Abstract
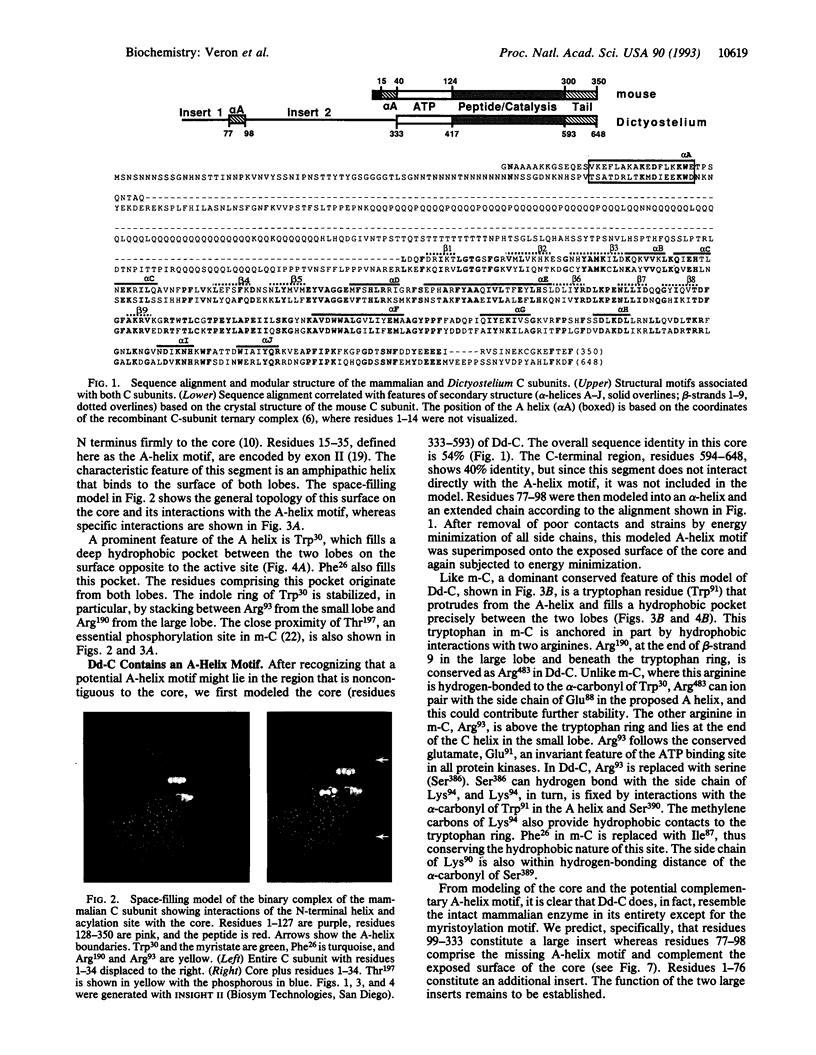
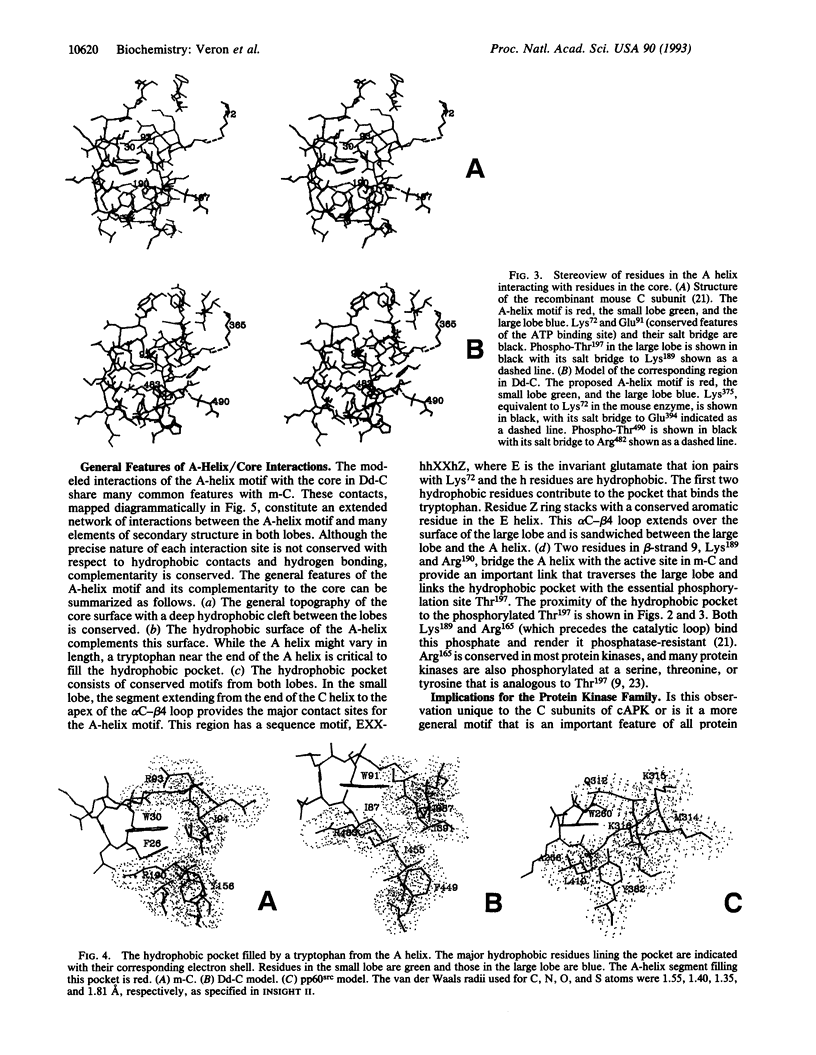
Residues 40-300 of the mammalian catalytic (C) subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase define a conserved bilobal catalytic core shared by all eukaryotic protein kinases. Contiguous to the core is an extended amphipathic alpha-helix (A helix). Trp30, a prominent feature of this helix, fills a deep hydrophobic pocket between the two lobes on the surface opposite to the active site. The C subunit in Dictyostelium discoideum shows sequence conservation of residues 40-350 with the mouse enzyme but contains an N-terminal extension of 332 residues. A sequence corresponding to the A helix contiguous to the core is absent. However, we have now identified a remote A-helix motif (residues 77-98). When the core of the Dictyostelium C subunit was modeled, based on the mouse C subunit, complementarity between this putative A helix and the surface of the core was found to be conserved. Analysis of other protein kinases reveals that the A-helix motif is not restricted to cAMP-dependent protein kinase. In the Src-related family of protein kinases, for example, an A helix is very likely contiguous to the core, thus serving as a linker between the conserved catalytic core and the Src homology 2 domain. We predict that an A-helix motif complementary to the core will be a conserved feature of most eukaryotic protein kinases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anjard C., Etchebehere L., Pinaud S., Véron M., Reymond C. D. An unusual catalytic subunit for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9532–9538. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Viral src gene products are related to the catalytic chain of mammalian cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beushausen S., Bergold P., Sturner S., Elste A., Roytenberg V., Schwartz J. H., Bayley H. Two catalytic subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase generated by alternative RNA splicing are expressed in Aplysia neurons. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):853–864. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Characterization of genomic clones coding for the C alpha and C beta subunits of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5739–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. L., Higgins G. C., Jackson F. R. Cloning, sequence, and expression of the Drosophila cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1676–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. E., Bagchi S., Lu X., Rubin C. S. Cloning, characterization, and expression of the gene for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Caenorhabditis elegans. Identification of highly conserved and unique isoforms generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6896–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G. A. Sequence of the cell division gene CDC2 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; patterns of splicing and homology to protein kinases. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Bell S. M., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. 2.0 A refined crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with a peptide inhibitor and detergent. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 May 1;49(Pt 3):357–361. