Abstract
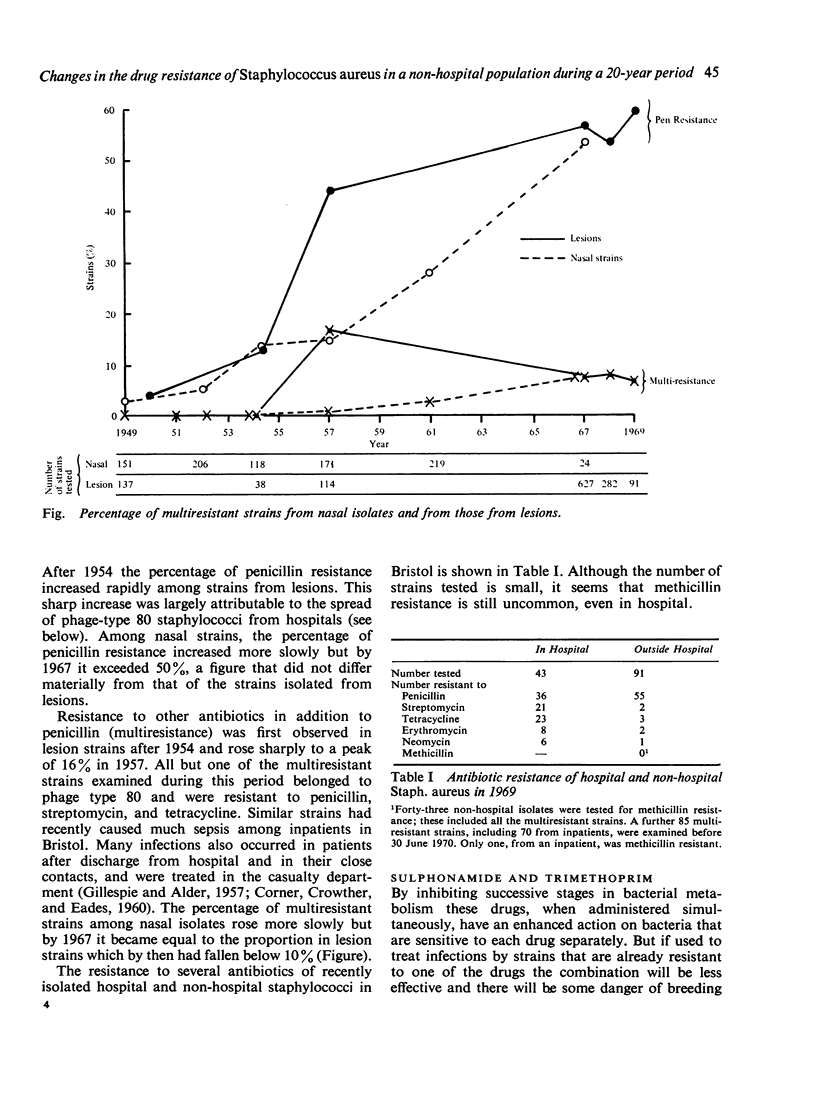
The antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Bristol from primary skin sepsis and nasal carriers outside hospital was recorded between 1949 and 1969. The proportion of penicillinase-forming strains rose to about 60% but resistance to other antibiotics remained un-common except for a peak about 1957, due to the spread of multiresistant phage-type 80 staphylococci. Reasons are discussed for the failure of other multiresistant staphylococci to increase outside hospital.
Recently isolated strains from inside and outside hospital were tested with sulphonamide and trimethoprim. All were sensitive to trimethoprim but 5% of non-hospital strains and 40% of hospital strains were resistant to sulphonamide. It is suggested that sulphonamide-resistant staphylococcal infections should not be treated with sulphonamide-trimethoprim mixtures because of the risk of breeding trimethoprim-resistant strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE S. K. R., DALGLEISH P. G., GILLESPIE W. A. Hospital cross-infections with staphylococci resistant to several antibiotics. Lancet. 1952 Jun 7;1(6719):1132–1135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNER B. D., CROWTHER S. T., EADES S. M. Control of staphylococcal infection in a maternity hospital; clinical survey of the prophylactic use of hexachlorophane. Br Med J. 1960 Jun 25;1(5190):1927–1929. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5190.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher G. M. A screening test for the detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):213–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J. Antibiotics in the treatment of E.N.T. infections. Br Med J. 1968 Oct 5;4(5622):55–55. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5622.55-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE W. A., ALDER V. G. Control of an outbreak of staphylococcal infection in a hospital. Lancet. 1957 Mar 23;272(6969):632–634. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen O., Rosendal K., Bülow P., Faber V., Eriksen K. R. Changing staphylococci and staphylococcal infections. A ten-year study of bacteria and cases of bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 18;281(12):627–635. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909182811201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Alder V. G., Gillespie W. A. The surivival of Staphylococcus aureus on human skin. An investigation using mixed cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):305–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., O'Grady F. W., Shooter R. A., Weaver P. C. Trial of phenoxymethylpenicillin, phenethicillin, and lincomycin in treatment of staphylococcal sepsis in a casualty department. Br Med J. 1968 Aug 17;3(5615):407–409. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5615.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H., PARKER M. T., JEVONS M. P., JOHN M. HIGH PENICILLINASE PRODUCTION CORRELATED WITH MULTIPLE ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Lancet. 1964 Feb 8;1(7328):293–296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92407-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON M. E., GILLESPIE W. A. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus by nurses. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(2):351–355. doi: 10.1002/path.1700750213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



