Summary
Aging is the greatest risk factor for a number of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Furthermore, normal aging is associated with a decline in sensory, motor, and cognitive functions. Emerging evidence suggests that synapse alterations, rather than neuronal cell death, are the causes of neuronal dysfunctions in normal aging, and in early stages of neurodegenerative diseases. However, little is known about the mechanisms underlying age-related synaptic decline. Here we uncover a surprising role of the anterograde molecular motor UNC-104/KIF1A as a key regulator of neural circuit deterioration in aging C. elegans. Through analyses of synapse protein localization, synaptic transmission, and animal behaviors, we find that reduced function of UNC-104 accelerates motor circuit dysfunction with age, while upregulation of UNC-104 significantly improves motor function at advanced ages and also mildly extends lifespan. In addition, UNC-104-overexpressing animals outperform wild-type controls in associative learning and memory tests. Further genetic analyses suggest that UNC-104 functions downstream of the DAF-2 signaling pathway, and is regulated by the FOXO transcription factor DAF-16, which contributes to the effects of DAF-2 in neuronal aging. Together, our cellular, electrophysiological, and behavioral analyses highlight the importance of axonal transport in the maintenance of synaptic structural integrity and function during aging, and raise the possibility of targeting kinesins to slow age-related neural circuit dysfunction.
Introduction
Both genes and environmental cues affect lifespan[1], and increasing evidence suggests that different tissues decline through distinct mechanisms[2]. Neurons are particularly vulnerable to the aging process, given their long lifespan, lack of cell renewal, and high degree of complexity[3].
Progressive neuronal dysfunction during normal aging is associated with a number of subtle changes at the functional and morphological levels, rather than the loss of neuronal cells[4]. For example, in aged mice and C. elegans, a subset of motor neurons exhibit abnormal sprouting of neurite branches and synapse deterioration, correlating with age-associated motility decline[5–8]. Moreover, changes in synapse density and morphology are closely associated with the degree of cognitive impairment in aged primates[9, 10], as well as cognitive decline in aged rats[11] and retinal defects in old mice[12]. At the cellular and molecular level, the decline of synaptic function during aging involves various aspects of synapse biology, including changes in synapse structure[8], changes of lipid and protein components of synaptic vesicles (SVs)[13, 14], and defects in synaptic release[15] and axonal transport[16, 17]. While these findings emphasize the importance of dissecting cellular and molecular events in aging synapses that contribute to age-associated neural dysfunction, the multitude of age-dependent synapse changes poses difficulties for the development of therapeutic interventions. Therefore, it is critical to identify key components in the maintenance of neuronal function with age.
Furthermore, maintenance of neuronal activity is also critical for the maintenance of non-neuronal tissue functions and longevity. For instance, neuronal activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) extends C. elegans lifespan[18] and improves metabolic homeostasis in mice[19]. In addition, neuronal function of the FOXO transcription factor DAF-16 contributes to lifespan regulation in C. elegans[20]. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms by which these lifespan- and homeostatic- regulatory pathways affect neuronal functions remain unclear.
To gain further understanding of the mechanisms that determine synaptic functions during aging, we performed candidate gene screens to identify regulators of synaptic function in motor neurons of aging C. elegans. We found that the anterograde kinesin motor UNC-104/KIF1A is a critical regulator of aging-associated neural circuit dysfunction. UNC-104 is required for the protective effects of insulin/IGF signaling (IIS) pathway downregulation in the maintenance of learning and memory as well as motor activity with age. These findings provide the first information about possible neuronal targets that mediate the protective effects of insulin signaling in neural circuit functions during aging, and highlight the unexpected role of axonal transport as a potential target for pharmaceutical interventions in the maintenance of health span.
Results
UNC-104 modifies age-dependent changes in synaptic vesicle (SV) distribution
Motility decline is one of the most prominent functional declines in aging animals. Consistent with previous reports[21–23], we found that the motor activity of aging worms gradually declines. For example, 18-day old (day 18) animals had severe motility defects compared with young (day 1) adults, as indicated by reduced body bend movements in liquid medium (Figure 1A). Recent studies in aged mammals and worms have suggested that this age-associated motility decay results from synapse alterations at neuromuscular junctions (NMJs)[8, 15], although the underlying molecular pathways are not well understood.
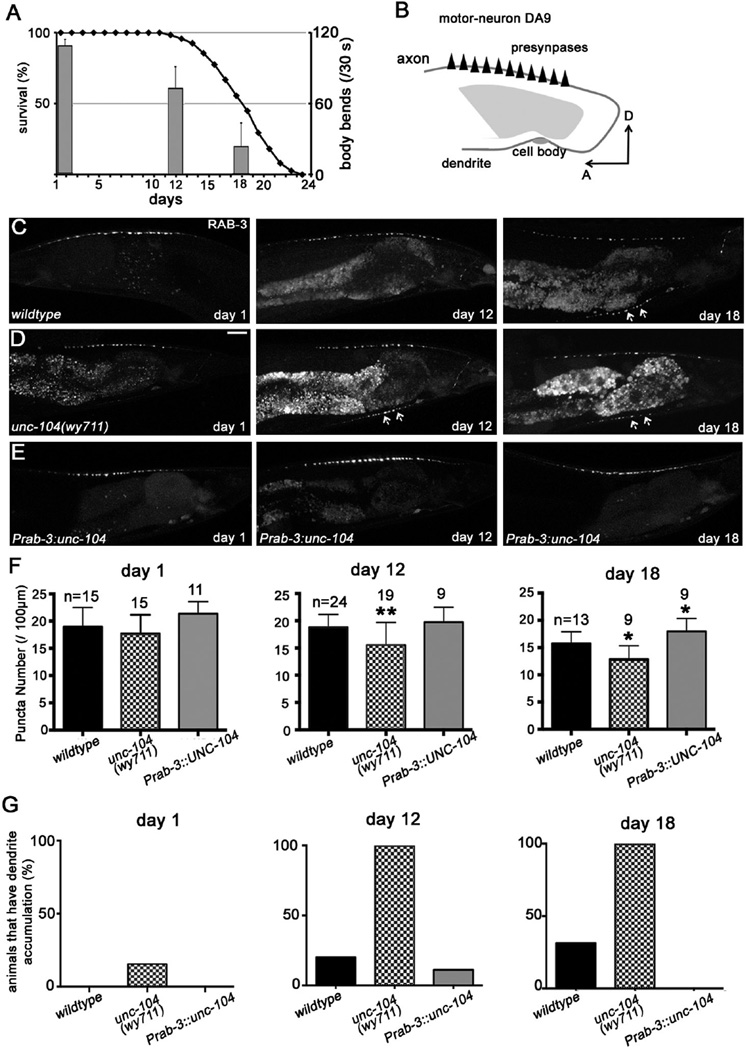
Figure 1. see also Figure S1, S2: UNC-104 modulates DA9 synapse distribution with age.
