Abstract
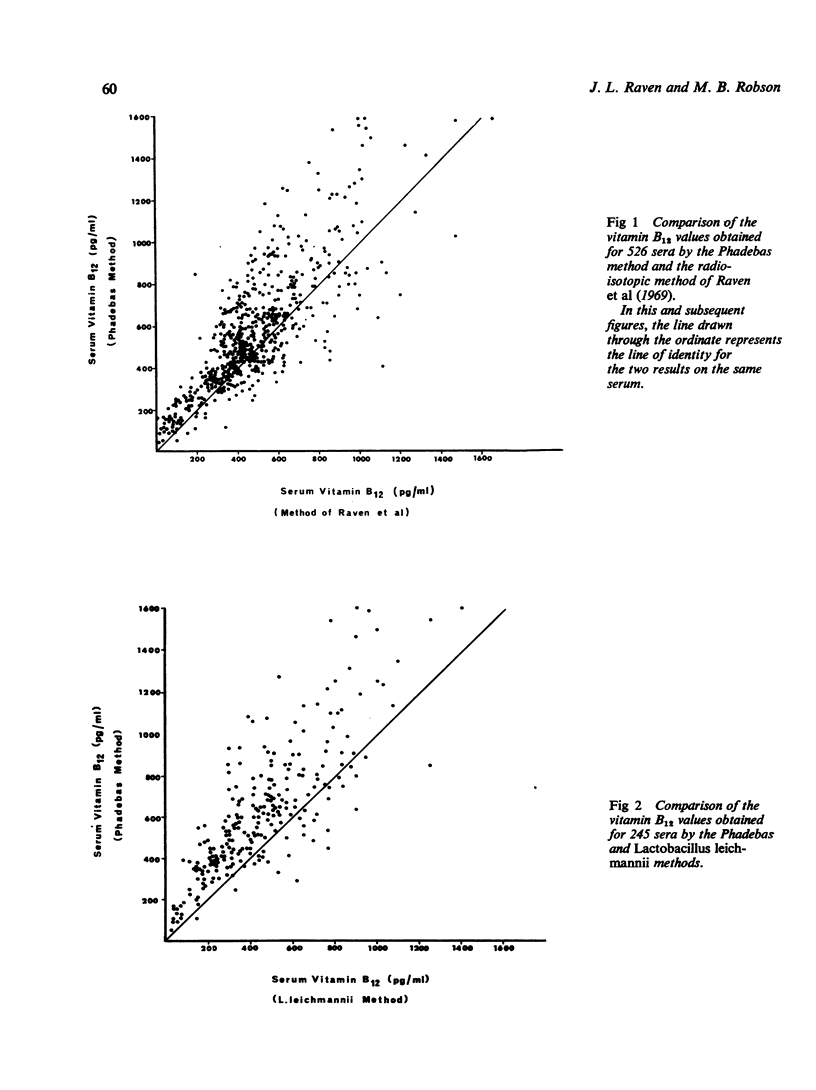
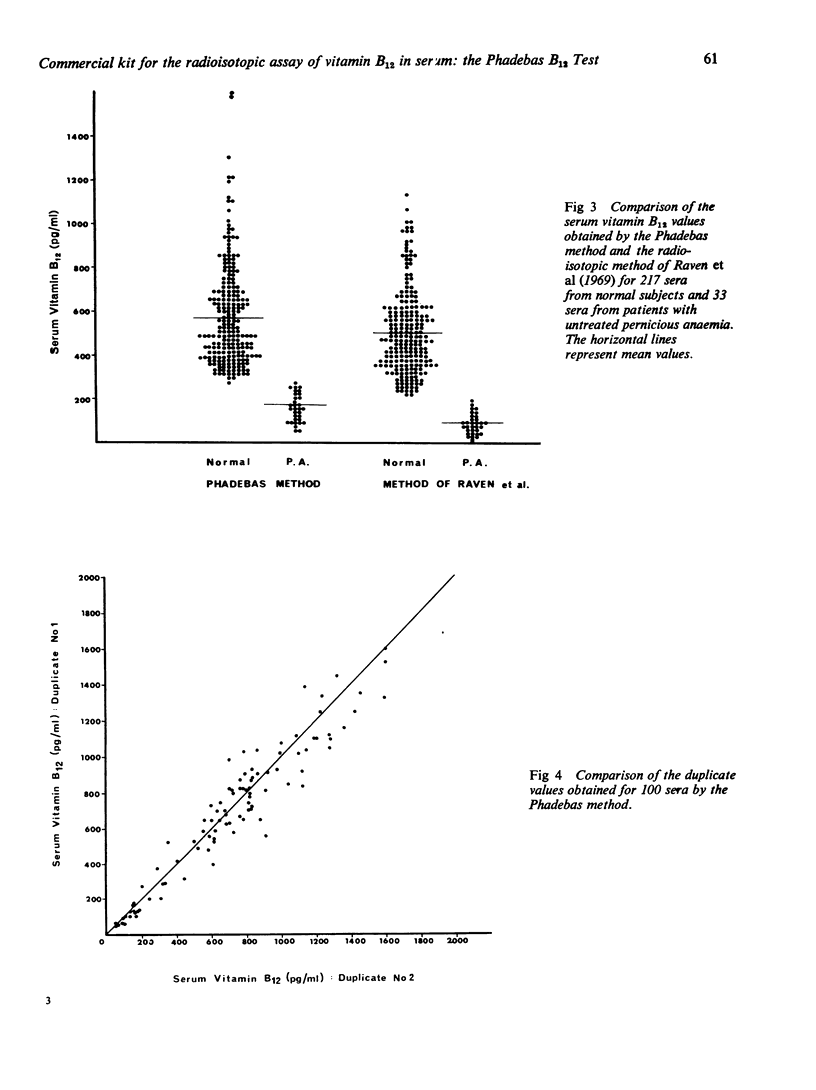
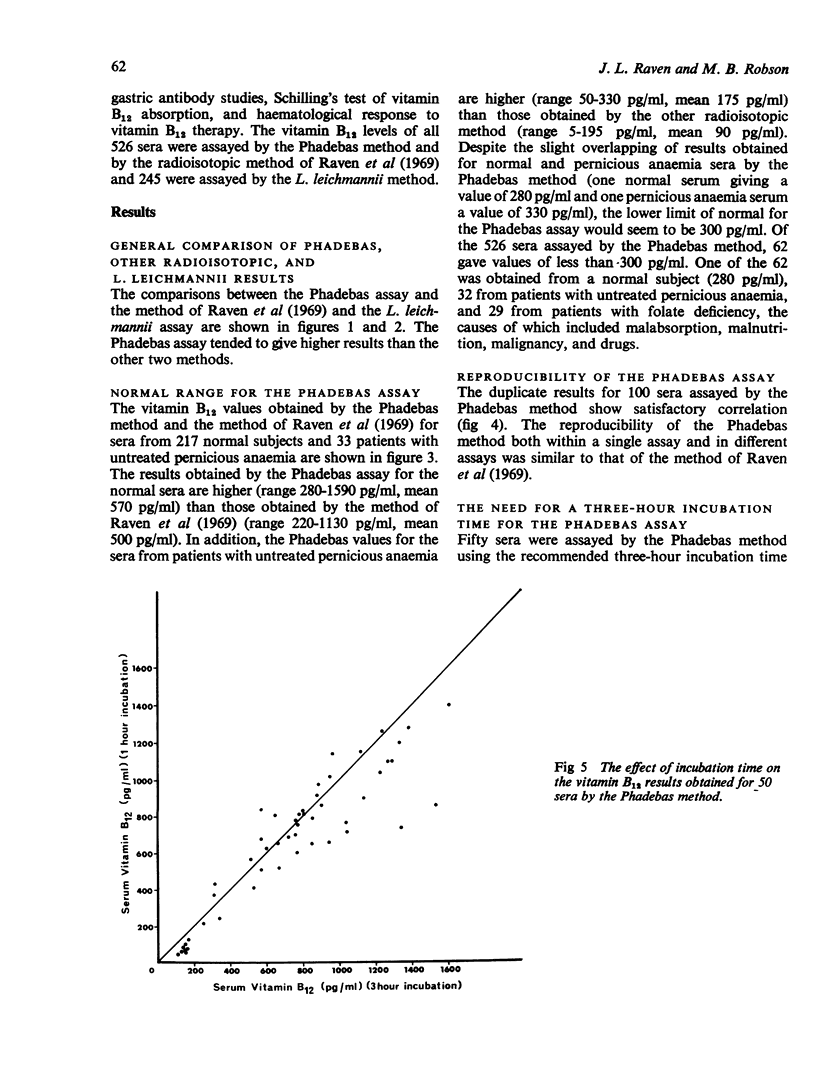
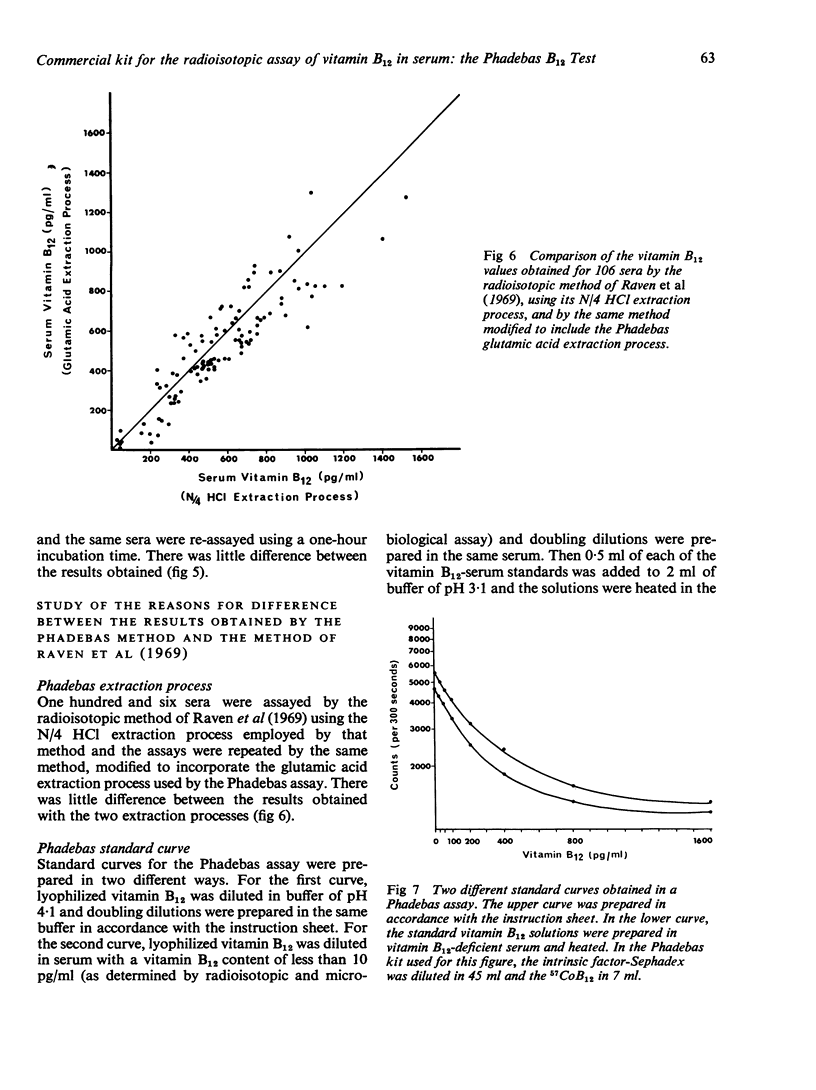
The first commercial kit for the radioisotopic assay of vitamin B12 in serum—the Phadebas B12 Test produced higher values than the radioisotopic method of Raven, Robson, Walker, and Barkham (1969) and the Lactobacillus leichmannii microbiological assay. Its normal range was 300-1100 pg/ml and its reproducibility was similar to that of the other radioisotopic method. It should be possible to lower the results obtained by the Phadebas method by modifying its standard curve and to reduce the time taken for the assay by shortening its incubation period.