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993000502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Cadena D. L., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M., Gill G. N. Structural features that specify tyrosine kinase activity deduced from homology modeling of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5001–5005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Pearson R. B., Sowadski J. M., Means A. R., Ten Eyck L. F., Taylor S. S., Kemp B. E. Structural basis of the intrasteric regulation of myosin light chain kinases. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):130–135. doi: 10.1126/science.1439761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga Y., Caccia N., Toyonaga B., Spolski R., Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone (YT16) encodes a protein with extensive homology to a family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1643–1646. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Pflugrath J. W. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10595–10600. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Yonemoto W. M., Taylor S. S., Firtel R. A. DdPK3, which plays essential roles during Dictyostelium development, encodes the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10701–10705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcote M. J., Knighton D. R., Basi G., Sowadski J. M., Brambilla P., Draetta G., Taylor S. S. A three-dimensional model of the Cdc2 protein kinase: localization of cyclin- and Suc1-binding regions and phosphorylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):5122–5131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding alpha and beta subunits of Drosophila melanogaster casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3409–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Roe B. A., Canaani E. Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Cauthron R. D., Symcox M. M., Shuntoh H. Autoactivation of catalytic (C alpha) subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by phosphorylation of threonine 197. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2332–2341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Semba K., Yamanashi Y., Nishizawa M., Miyajima N., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Characterization of cDNA clones for the human c-yes gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Knighton D. R., Zheng J., Sowadski J. M., Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. A template for the protein kinase family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)80001-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Knighton D. R., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Sowadski J. M. Structural framework for the protein kinase family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:429–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., McGlone M. L., Taylor S. S. N-myristylation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase conveys structural stability. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2348–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M., Ten Eyck L. F. Crystal structures of the myristylated catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase reveal open and closed conformations. Protein Sci. 1993 Oct;2(10):1559–1573. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., ten Eyck L. F., Karlsson R., Xuong N., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2154–2161. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]