(A) C. elegans undergoes aging-associated motility decay. The solid black curve is drawn according to the Y axis on the left, representing the percentage of animals that remain alive at a particular age (X axis), and the grey bars are drawn according to the Y axis on the right, representing the body bends behavior of an animal at a certain age. (B) A schematic showing the morphology and synaptic pattern of the C. elegans DA9 neuron. A, anterior, D, dorsal. (C–E) confocal microscopy images of the GFP::RAB-3 distribution in DA9 neurons. Scale bar, 20µm. (C) aging is associated with a decrease of SV puncta in the presynaptic region, and ectopic accumulation in the dendrite (arrows) and asynaptic regions. (D) the unc-104 loss-of-function allele wy711 does not affect the synapse distribution in d1 worms (left), but exacerbates the synapse changes in aged worms (day 12, middle; day 18, right). (E) overexpression of UNC-104 with a pan-neuronal promoter Prab-3 strongly suppresses the aging-associated synapse changes in wild-type backgrounds. (F) Quantification of the RAB-3 puncta density. (G) quantification of the population of the worms that develop ectopic accumulation of RAB-3 in the dendrite. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA, with post-test: Turkey’s multiple comparison in F, chi-square test in G. The error bars stand for standard deviation (SD).
To explore the cellular and molecular basis of synapse aging, we examined the synapse morphology in the DA9 motor neurons, which form approximately 25 en passant presynaptic specializations within a discrete and stereotyped location along its axon (Figure 1B). Our previous studies showed that the DA9 synapses can be reliably labeled by GFP-tagged synaptic vesicle (SV) proteins such as RAB-3[24] (Figures 1B, 1C). Aging wild-type animals display gradually reduced SV density in the DA9 presynaptic region, and ectopic accumulation of synaptic vesicle proteins such as RAB-3 and SNB-1 in the dendritic and asynaptic axonal regions (Figures 1C, F, G and Figures S1A–C). These observations suggest that presynaptic integrity is compromised in the motor neurons of aging C. elegans.
We next performed a small-scale candidate screen to identify presynaptic-related mutants that show enhanced DA9 synapse defects during aging. From this screen, we identified two molecules that affect SV transport: the anterograde molecular motor for SV transport UNC-104/KIF1A, and its regulator, a small GTPase ARL-8[25], both emerged as modulators of synapse decline during aging. ARL-8 is a SV-bound small GTPase that binds to and activates UNC-104 to promote synaptic vesicle and active zone protein trafficking[25]. The weak loss-of-function mutant unc-104 allele wy711 showed a low-penetrance RAB-3 mislocalization phenotype on day 1 of adulthood (day 1), where RAB-3 proteins were ectopically localized to asynaptic regions and dendrites. Both the severity and penetrance of this phenotype were dramatically enhanced by day 12, to a level significantly higher than the day 12 wild-type animals (Figures 1D–G). We also observed a similarly exacerbated RAB-3 mislocalization phenotype in aging heterozygous mutants of a strong loss-of-function unc-104 allele e1265 (e1265/+) (Figures S1D–E, G–H, J). Similar to unc-104 mutants, partial loss-of-function of ARL-8 also showed an age-dependent enhancement of the SV mislocalization phenotype (Figures S2F, I, J). Thus, reduction of UNC-104 activity, either due to the loss-of-function mutation in itself or in its activator ARL-8, greatly accelerates aging-associated SV mislocalization.
To test whether aging-associated synapse alterations are specifically affected by SV trafficking defects, we examined a number of mutants in which other aspects of synapse development or functions are affected. These include presynapse assembly mutants syd-2/liprin-α (ju37)[26] and nab-1/neurabin (ok943)[27], synaptic transmission mutants unc-10/rim(e102)[28], unc-57/endophilin (ok310)[29, 30] and unc-11/AP180(e47)[31], and synaptic patterning mutants in the Wnt signaling pathway: dsh-1/disheveled (ok1445) and lin-44(n1792)[24]. None of these mutants showed changes in RAB-3 localization patterns between day 1 and day 12 (data not shown). These observations suggest that UNC-104 regulated SV transport deteriorates during aging and contributes to age-associated synapse abnormalities. Strikingly, over-expression of UNC-104 with a pan-neuronal promoter (Prab-3) rescued the ectopic localization of SV proteins in aging wild-type animals, suggesting that the age-dependent neuronal phenotype is due to a reduction of UNC-104 function (Figures 1E–1G). In addition to DA9 neurons, aging-associated synapse loss in other motor neurons such as cholinergic DB and GABAergic DD neurons was also modulated by UNC-104 dosage, and can be rescued cell autonomously (Figure S2 and data not shown), indicating that UNC-104 regulates synapse aging broadly. These observations suggest that UNC-104-regulated SV transport deteriorates during aging and contributes to age-associated synapse phenotypes.
UNC-104 mediates age-dependent motor function decline by regulating presynaptic transmission
We next asked whether the unc-104-dependent SV trafficking phenotype is relevant for age-related behavioral declines. As described previously[32], we found that worm thrashing activity declined in an age-dependent manner. Furthermore, mutants of UNC-104 (wy711 and e1265/+) exacerbated this decline of motility with age (Figure 2A). By contrast, over-expression of UNC-104 in neurons either from a pan-neuronal promoter or from the endogenous UNC-104 promoter significantly rescued the thrashing defects of aged worms (Figure 2A and Figure S3B). This improvement in motility is especially dramatic at advanced ages (day 18 and 21).
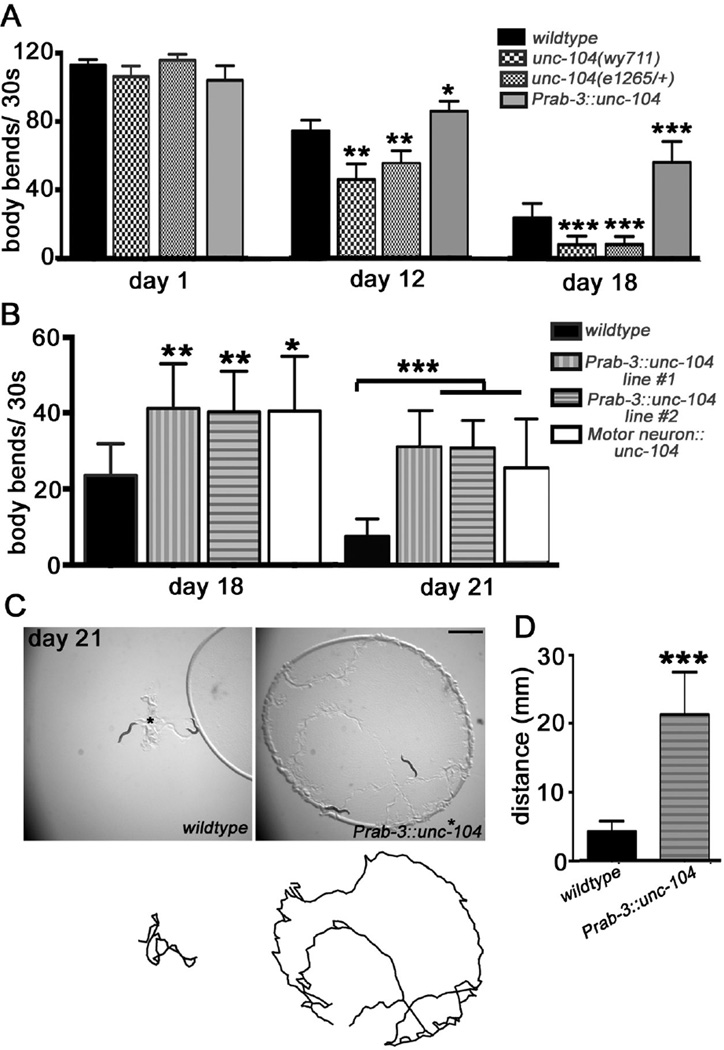
Figure 2. see also Figure S3: UNC-104 modulates aging-associated motility decay.
