, S. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o1116–o1117.
- Suganya, S., Velmathi, S. & MubarakAli, D. (2014). Dyes Pigments, 104, 116–122.
- Tanaka, K. & Toda, F. (2000). Chem. Rev. 100, 1025–1074. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wiedermann, J., Kirchner, K. & Mereiter, K. (2005). Private communication (refcode NAWMAA). CCDC, Cambridge, England.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, IV, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016002516/sj5495IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






