Abstract
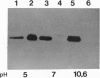
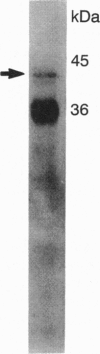
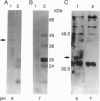
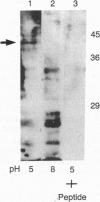
Two lysosomal proenzymes, procathepsins L and D, bind to mouse fibroblast microsomal membranes at acidic pH. This membrane association is independent of the mannose-6-phosphate receptors and requires the presence of the N-terminal propeptides of the enzymes. We have identified the protein that specifically binds procathepsin L at pH 5. A 43-kDa membrane protein coimmunoprecipitated with procathepsin L at pH 5 but not at pH 7 when cells were denatured with detergents. Similarly, a 43-kDa integral membrane protein bound procathepsin L in three kinds of ligand blots at pH 5 but not at pH 7. A synthetic peptide containing the 24 N-terminal residues of mouse procathepsin L blocked the binding of procathepsin L to this integral membrane protein on ligand blots. These results indicate that the 43-kDa integral membrane protein is a lysosomal proenzyme receptor that specifically binds the procathepsin L activation peptide at acidic pH.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burge V., Mainferme F., Wattiaux R. Transient membrane association of the precursors of cathepsin C during their transfer into lysosomes. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2750797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. E. The role of the cathepsin D propeptide in sorting to the lysosome. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21738–21745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Azzo A., Hoogeveen A., Reuser A. J., Robinson D., Galjaard H. Molecular defect in combined beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase deficiency in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4535–4539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diment S., Leech M. S., Stahl P. D. Cathepsin D is membrane-associated in macrophage endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6901–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst W., Machleidt W., Sandhoff K. The precursor of sulfatide activator protein is processed to three different proteins. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369(5):317–328. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Gottesman M. M. The major excreted protein of transformed fibroblasts is an activable acid-protease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1760–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille A., Waheed A., von Figura K. The ligand-binding conformation of Mr 46,000 mannose 6-phosphate-specific receptor. Acquisition of binding activity during in vitro synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13460–13467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoflack B., Fujimoto K., Kornfeld S. The interaction of phosphorylated oligosaccharides and lysosomal enzymes with bovine liver cation-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoflack B., Kornfeld S. Purification and characterization of a cation-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor from murine P388D1 macrophages and bovine liver. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12008–12014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Bankaitis V. A., Emr S. D. Distinct sequence determinants direct intracellular sorting and modification of a yeast vacuolar protease. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Banta L. M., Emr S. D. Intracellular sorting and processing of a yeast vacuolar hydrolase: proteinase A propeptide contains vacuolar targeting information. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2105–2116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Mellman I. The biogenesis of lysosomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:483–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste C. H., Graham T., Kaplan A. A sequence in beta-hexosaminidase from Dictyostelium discoideum required for sorting of proteins to a compartment involved in developmentally induced secretion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5942–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Mélèse T. Identification and characterization of a nuclear localization sequence-binding protein in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig T., Griffiths G., Hoflack B. Distribution of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes in the endocytic pathway of normal rat kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1561–1572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Z. M., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S. Cloning, sequencing, and functional characterization of the murine 46-kDa mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10589–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre G. F., Erickson A. H. Procathepsins L and D are membrane-bound in acidic microsomal vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15438–15445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Blobel G. A nuclear localization signal binding protein in the nucleolus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2235–2245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Jr, Cardelli J. A., Dimond R. L. Pathways involved in targeting and secretion of a lysosomal enzyme in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Kretz K. A., Dewji N., Wenger D. A., Esch F., Fluharty A. L. Coding of two sphingolipid activator proteins (SAP-1 and SAP-2) by same genetic locus. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1098–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.2842863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owada M., Neufeld E. F. Is there a mechanism for introducing acid hydrolases into liver lysosomes that is independent of mannose 6-phosphate recognition? Evidence from I-cell disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):814–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Erickson A. H., Kochan J., Ravetch J. V., Unkeless J. C. Cloning and characterization of a mouse cysteine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14697–14703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnboutt S., Aerts H. M., Geuze H. J., Tager J. M., Strous G. J. Mannose 6-phosphate-independent membrane association of cathepsin D, glucocerebrosidase, and sphingolipid-activating protein in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4862–4868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnboutt S., Kal A. J., Geuze H. J., Aerts H., Strous G. J. Mannose 6-phosphate-independent targeting of cathepsin D to lysosomes in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23586–23592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome L. H., Weissmann B., Neufeld E. F. Direct demonstration of binding of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-L-iduronidase, to receptors on cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2331–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Sadler I., Osborne M. A. Yeast proteins that recognize nuclear localization sequences. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):983–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong P. Y., Gregory W., Kornfeld S. Ligand interactions of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. The stoichiometry of mannose 6-phosphate binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7962–7969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong P. Y., Kornfeld S. Ligand interactions of the cation-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Comparison with the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7970–7975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: the localization determinant of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y resides in the propeptide. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Winther J. R., Stevens T. H. Yeast carboxypeptidase Y vacuolar targeting signal is defined by four propeptide amino acids. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):361–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Pohlmann R., Hasilik A., von Figura K., van Elsen A., Leroy J. G. Deficiency of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase in organs of I-cell patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1052–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K. Molecular recognition and targeting of lysosomal proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90035-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]