(A) Worm motility decline is enhanced in unc-104 lof mutant, but mitigated in UNC-104 overexpression backgrounds. Total number analyzed: day 1: 15 (wildtype), 9 (unc-104(wy711)), 7 (unc-104(e1265/+), 7 (Prab-3::unc-104); day 12: 36 (wildtype), 20 (unc-104(wy711)), 23 (unc-104(e1265/+), 28 (Prab-3::unc-104); day 18: 25 (wildtype), 15 (unc-104(wy711)), 17 (unc-104(e1265/+), 21 (Prab-3::unc-104); (B) UNC-104 improves the motility defect at advanced ages (d21), and has similar protective functions when expressed in motor neurons (Punc-17 + Punc-47). Total animals analyzed: day 18: 25 (wildtype), 16 (Prab-3::unc-104 line #1), 16 (Prab-3::unc-104 line #2), 13 (Motor neuron::unc-104);*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA. (C) UNC-104 over-expressing animals are more active at d21. Upper panel, representative images of the locomotion traces left on the bacterial lawns in three hours. Lower panel, locomotion trajectories. The asterisks mark the starting points where animals are placed on the plates. (D) Quantification of the total distance the worms moved in three hours. Total animals analyzed: 13(wildtype), 15 (Prab-3::unc-104 line #2). ***, P<0.001. Unpaired student t test. The error bars stand for 95% confidence intervals (CI).
To identify the neurons in which UNC-104 functions to regulate motility decline, we expressed UNC-104 in different combinations of motor neurons that directly synapse onto muscles (Figure S3A). Expression of UNC-104 in all of the six classes of motor neuron had protective effects that were similar to pan-neuronal-expression of UNC-104 (Figure 2B), whereas expressing UNC-104 in the cholinergic or GABAergic neurons alone had no beneficial effects (Figure S3B). Furthermore, we found that UNC-104 over-expressing animals showed not only improved swimming behaviors, but also enhanced motility on solid plates (Figures 2C–2D).
To test the specificity of the protective effects of UNC-104 with age, we asked if mutations that cause hyperactive behaviors or affect other components of the SV transport pathways also improve motility at advanced ages. Unlike strains overexpressing UNC-104, hyperactive mutants such as diacylglycerol kinase theta (dgk-1(nu62)) and the G protein alpha subunit Go (goa-1(sa734)) showed exacerbated motility defects in aged worms (Figure S3C). In addition, reduced function of DHC-1 (dhc-1(or195ts)), a component of the cytoplasmic dynein complexes that antagonizes the anterograde trafficking of SVs mediated by UNC-104 [33], caused mild motility defects in young adults (day 1). However, this defect did not change with age, suggesting that reduced function of DHC-1 does not affect the age-associated motility decline (Figure S3D). Together, these results highlight a specific role of UNC-104 in motor neurons in the maintenance of presynaptic integrity and motor circuit function with age.
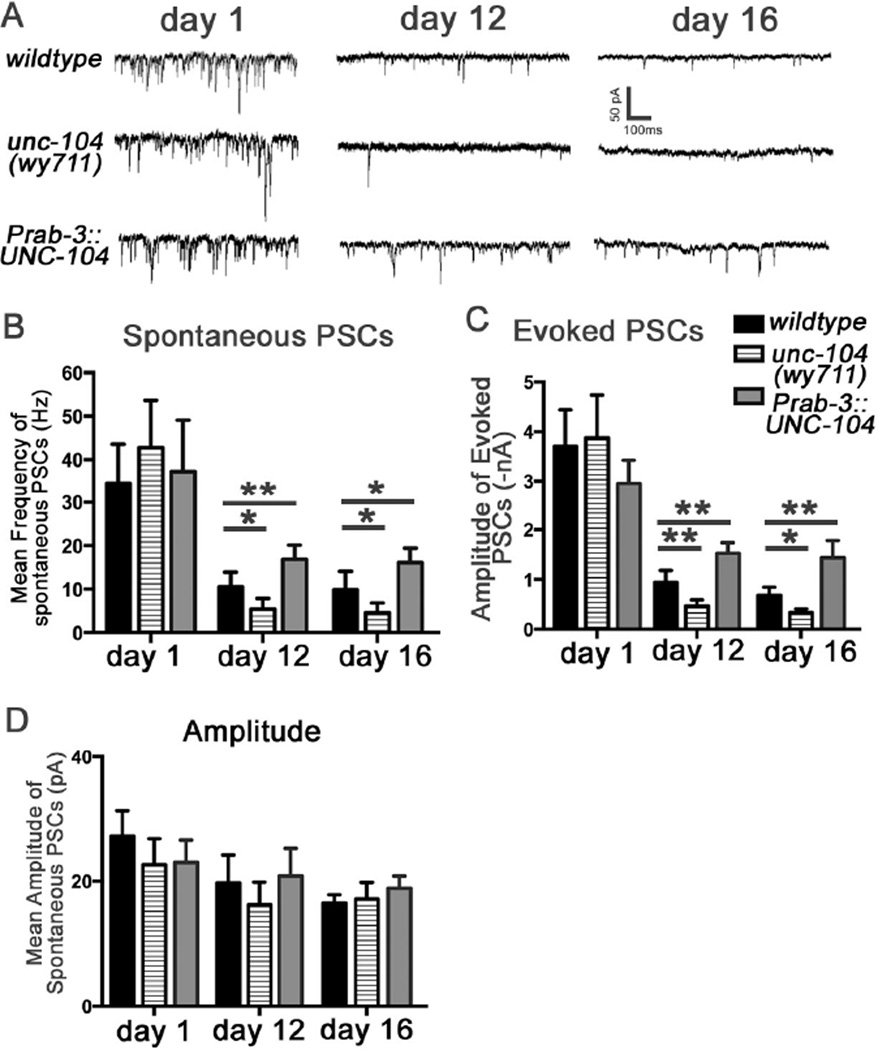
To directly test whether UNC-104 modulates synaptic transmission during aging, we recorded synaptic currents at the neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) of various genotypes at different ages by patch-clamp. Our previous studies showed that during aging, the worm motor circuit first developed a presynaptic defect in synaptic transmission in early-mid ages (days 7–12), as indicated by a decrease in the frequency of spontaneous post-synaptic currents (PSCs)[15]. This is followed by body-wall muscle deterioration in the mid-late ages (~day 12). Reduced function or upregulation of UNC-104 did not affect the frequency or the amplitude of spontaneous PSCs, or the amplitude of evoked PSCs in day 1 adults, suggesting that synaptic transmission is not affected by these manipulations of UNC-104 dosage in young animals (Figures 3A–3D, Figure S4). At days 12 and 16, wy711 mutation further reduced the frequency of spontaneous PSCs and the amplitude of evoked responses, while UNC-104 overexpressing animals showed an increased frequency of spontaneous PSCs and increased amplitude of evoked responses compared to wild-type of the same ages (Figures 3A–3D). These effects of UNC-104 are likely to be caused by changes in presynaptic function, since the amplitude of spontaneous PSCs was not affected in unc-104 mutants at day 12 or 16 compared to wild-type (Figure 3D). Together with the motor neuron rescue data, these results support the notion that reduced presynaptic function in motor neurons is primarily responsible for the motor defects observed in aging worms. Furthermore, upregulation of UNC-104 is sufficient to improve the presynaptic structural integrity and function in aged animals.
