Abstract
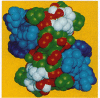
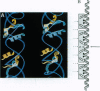
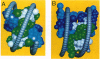
The histone octamer core of the nucleosome is a protein superhelix of four spirally arrayed histone dimers. The cylindrical face of this superhelix is marked by intradimer and interdimer pseudodyad axes, which derive from the nature of the histone fold. The histone fold appears as the result of a tandem, parallel duplication of the "helix-strand-helix" motif. This motif, by its occurrence in the four dimers, gives rise to repetitive structural elements--i.e., the "parallel beta bridges" and the "paired ends of helix I" motifs. A preponderance of positive charges on the surface of the octamer appears as a left-handed spiral situated at the expected path of the DNA. We have matched a subset of DNA pseudodyads with the octamer pseudodyads and thus have built a model of the nucleosome. In it, the two DNA strands coincide with the path of the histone-positive charges, and the central 12 turns of the double helix contact the surface of the octamer at the repetitive structural motifs. The properties of these complementary contacts appear to explain the preference of histones for double-helical DNA and to suggest a possible basis for allosteric regulation of nucleosome function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arents G., Burlingame R. W., Wang B. C., Love W. E., Moudrianakis E. N. The nucleosomal core histone octamer at 3.1 A resolution: a tripartite protein assembly and a left-handed superhelix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10148–10152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavykin S. G., Usachenko S. I., Zalensky A. O., Mirzabekov A. D. Structure of nucleosomes and organization of internucleosomal DNA in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 5;212(3):495–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90328-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G. A., Lewit-Bentley A., Finch J. T., Podjarny A. D., Roth M. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 16 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):55–75. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr Histone packing in the nucleosome core particle of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Moudrianakis E. N. The compaction of DNA helices into either continuous supercoils or folded-fiber rods and toroids. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Tullius T. D., Wolffe A. P. The structure of DNA in a nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hol W. G., van Duijnen P. T., Berendsen H. J. The alpha-helix dipole and the properties of proteins. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):443–446. doi: 10.1038/273443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Rhodes D., Smith J., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. A low resolution structure for the histone core of the nucleosome. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):509–516. doi: 10.1038/287509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave D. R., Sandman K. M., Reeve J. N. DNA binding by the archaeal histone HMf results in positive supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10397–10401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]