Abstract
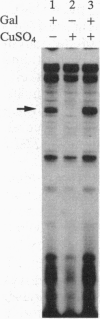
Controlled excision of DNA segments to yield intracellular DNA rings of well-defined sequences was utilized to study the determinants of transcriptional supercoiling of closed circular DNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In delta top1 top2ts strains of S. cerevisiae expressing Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I, accumulation of positive supercoils in intracellular DNA normally occurs upon thermal inactivation of DNA topoisomerase II because of the simultaneous generation of positively and negatively supercoiled domains by transcription and the preferential relaxation of the latter by the bacterial enzyme. Positive supercoil accumulation in DNA rings is shown to depend on the presence of specific sequence elements; one likely cause of this dependence is that the persistence of oppositely supercoiled domains in an intracellular DNA ring requires the presence of barriers to rotation of the DNA segments connecting the domains. Analysis of the S. cerevisiae 2-microns plasmid partition system by this approach suggests that the plasmid-encoded REP1 and REP2 proteins are involved in forming such a barrier in DNA containing the REP3 sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki H., Jearnpipatkul A., Tatsumi H., Sakurai T., Ushio K., Muta T., Oshima Y. Molecular and functional organization of yeast plasmid pSR1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki H., Nakanishi N., Evans B. R., Matsuzaki H., Jayaram M., Oshima Y. Site-specific recombinase, R, encoded by yeast plasmid pSR1. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 5;225(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91023-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. A role for the nuclear envelope in controlling DNA replication within the cell cycle. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):546–548. doi: 10.1038/332546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. M., Shea C., Fields S., Taub R. N., Van der Ploeg L. H., Tse D. B. Architectural organization in the interphase nucleus of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei: location of telomeres and mini-chromosomes. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2611–2619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton and the topology of replication. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90109-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Worcel A. Letter: Electron microscopic visualization of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):107–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90577-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Ward D. C. Cell cycle dependent chromosomal movement in pre-mitotic human T-lymphocyte nuclei. Chromosoma. 1992 Aug;101(9):557–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00660315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabiki H., Hagan I., Uzawa S., Yanagida M. Cell cycle-dependent specific positioning and clustering of centromeres and telomeres in fission yeast. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):961–976. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Wang J. C. Positive supercoiling of DNA greatly diminishes mRNA synthesis in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11461–11465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayama S., Kataoka T., Wachi M., Tamura G., Nagai K. Periodic formation of the oriC complex of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3761–3765. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast plasmid. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):860–865. doi: 10.1038/286860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozák P., Hassan A. B., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Visualization of replication factories attached to nucleoskeleton. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90235-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A. Structure-function relationships in eukaryotic nuclei. Bioessays. 1991 Jan;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram M., Li Y. Y., Broach J. R. The yeast plasmid 2mu circle encodes components required for its high copy propagation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Spector D. L. In vivo evidence that transcription and splicing are coordinated by a recruiting mechanism. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90159-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Williamson D. H. An alkaline sucrose gradient analysis of the mechanism of nuclear DNA synthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 17;164(2):217–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00267387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Najarian R., Haslinger A., Valenzuela P., Welch J., Fogel S. Primary structure and transcription of an amplified genetic locus: the CUP1 locus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):337–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y. Yeast plasmid requires a cis-acting locus and two plasmid proteins for its stable maintenance. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. A view of interphase chromosomes. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1533–1540. doi: 10.1126/science.2274784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki H., Araki H., Oshima Y. Gene conversion associated with site-specific recombination in yeast plasmid pSR1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):955–962. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki H., Nakajima R., Nishiyama J., Araki H., Oshima Y. Chromosome engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by using a site-specific recombination system of a yeast plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):610–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.610-618.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden G. B., Pratt M. J., Schaechter M. The replicative origin of the E. coli chromosome binds to cell membranes only when hemimethylated. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Stotz A., Scherf C. DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:169–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Pettijohn D. E. Chromosomes in living Escherichia coli cells are segregated into domains of supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):224–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J., Hamer D. H. Tandemly duplicated upstream control sequences mediate copper-induced transcription of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae copper-metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veit B. E., Fangman W. L. Copy number and partition of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 micron plasmid controlled by transcription regulators. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4949–4957. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y., Johnson C. V., Dobner P. R., Lawrence J. B. Higher level organization of individual gene transcription and RNA splicing. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1326–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.8446901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]