Figure 3. see also Figure S4: UNC-104 regulates synaptic transmission in aged worms.
(A) Representative traces of spontaneous PSCs recorded from the NMJs at the ventral nerve cord. Membrane voltage was clamped at −60mV during the recording. (B) Quantification of the frequency of spontaneous PSCs. (C) quantification of the amplitude of evoked PSCs. (D) Quantification of the amplitude of spontaneous PSCs. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; One-way ANOVA, with post-test: Turkey’s multiple comparison. Total animals analyzed: day1: 17 (wildtype), 17 (unc-104(wy711)), 16 (Prab-3::unc-104); day 12: 10 (wildtype), 12 (unc-104(wy711)), 12 (Prab-3::unc-104); day 16: 10 (wildtype), 10 (unc-104(wy711)), 10 (Prab-3::unc-104);. The error bars stand for 95% confidence intervals (CI).
UNC-104 activity is down-regulated with age
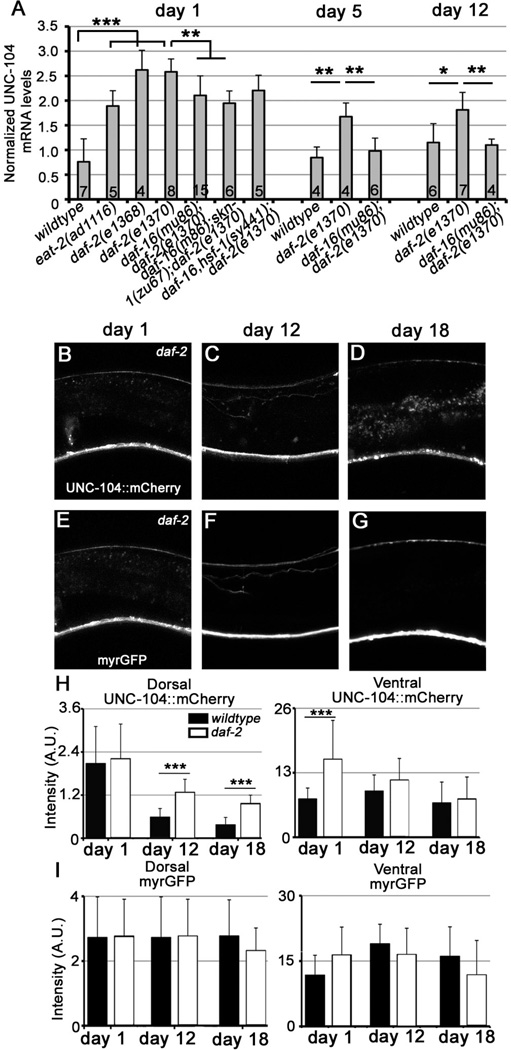
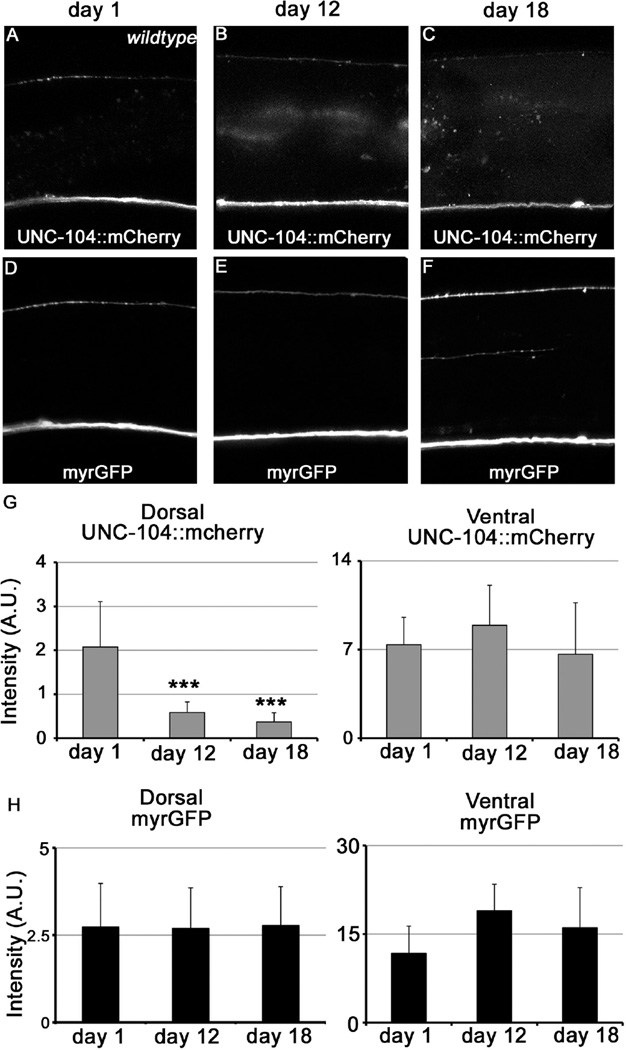
To further understand the mechanisms by which UNC-104 alterations affect neuronal function, we next examined the steady state level of UNC-104 mRNA in young (day 1) and aged (days 5, 12) animals. Unc-104 mRNA at the whole organism level remains similar between young and older worms (Fig. 7A), suggesting that aging does not affect UNC-104 at the mRNA level. Next, we used a Punc-104::unc-104::mcherry transgene to examine the level and localization of UNC-104 protein in young and old (days 12, 18) worms. The ventral nerve cord (VNC) is composed of axons, dendrites, and cell bodies from ~80 different neurons, while the dorsal nerve cord (DNC) primarily contains axons from the motor neurons. Interestingly, the UNC-104::mcherry signal is specifically decreased in the DNC, but not VNC, of day 12 and day 18 animals compared to that of day 1, indicative of compromised UNC-104 activity and kinesin motor’s failure to travel to distal axons with age (Figures 4A–C, G). We also measured the control fluorescent signal of Punc-104::myrgfp and found no difference between young and old worms in either DNC or VNC (Figures 4D–F, H). These results suggest that the neither the Punc-104 promoter activity, nor the general translation processes is affected by aging. Furthermore, there is unlikely a dramatic loss of axons in the aging DNC, consistent with previous reports[7]. In addition, we also examined the UNC-104 protein localization by analyzing the effects of age on a UNC-104::GFP reporter expressed specifically in the cholinergic DA9 neuron. Consistent with the results observed in the DNC, we found that presynaptic localization of UNC-104::GFP is decreased in day 12 animals compared to day 1 animals, whereas the control DsRed intensity is increased over time (Figure S5). These results suggest that aging specifically reduces the activity but not the overall level of UNC-104 mRNA or protein.
Figure 7. see also Figure S7: UNC-104 mRNA and protein is maintained in daf-2 mutants with age.
(A) qRT-PCR analyses of the unc-104 mRNA levels. The steady state level of unc-104 mRNA is increased in daf-2 mutants, and partially suppressed in daf-16;daf-2 and daf-16;skn-1;daf-2 mutants. The number of replicates are indicated on the corresponding bars on the chart. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA. The error bars stand for standard deviation (SD). (B–G) Confocal images of UNC-104mcherry (B–D) in the dorsal and ventral nerve cord of daf-2 mutants, which are labeled with myrGFP (E-G), in young (day 1) and aged (days 12, 18) worms. (H–I) Quantification of myrGFP and UNC-104mcherry fluorescence in young and old daf-2 animals compared to wild-type. The age-associated decrease of UNC-104 in DNC is mitigated in daf-2 mutants. Total animals analyzed: daf-2: day 1: 13, day 12: 9, day18: 12. ***: P<0.001. Unpaired student t test.
