Abstract
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) contains an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) integrin recognition sequence. In vitro mutagenesis was used to alter this RGD sequence to Trp-Gly-Asp (WGD). Migration of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the wild-type protein was more than 3-fold greater in 48 hr compared with cells expressing the WGD mutant form of IGFBP-1. Similarly, wild-type IGFBP-1 added to the media of control CHO cells stimulated migration 2-fold compared with the WGD protein. A synthetic RGD-containing peptide, when added to the medium with wild-type IGFBP-1, blocked the effect of IGFBP-1 on cell migration. The addition of IGF-I to the culture medium had no effect on the migration of cells expressing IGFBP-1 or vector alone. Affinity chromatography of 125I-labeled CHO cell membrane proteins, using IGFBP-1 coupled to agarose, identified the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin (fibronectin receptor) as the only cell surface molecule capable of binding IGFBP-1 in an RGD-dependent manner. Furthermore, wild-type IGFBP-1, but not the WGD mutant form, could be coprecipitated from CHO cells with an antibody directed against the alpha 5 integrin subunit. These studies demonstrate that IGFBP-1 stimulates CHO cell migration and binds to the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin receptor, both by an RGD-dependent mechanism. The effect of IGFBP-1 on migration is independent of IGF-I and is probably mediated through the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard J., Baxter R., Binoux M., Clemmons D., Drop S., Hall K., Hintz R., Rechler M., Rutanen E., Schwander J. On the nomenclature of the IGF binding proteins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Nov;121(5):751–752. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. S., Schreiner C. L., Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E., Juliano R. L. Motility of fibronectin receptor-deficient cells on fibronectin and vitronectin: collaborative interactions among integrins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):477–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Ruoslahti E. Tenascin mediates cell attachment through an RGD-dependent receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1149–1155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch W. M., Correa J., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. The 25-kilodalton insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein inhibits both basal and IGF-I-mediated growth of chick embryo pelvic cartilage in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):173–180. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Jr, Klapper D. G., Clemmons D. R. Purification of a 31,000-dalton insulin-like growth factor binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Isolation of two forms with different biologic actions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14203–14210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Snyder D. K., Clemmons D. R. Radioimmunoassay of a 26,000-dalton plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein: control by nutritional variables. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1225–1230. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürk R. R. A factor from a transformed cell line that affects cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):369–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Hubner C., Busby W. H., Jr, McCusker R. H., Wright G., Clemmons D. R. Identification of the forms of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins produced by human fibroblasts and the mechanisms that regulate their secretion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11949–11956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Smith E. P., van Wyk J. J., Joseph D. R., Hynes M. A., Hoyt E. C., Lund P. K. Isolation of rat testis cDNAs encoding an insulin-like growth factor I precursor. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):325–330. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A., Beck K., Chiquet M. Tenascin interferes with fibronectin action. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohick W. S., Clemmons D. R. The insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:131–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport M. L., Clemmons D. R., Miles M. V., Camacho-Hubner C., D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E. Regulation of serum insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding proteins during rat pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1278–1286. