Abstract
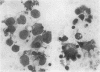
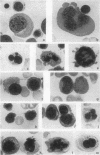
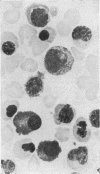
Bone marrow preparations were examined from 80 patients with aplastic anaemia. The degree of cellularity varied greatly and in a third of the cases it was normal or even hypercellular at one site of aspiration. In the severely hypoplastic marrows lymphoid cells were predominant and this situation was associated with a worse prognosis. There was no correlation between marrow lymphoid cell content and blood lymphocyte count but there was an inverse relationship between blood lymphocyte count and marrow erythroblasts and a close direct relationship between the blood neutrophil count and marrow myeloid cell content.
In all cases a proportion of the erythroblasts showed morphological abnormalities. These included especially megaloblastic changes and asynchrony of nuclear-cytoplasmic maturation. There were also binucleated cells, internuclear chromatin bridges, intercellular cytoplasmic connexions, nuclear degenerative changes, namely, blurred outlines, irregular shapes, budding and fragmentation, and atypical mitotic figures. These appearances illustrate the extent to which a qualitative defect of erythropoiesis occurs as part of the haematological pattern in aplastic anaemia, and in some cases dominates the bone marrow picture.
Similar cytological features were found in all cases, including five patients with Fanconi's anaemia.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy M., Dinçol K., Akgün T., Erdem S., Dinçol G. Haematological effects of chronic benzene poisoning in 217 workers. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jul;28(3):296–302. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.3.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E. A., Buehler F., Armentrout S. A., Lüdin H. Early hematological abnormalities associated with chloramphenicol therapy. Helv Med Acta. 1972;36(4):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger L. E., Rausing A. Pure red cell anemia: immunosuppressive treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):593–597. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. G., Hoffbrand A. V., Worlledge S. M. Increased agglutinability by anti-i of red cells in sideroblastic and megaloblastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1968 Oct;15(4):381–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delamore I. W., Geary C. G. Aplastic anaemia, acute myeloblastic leukaemia, and oxymetholone. Br Med J. 1971 Jun 26;2(5764):743–745. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5764.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus B., Sultan C., Rochant H., Salmon C., Mannoni P., Cartron J. P., Boivin P., Galand C. Anomalies of blood group antigens and erythrocyte enzymes in two types of chronic refractory anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1969 Mar;16(3):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANCONI G. DIE FAMILIAERE PANMYELOPATHIE. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1964 Sep 19;94:1309–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepson J. H., Lowenstein L. Inhibition of erythropoiesis by a factor present in the plasma of patients with erythroblastopenia. Blood. 1966 Apr;27(4):425–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knospe W. H., Crosby W. H. Aplastic anaemia: a disorder of the bone-marrow sinusoidal microcirculation rather than stem-cell failure? Lancet. 1971 Jan 2;1(7688):20–22. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B., Kao V. Studies on red cell aplasia. I. Demonstration of a plasma inhibitor to heme synthesis and an antibody to erythroblast nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):493–500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B., Kao V. Studies on red cell aplasia. II. Report of a second patient with an antibody to erythroblast nuclei and a remission after immunosuppressive therapy. Blood. 1969 Jul;34(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS S. M. COURSE AND PROGNOSIS IN APLASTIC ANAEMIA. Br Med J. 1965 Apr 17;1(5441):1027–1031. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5441.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS S. M. Red-cell abnormalities and haemolysis in aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1962 Oct;8:322–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Dacie J. V. The aplastic anaemia--paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1967 Mar;13(2):236–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Grammaticos P., Dacie J. V. Lysis by anti-I in dyserythropoietic anaemias: role of increased uptake of antibody. Br J Haematol. 1970 Apr;18(4):465–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Verwilghen R. L. Dyserythropoiesis and dyserythropoietic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1972 Jul;23(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb03452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F. P., Alter B. P., Nathan D. G. The mortality of acquired aplastic anemia in children. Blood. 1972 Aug;40(2):153–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Transformation of granulocytes to macrophages in bone marrow colonies in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):277–280. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONDANELLI E. G., GORINI P., PECORARI D., TROTTA N., COLOMBI R. [Effects of benzene on erythroblastic mitosis. Investigations by phase contrast microcinematography]. Acta Haematol. 1961;26:281–302. doi: 10.1159/000206664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Douglass C. C., Sharkey O., Jr The monocytopenia of aplastic anemia. Blood. 1973 Feb;41(2):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUNIS A. A., BLOOMBERG G. R. CHLORAMPHENICOL TOXICITY: CLINICAL FEATURES AND PATHOGENESIS. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:138–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]