Figure 4. see also Figure S5, S6: The steady state level of UNC-104 protein decreases with age.
(A–C) Confocal images of UNC-104::mCherry in the dorsal and ventral nerve cord, which are labeled with myrGFP (D-F), in young (A, D) and aged (B, E, C, F) worms. (G–H) Quantification of myrGFP and UNC-104::mCherry fluorescence in young and old animals. The steady state level of UNC-104::mcherry is specifically decreased in the dorsal nerve cord in aged animals. ***: P<0.001. Unpaired student t test. Total animals analyzed: day1: 12, day 12: 14,day 18: 17.
To further understand the effects of aging on UNC-104 mediated SV transport, we next examined the dynamics of SV movement in DA9 neuron in aged animals. Compared with day 1 adults, day 8 and day 12 wild type adults displayed slower anterograde trafficking speed of synaptic vesicle markers (Figures S6A, D and E). In UNC-104 overexpressing animals, this age-dependent decline is absent suggesting that the dosage of UNC-104 in aging animals might be responsible for the reduction of transport speed. Consistent with previous findings [25], although unc-104(wy711) mutants do not have obvious SV distribution defects at day 1, the speed of anterograde trafficking is already severely reduced (Figures S6 B, D, E). Although the speed defect of unc-104(wy711) is not exacerbated by age, the total anterograde moving events are reduced by day 12, which may contribute to the exacerbation of synapse abnormalities in wy711 mutants with age. (Figures S6F). These results further suggest that UNC-104 activity is gradually decreased over age, which leads to defective SV trafficking over time and eventually causes synaptic dysfunction.
UNC-104 regulates the age-related decline of learning and memory
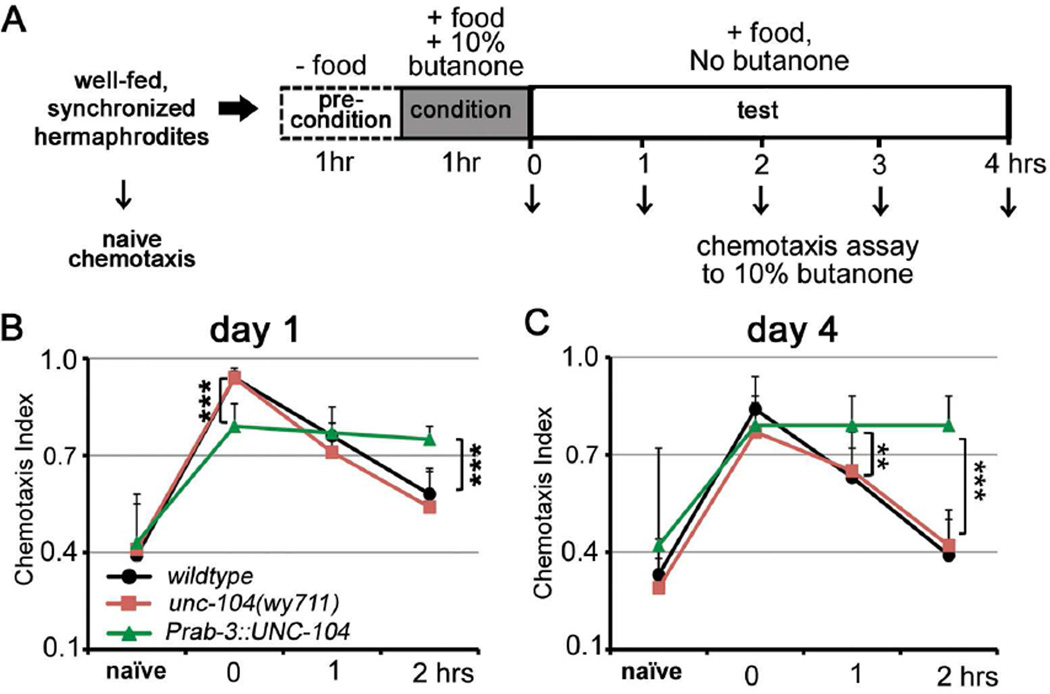
To understand whether the effects of UNC-104 in neuronal aging extend to other neural circuits in addition to motor circuits, we next assessed learning and memory behaviors of unc-104(wy711) mutant and over-expression animals at different ages (Figure 5A). We previously found that similar to Drosophila, mice, and other higher organisms[3], C. elegans’ associative learning and memory also decline with age; this happens at a much faster rate than many other types of aging-associated neuronal dysfunctions[34, 35]. For example, unlike chemotaxis (Figures 5B–C naïve) and motility behaviors, which remain intact during the first 7 days of adulthood, long-term associative memory (16 hr) declines as early as day 4 in wild-type animals[34]. Short-term memory (2 hr) becomes defective with age as well [34]. Because short-term memory requires translation[36] (likely at the synapse) rather than CREB-dependent transcription as in long-term memory[34, 36], we explored the impact of UNC-104 dosage on short-term memory and its maintenance with age by examining day 1 and day 4 animals when short-term memory of wild-type animals have not severely deteriorated.
Figure 5. Effects of UNC-104 dosage alterations in learning and memory.
(A) Schematic of the experimental procedure of learning and short-term associative memory assay. (B–C) Up-regulation of UNC-104 improves short-term memory in both day 1 (B) and day 4 (C) animals. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA. Total replicates: day1: 15 (wildtype), 15 (unc-104(wy711)), 15 (Prab-3::unc-104); day 4: 15 (wildtype), 15 (unc-104(wy711)), 15 (Prab-3::unc-104).
UNC-104 alterations did not affect the naïve (untrained) chemotaxis behaviors of day 1 or day 4 adults (Figures 5B–C naïve), suggesting that the primary functions of sensory and interneurons involved in this behavior are not affected. While reduced function of unc-104 did not affect learning or memory, we found that over-expression of UNC-104 significantly improved short-term memory, in both young and older animals. On day 1, over-expression of unc-104 caused a slight defect in learning (Figure 5B, 0hr), which may be caused by excessive expression of unc-104. However, it significantly increased short-term memory: the animals exhibited no decline in chemotaxis by 2 hrs post-training (Figure 5B, 2hrs). Overexpression of UNC-104 dramatically improved maintenance of short-term memory on day 4, showing no decline at either one or two hrs post-training (Figure 5C). These results suggest that similar to UNC-104’s role in maintenance of motor function, upregulation of UNC-104 alone is sufficient to improve the short-term memory of both young and aging animals.