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport M. L., Svoboda M. E., Koerber K. L., Van Wyk J. J., Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E. Serum concentrations of insulin-like growth factor II are not changed by short-term fasting and refeeding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defilippi P., Silengo L., Tarone G. Alpha 6.beta 1 integrin (laminin receptor) is down-regulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18303–18307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Shalloway D. Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):690–692. doi: 10.1038/358690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Clemmons D. R., Wilson S., Han V. K., Strain A. J., Milner R. D. Immunological distribution of one form of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein and IGF peptides in human fetal tissues. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;2(1):31–38. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0020031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Lander A. D. Contact and adhesive specificities in the associations, migrations, and targeting of cells and axons. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90472-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
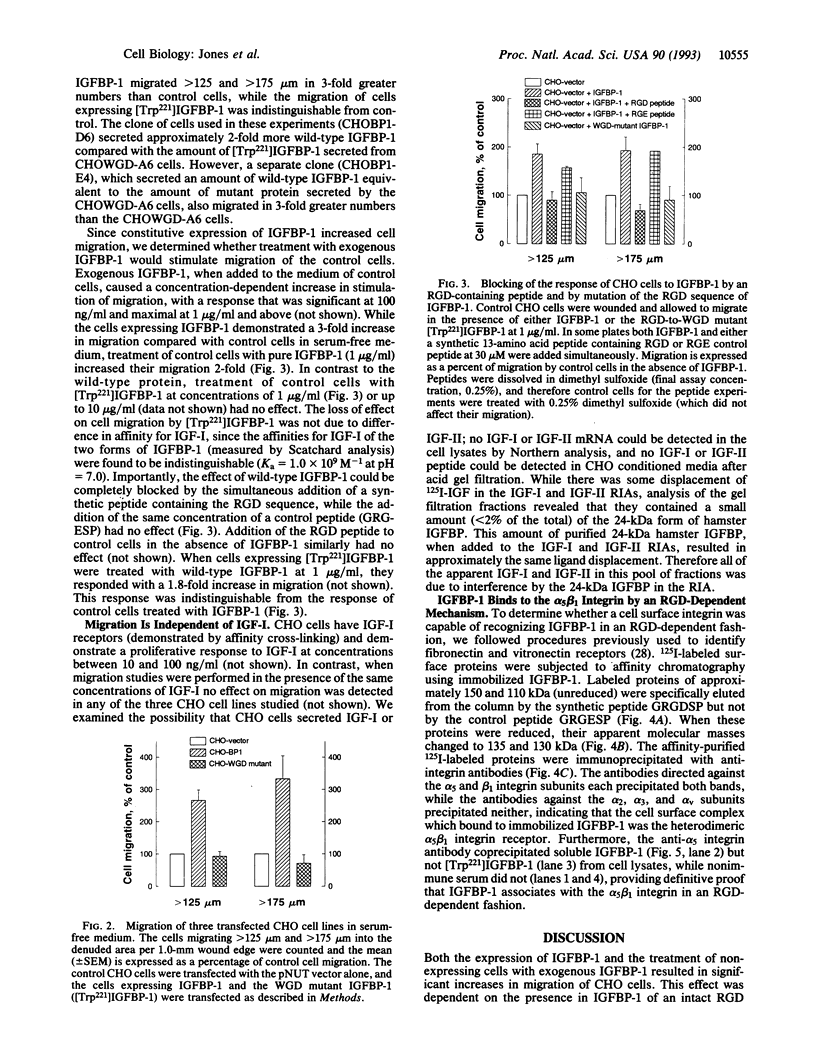
- Jones J. I., Busby W. H., Jr, Wright G., Smith C. E., Kimack N. M., Clemmons D. R. Identification of the sites of phosphorylation in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1. Regulation of its affinity by phosphorylation of serine 101. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1125–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. I., D'Ercole A. J., Camacho-Hubner C., Clemmons D. R. Phosphorylation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein 1 in cell culture and in vivo: effects on affinity for IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7481–7485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Aalto-Setälä K., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A., Kontula K. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein/placental protein 12 and tissue-specific expression of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Zhang K., Chen J. D., Wynn K. C., Kramer R. H., Woodley D. T. Mechanism of human keratinocyte migration on fibronectin: unique roles of RGD site and integrins. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jun;151(3):443–450. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L. J., Earp H. S., Turner C. E., Prockop C., Juliano R. L. Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of beta 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
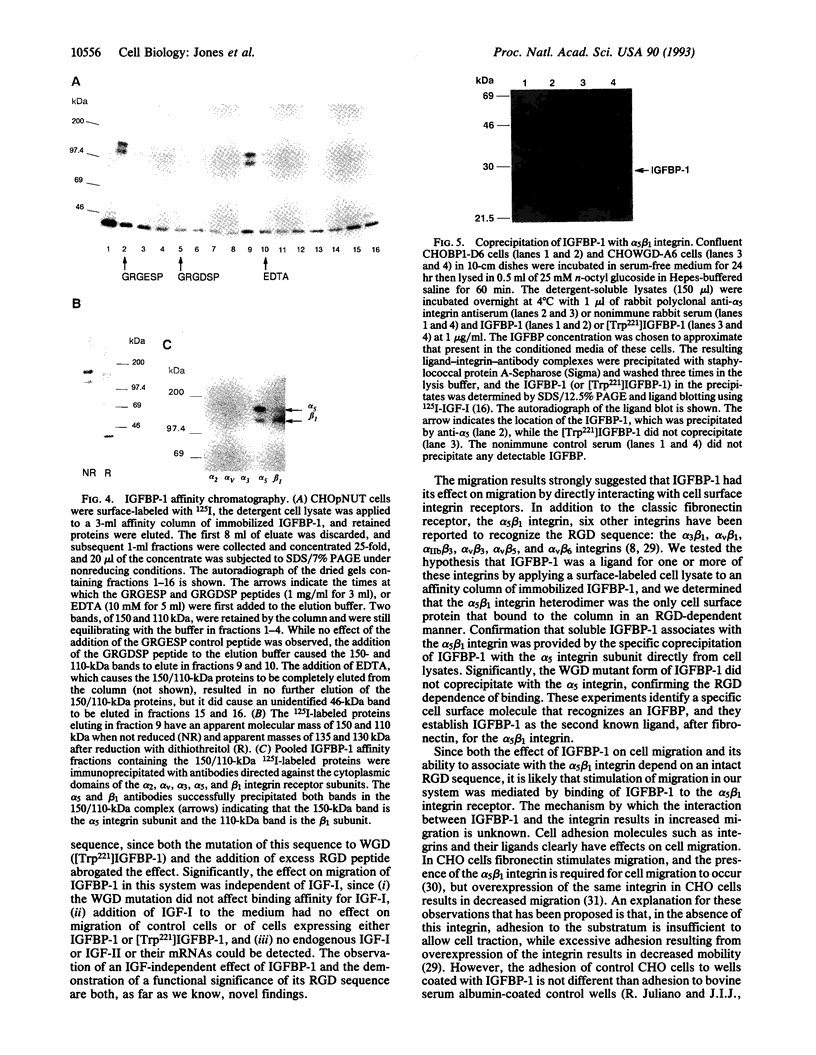
- Mohn K. L., Melby A. E., Tewari D. S., Laz T. M., Taub R. The gene encoding rat insulinlike growth factor-binding protein 1 is rapidly and highly induced in regenerating liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1393–1401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Behringer R. R., Quaife C. J., Maxwell F., Maxwell I. H., Brinster R. L. Cell lineage ablation in transgenic mice by cell-specific expression of a toxin gene. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Argraves S., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid adhesion receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:475–489. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Report on the nomenclature of the IGF binding proteins. Endocrinology. 1992 Mar;130(3):1736–1737. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.3.1371456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. The Walter Herbert Lecture. Control of cell motility and tumour invasion by extracellular matrix interactions. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):239–242. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C., Ingber D. E. Insoluble fibronectin activates the Na/H antiporter by clustering and immobilizing integrin alpha 5 beta 1, independent of cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7849–7853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Bruni C. B., Frunzio R., Terrell J. E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding rat insulin-like growth factor-II precursor. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):277–280. doi: 10.1038/312277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Nikaido T., Nojima Y., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of human CD4 T lymphocytes. Interaction of fibronectin with VLA-5 receptor on CD4 cells induces the AP-1 transcription factor. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]