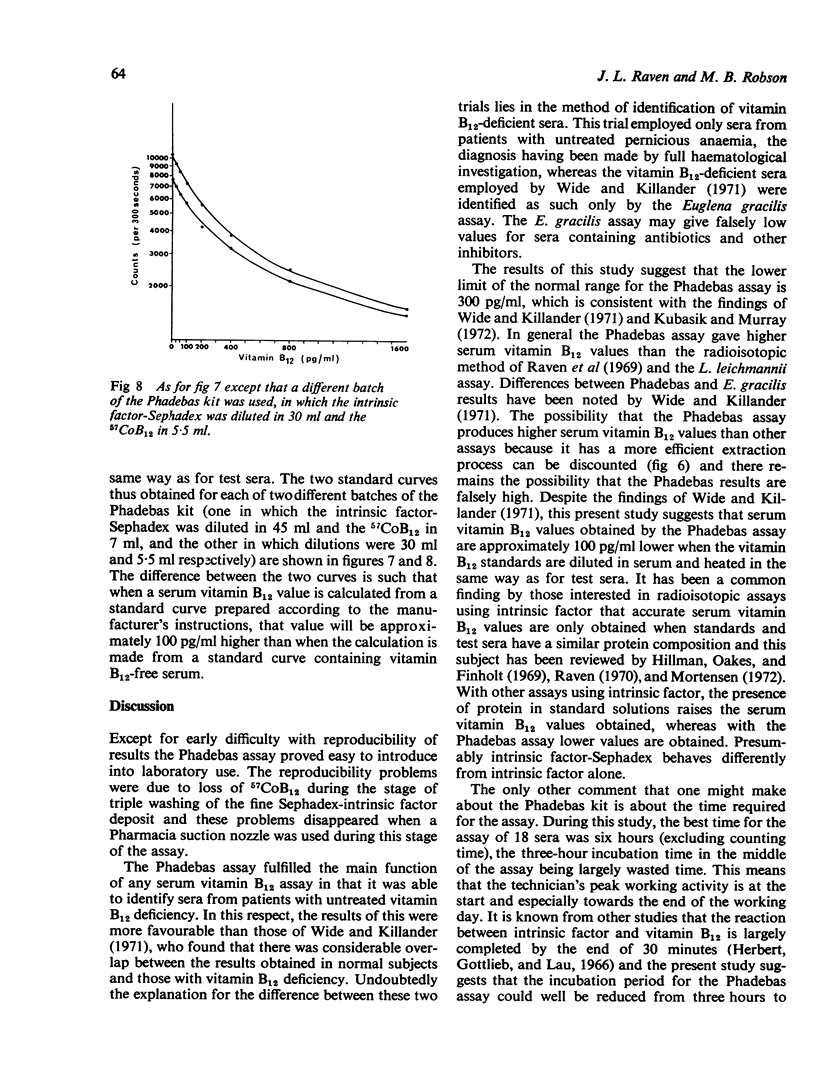
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardeman S., Chanarin I., Krafchik B., Singer W. Addisonian pernicious anaemia and intrinsic factor antibodies in thyroid disorders. Q J Med. 1966 Jul;35(139):421–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman R. S., Oakes M., Finholt C. Hemoglobin-coated charcoal radioassay for serum vitamin B12. A simple modification to improve intrinsic factor reliability. Blood. 1969 Sep;34(3):385–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubasik N. P., Murray M. H. Comparison of two radioassay methods for vitamin B 12 . Clin Chem. 1972 Jul;18(7):740–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAU K. S., GOTTLIEB C., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. MEASUREMENT OF SERUM VITAMIN B12 LEVEL USING RADIOISOTOPE DILUTION AND COATED CHARCOAL. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS D. M. Observations on the estimation of serum vitamin B12 using Lactobacillus leichmannii. Clin Sci. 1962 Feb;22:101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen E. Negative interference by residual proteins in the supernatant fluid used in radioisotopic assay of serum vitamin B 12 . Clin Chem. 1972 Sep;18(9):895–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL H. L., SARETT H. P. The determination of vitamin B12 activity in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):433–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven J. L., Robson M. B., Morgan J. O., Hoffbrand A. V. Comparison of three methods for measuring vitamin B 12 in serum: radioisotopic, euglena gracilis and Lactobacillus leichmannii. Br J Haematol. 1972 Jan;22(1):21–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven J. L., Robson M. B., Walker P. L., Barkhan P. Improved method for measuring vitamin B12 in serum using intrinsic factor, 57CoB12, and coated charcoal. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Mar;22(2):205–211. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven J. L., Robson M. B., Walker P. L., Barkhan P. The effect of cyanide, serum and other factors on the assay of vitamin B12 by a radio-isotope method using 57CoB12, intrinsic factor and coated charcoal. Guys Hosp Rep. 1968;117(2):89–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAY G. H. An improved method for the rapid estimation of vitamin B12 in serum. Clin Sci. 1955 Nov;14(4):661–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wide L., Killander A. A radiosorbent technique for the assay of serum vitamin B12. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Apr;27(2):151–159. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