UNC-104 functions downstream of DAF-2 in regulation of motility decline, longevity, and short-term memory
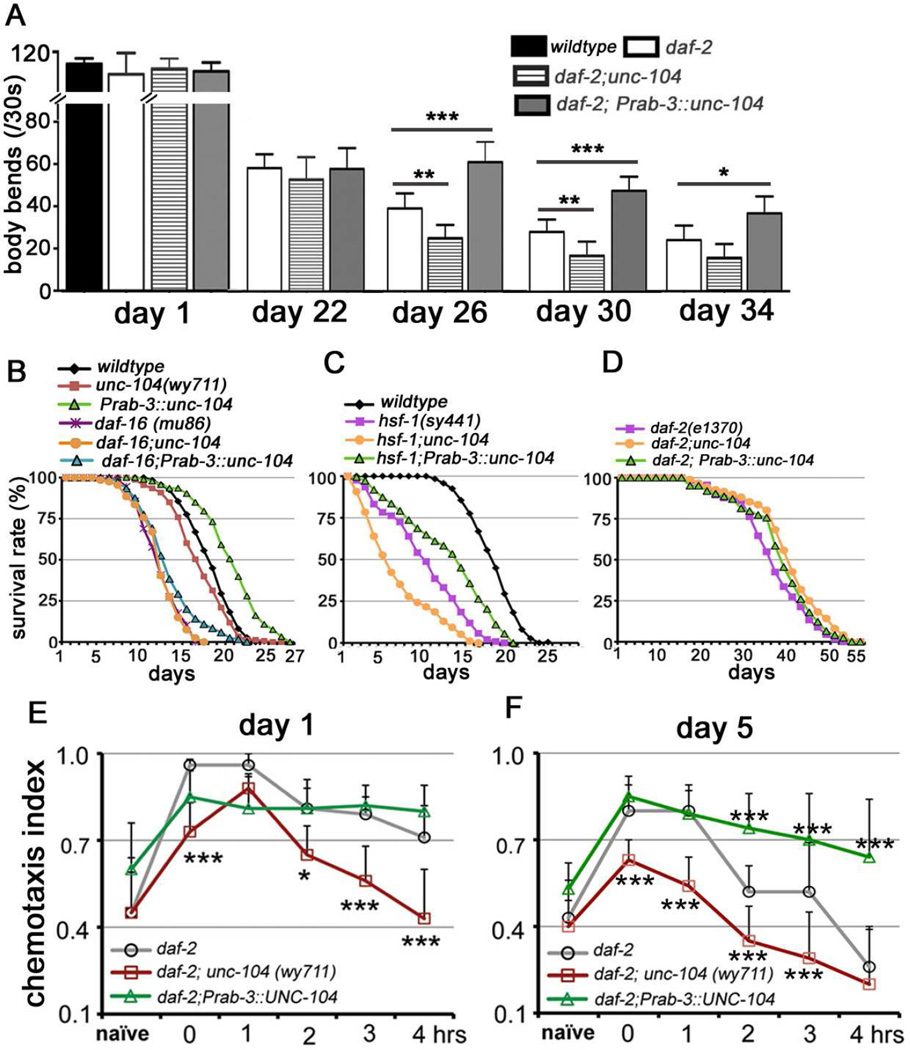
We next investigated the interactions of UNC-104 with other aging-regulatory pathways. daf-2/insulin-IGF-1 like receptor mutants reduce insulin signaling, subsequently extending lifespan[37] and improving maintenance with age, including slowing age-associated motility decay[37–39]. Although unc-104 alterations did not affect the locomotory behaviors of daf-2 up to 22 days, changes in unc-104 dosage did modulate motor activities of daf-2 at later ages (day 26–34) (Figure 6A): reduction of unc-104 reduced motility of aged daf-2 mutants, while over-expression of unc-104 in daf-2 mutants improved motility. Thus the dosage effect of unc-104 is extended to old animals in the long-lived daf-2 mutants.
Figure 6. see also Table S1: unc-104 is regulated by daf-16 and modulates the aging-associated motility decline of daf-2, longevity, and short-term memory.
(A) Alterations of unc-104 do not affect the body-bend behaviors of daf-2 in early-mid ages, but regulate the further motility decline in mid-late stages. Total animals analyzed: day1: 6 (daf-2), 7 (daf-2;unc-104), 8 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); day 22: 7 (daf-2), 11 (daf-2;unc-104), 7 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); day26: 18 (daf-2), 18 (daf-2;unc-104), 16 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); day 30: 21 (daf-2), 15 (daf-2;unc-104), 19 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); day 30: 21 (daf-2), 15 (daf-2;unc-104), 19 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); day 34: 20 (daf-2), 20 (daf-2;unc-104), 11 (daf-2; Ex[Prab-3::unc-104]); *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA. The error bars stand for 95% confidence intervals (CI). (B–D) Lifespan analyses. (B) Upregulation of unc-104 in the nervous system causes medium extension of the lifespan of wild-type worms, which is abolished in daf-16 mutants. Total animals analyzed: wildtype: 187, unc-104(wy711): 153, Prab-3::unc-104: 93, daf-16(mu86): 254, daf-16;unc-104: 200, daf-16;Prab-3::unc-104: 109. (C) Alterations of unc-104 still modify the shortened lifespan phenotypes of hsf-1. Total animals analyzed: hsf-1(sy441): 244, hsf-1;unc-104: 194, hsf-1; Prab-3::unc-104: 182. (D) Alterations of unc-104 have subtle effects on the long lifespan phenotypes of daf-2 mutants. Total animals analyzed: daf-2(1370): 113, daf-2;unc-104: 176, daf-2; Prab-3::unc-104: 123. Log-rank analysis. (E-F) UNC-104 is required for the effects of DAF-2 in the maintenance of short-term memory in both day 1 (E) and day 5 (F) animals. Up-regulation of UNC-104 improves the short-term memory of daf-2 animals at d5 (F). Total replicates: day 1: daf-2(1370): 8, daf-2;unc-104: 8, daf-2; Prab-3::unc-104: 8; day 5: daf-2(1370): 12, daf-2;unc-104: 12, daf-2; Prab-3::unc-104: 12.*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. One-way ANOVA.
We also examined the effects of UNC-104 on longevity. In contrast to their dramatic effects on age-associated motility decline, unc-104 partial loss-of-function alleles (wy711 or e1265/+) only had subtle effects on lifespan (Figure 6B and Table S1). By contrast, upregulation of unc-104 in the wild-type background caused a significant increase in lifespan, suggesting that maintenance of neuronal function during aging promotes longevity. The lifespan extension phenotype of UNC-104 upregulation is abolished in daf-16 mutants (Figure 6B and Table S1), but is maintained in hsf-1 mutants (Figure 6C). In addition, reduced function of unc-104 did not affect the lifespan of daf-16, but strongly enhanced the short lifespan phenotype of hsf-1 mutant (Figures 6C, D, Table S1). Together, these results suggest that unc-104 functions in the same pathway as daf-16 in regulation of lifespan, but independent of hsf-1. Moreover, in a daf-2 mutant that is already long-lived, over-expression of unc-104 only had a subtle beneficial effect on the median lifespan (Figure 6D and Table S1). Together, these results suggested that unc-104 is an important neuronal target of the insulin signaling pathway in the regulation of aging-associated neuronal dysfunction, and contributes to longevity as well. Furthermore, while lifespan and tissue functions are correlated, they can be distinct and separable phenotypes during the aging process.
We next examined the potential interactions between UNC-104 and DAF-2 in the regulation of learning and memory. daf-2 mutants extend short-term memory three-fold in day 1 animals[34], and slow age-related decline in short-term memory[34]. Interestingly, we found that UNC-104 is required both for daf-2 mutants’ improvement in learning and shortterm memory on both day 1 and day 5 (Figures 6E, F). These results are consistent with the hypothesis that UNC-104 functions downstream of DAF-2 to generate beneficial effects on short-term memory in aged animals (Figure 6F, 1 hr). At the same time, we found that unexpectedly, unc-104 is also required for normal learning and memory behaviors of day 1 daf-2 animals. It raised the possibility that reduced UNC-104 motor activity causes detrimental effects on learning behavior. Remarkably, over-expression of unc-104 extends short-term memory to more than 4 hours even in day 5 animals, suggesting that the decline of short-term memory of daf-2 animals in young and older animals may be due to reduction of UNC-104 function. Thus, UNC-104 functions as a neural target that at least partially mediates the protective effects of DAF-2 in the nervous system.
UNC-104 mRNA and protein is maintained in daf-2 mutants with age
The above results, together with a recent study showing that daf-2 ameliorates motor circuit function decline by affecting presynaptic transmission [15], raise the possibility that unc-104 functions downstream of DAF-2 in the regulation of presynaptic transmission during aging. Consistent with this hypothesis, we found that the steady state level of unc-104 mRNA is increased in daf-2 mutants, and to a much less degree in eat-2 mutants, which regulate longevity through calorie-restriction (Figure 7A). To further understand the downstream pathways that regulate UNC-104, we next examined the effects of several transcription factors that function downstream of daf-2, including the FOXO transcription factor DAF-16 [21, 40, 41], heat shock factor HSF-1 [42], and oxidative stress response factor SKN-1/NRF [13, 43]. We found that daf-16;daf-2 double mutants showed a significant decrease of unc-104 mRNA levels compared to daf-2 mutants at day1 suggesting that DAF-16 mediates the effects of daf-2 on unc-104 transcription. To examine whether other transcription factors also regulate unc-104 expression, we analyzed the unc-104 mRNA levels in triple mutants daf-16; skn-1; daf-2 and daf-16; hsf-1; daf-2. However, these triple mutants showed similar UNC-104 mRNA levels compared to daf-16;daf-2 double mutants (Figure 7A). We also found that unc-104 mRNA levels remain higher in daf-2 animals than in wildtype with age (day 5 and day 12), and this effect is abolished in daf-16;daf-2 mutants. Together, these results suggest that daf-2 regulates the transcription of unc-104 primarily through daf-16 in aged animals.
To further understand the mechanism by which daf-2 affects UNC-104 with age, we next examined the level and localization of UNC-104 protein in aged daf-2 animals using unc-104::mcherry as a readout. We found that the age-dependent decrease of UNC-104::mcherry in DNC is less dramatic in daf-2 mutants (days 12, 18) compared to wild-type animals (Figures 7B–D H,), whereas the control fluorescence signal of myrGFP in either DNC or VNC is not changed in daf-2 mutants with age (Figures 7E–G, I). Furthermore, consistent with the observation that UNC-104 is naturally upregulated in daf-2 mutants, we found that the distribution of DA9 synapses was maintained in aged (day 18 and day30) daf-2 animals (Figure S7). These results suggest that UNC-104 activity is maintained better in aged daf-2 mutants, which may contribute to improved motility of daf-2 animals at later ages.
Discussion
Aging neurons become more susceptible to UNC-104 dosage alterations
In this study, we discovered an unconventional role of the neuronal kinesin UNC-104/KIF1A as a key regulator of aging-associated neural circuit decline in C. elegans. The UNC-104/KIF1A family of kinesins specifically transports both SV precursors and active zone proteins, the essential components for the presynaptic specialization[44–46]. Since slight reduction of UNC-104 does not affect synapse development, but exacerbates aging-associated synapse defects at older ages, neurons may become more susceptible to UNC-104 dosage alterations with age. Aging-related reduction of UNC-104 activity could be due to a reduction of neural expression of UNC-104, a change of UNC-104 localization, or decreased UNC-104 activation. Since the steady-state level of unc-104 mRNA is not affected during aging at the whole organism level, aging may affect UNC-104 localization and/or activation. Consistent with the latter possibility, we found that the level of UNC-104mcherry is specifically decreased in the axon-rich DNC in aged animals, but not VNC. These results suggest that the aging process is likely to affect the motor activity of UNC-104 and prevent its localization in the axons, thereby resulting in higher vulnerability of aged neural circuits. Consistent with this hypothesis, kymograph analyses of SV trafficking of aged animals revealed that the speed of anterograde trafficking, the percentage of anterograde events, and the total number of anterograde movements, are decreased during aging, further suggesting a decrease of the motor activity. In addition, a recent study found that the synaptosome component phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), is substantially reduced in hippocampal synaptic membranes in old mice, contributing to the reduced cognition[14]. Interestingly, the binding between SV PI(4,5)P2 to the PH domain of UNC-104 is required to activate the motor and initiate the vesicle transport [47]. Thus the UNC-104 protein activity may also be decreased in aged animals because of altered lipid metabolism on synaptic vesicle cargoes.
UNC-104 slows down the age-dependent deterioration of neural circuit function, and is required for the protective effects of DAF-2
Remarkably, increasing the dosage of unc-104 can significantly slow aging-associated synapse dysfunction, as well as motility decline and the loss of short-term memory. These results suggest that UNC-104 is one of the critical rate-limiting factors for synaptic aging. It is possible that upregulation of UNC-104 preserves synapse function by promoting the transport of SV precursors and active zone proteins during aging. Interestingly, we also found that UNC-104 over-expressing animals behave similarly to daf-2 mutants in the maintenance of short-term memory and motility, and that UNC-104 is required for the protective effects of DAF-2 in these behavioral tests. In addition, aged daf-2 mutants have higher levels of unc-104 mRNA and UNC-104 protein in motor neuron axons than the wild-type animals, suggesting that UNC-104 protein is maintained at both the mRNA and protein levels in aged daf-2 mutants. These results raise the possibility that UNC-104 functions downstream of the DAF-2 signaling pathway in mediating the beneficial effects in aging neurons, although other cellular factors are likely to contribute daf-2 effects as well, since unc-104 manipulation did not show an effect until 26 days in daf-2 mutants.
Consistent with this hypothesis, UNC-104 mRNA is up-regulated in daf-2 mutants, which is partially suppressed by loss-of-function of the FOXO transcription factor daf-16 in day 1 animals and completely abolished by a daf-16 mutation in day 5 and day 12 animals. These results suggest that unc-104 is specifically regulated by DAF-16 at the transcriptional level during aging. Sequence analyses of the unc-104 promoter region identified two potential DAF-16 binding sites: TTGTTTAC[48] and GTAAATA[49], at positions of −1420 b.p. and −3835 b.p., respectively, raising the possibility that UNC-104 might be a direct target of DAF-16. However, genome-wide chromatin profiling (modENCODE database)[50] did not report DAF-16 binding directly to these regions. Thus, whether UNC-104 is directly regulated by DAF-16 needs to be studied further.
In addition to transcriptional regulation, more UNC-104 protein accumulates in distal axon in aging daf-2 mutants, suggesting that DAF-2-dependent mechanisms might be also required to stimulate the activity of UNC-104 in aging animals. Surprisingly, upregulation of unc-104 in the neurons alone can increase lifespan, suggesting that maintenance of neuronal functions significantly promotes longevity. Together, these findings identify a novel regulator in aging-associated motor circuit dysfunction, and highlight the importance of axonal transport in age-related behavioral changes, as well as longevity.
Experimental Procedures
Worms were raised on NGM plates at 20°C, using OP50 E.coli as a food source. N2 Bristol was used as the wild-type reference strain. The mutant strains CB1265 unc-104(e1265), CB1370 daf-2(e1370), syd-2(ju37), unc-10(e102), nab-1(ok943), unc-57(ok310),unc-11(e47),dsh-1(ok1445),lin-44(n1792), daf-16(mu86), hsf-1(sy441), skn-1(zu67)/nT1[unc-(n754)let-](IV;V), daf-2(e1370), were obtained through the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center. The wy711 mutant was described as previously[25].
For aging experiments, worms were transferred every 2–3 days to fresh NGM plates to separate the adults from the larvae. Transgenic constructs were cloned into the pSM vector, a derivative of pPD49.26 (A.Fire) with extra cloning sites. The transgenic strains were generated using standard techniques.
Images of fluorescently tagged fusion proteins were captured in live C. elegans using a plan-Apochromat 40× 1.3 objective on a Zeiss LSM710 confocal microscope, using identical image and laser setting for each genotype. The electrophysiology recordings were performed as previously described [15].
The details of the above and other experiments are included in the Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Aging neurons exhibit decreased activity of UNC-104/KIF1A, a neuronal kinesin.
UNC-104 plays a critical role in synaptic and behavioral decline in aged worms.
UNC-104 functions downstream of DAF-2 and is regulated by DAF-16.
Acknowledgments
We thank the international Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) for strains. We also thank C. Gao for technical assistance. This work is supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and the National Institute of Health (K.S.), and by the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) (LB. L). RNA is supported by an NRSA, and CTM is the Director of the Glenn Center for Aging Research at Princeton.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Author Contribution
Conceptualization, L.B.L. X.Z.X, C.T.M., and K.S.; Methodology, L.B.L, X.Z.X, C.T.M., and K.S.; Investigation, L.B.L,, H.L., R.N.A., and P.L.; Writing - Original Draft, L.B.L. and K.S.; Writing - Review & Editing, L.B.L., X.Z.X., C.T.M., and K.S.; Funding Acquisition, L.B.L. X.Z.X, C.T.M., and K.S.; Resources, X.Z.X., C.T.M., and K.S.; Supervision, J.Liu, X.Z.X., C.T.M., and K.S.
References
- 1.Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464:504–512. doi: 10.1038/nature08980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lopez-Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153:1194–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bishop NA, Lu T, Yankner BA. Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline. Nature. 2010;464:529–535. doi: 10.1038/nature08983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Morrison JH, Baxter MG. The ageing cortical synapse: hallmarks and implications for cognitive decline. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:240–250. doi: 10.1038/nrn3200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pan CL, Peng CY, Chen CH, McIntire S. Genetic analysis of age-dependent defects of the Caenorhabditis elegans touch receptor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:9274–9279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011711108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tank EM, Rodgers KE, Kenyon C. Spontaneous age-related neurite branching in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci. 2011;31:9279–9288. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6606-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Toth ML, Melentijevic I, Shah L, Bhatia A, Lu K, Talwar A, Naji H, Ibanez-Ventoso C, Ghose P, Jevince A, et al. Neurite sprouting and synapse deterioration in the aging Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system. J Neurosci. 2012;32:8778–8790. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1494-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Valdez G, Tapia JC, Kang H, Clemenson GD, Jr, Gage FH, Lichtman JW, Sanes JR. Attenuation of age-related changes in mouse neuromuscular synapses by caloric restriction and exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:14863–14868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002220107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Peters A, Sethares C, Luebke JI. Synapses are lost during aging in the primate prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. 2008;152:970–981. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dumitriu D, Hao J, Hara Y, Kaufmann J, Janssen WG, Lou W, Rapp PR, Morrison JH. Selective changes in thin spine density and morphology in monkey prefrontal cortex correlate with aging-related cognitive impairment. J Neurosci. 2010;30:7507–7515. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6410-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bories C, Husson Z, Guitton MJ, De Koninck Y. Differential balance of prefrontal synaptic activity in successful versus unsuccessful cognitive aging. J Neurosci. 2013;33:1344–1356. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3258-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Samuel MA, Voinescu PE, Lilley BN, de Cabo R, Foretz M, Viollet B, Pawlyk B, Sandberg MA, Vavvas DG, Sanes JR. LKB1 and AMPK regulate synaptic remodeling in old age. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:1190–1197. doi: 10.1038/nn.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lu T, Pan Y, Kao SY, Li C, Kohane I, Chan J, Yankner BA. Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature. 2004;429:883–891. doi: 10.1038/nature02661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Trovo L, Ahmed T, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Buzzi A, Bagni C, Chuah M, Vandendriessche T, D'Hooge R, Balschun D, Dotti CG. Low hippocampal PI(4,5)P(2) contributes to reduced cognition in old mice as a result of loss of MARCKS. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16:449–455. doi: 10.1038/nn.3342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu J, Zhang B, Lei H, Feng Z, Hsu AL, Xu XZ. Functional aging in the nervous system contributes to age-dependent motor activity decline in C. elegans. Cell Metab. 2013;18:392–402. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Falzone TL, Gunawardena S, McCleary D, Reis GF, Goldstein LS. Kinesin-1 transport reductions enhance human tau hyperphosphorylation, aggregation and neurodegeneration in animal models of tauopathies. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:4399–4408. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stokin GB, Lillo C, Falzone TL, Brusch RG, Rockenstein E, Mount SL, Raman R, Davies P, Masliah E, Williams DS, et al. Axonopathy and transport deficits early in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 2005;307:1282–1288. doi: 10.1126/science.1105681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Taylor RC, Dillin A. XBP-1 is a cell-nonautonomous regulator of stress resistance and longevity. Cell. 2013;153:1435–1447. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Williams KW, Liu T, Kong X, Fukuda M, Deng Y, Berglund ED, Deng Z, Gao Y, Sohn JW, Jia L, et al. Xbp1s in Pomc neurons connects ER stress with energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2014;20:471–482. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wolkow CA, Kimura KD, Lee MS, Ruvkun G. Regulation of C. elegans life-span by insulinlike signaling in the nervous system. Science. 2000;290:147–150. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5489.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dillin A, Hsu AL, Arantes-Oliveira N, Lehrer-Graiwer J, Hsin H, Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Ahringer J, Kenyon C. Rates of behavior and aging specified by mitochondrial function during development. Science. 2002;298:2398–2401. doi: 10.1126/science.1077780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Herndon LA, Schmeissner PJ, Dudaronek JM, Brown PA, Listner KM, Sakano Y, Paupard MC, Hall DH, Driscoll M. Stochastic and genetic factors influence tissue-specific decline in ageing C. elegans. Nature. 2002;419:808–814. doi: 10.1038/nature01135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hsu AL, Feng Z, Hsieh MY, Xu XZ. Identification by machine vision of the rate of motor activity decline as a lifespan predictor in C. elegans. Neurobiol Aging. 2009;30:1498–1503. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Klassen MP, Shen K. Wnt signaling positions neuromuscular connectivity by inhibiting synapse formation in C. elegans. Cell. 2007;130:704–716. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wu YE, Huo L, Maeder CI, Feng W, Shen K. The balance between capture and dissociation of presynaptic proteins controls the spatial distribution of synapses. Neuron. 2013;78:994–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhen M, Jin Y. The liprin protein SYD-2 regulates the differentiation of presynaptic termini in C. elegans. Nature. 1999;401:371–375. doi: 10.1038/43886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sieburth D, Ch'ng Q, Dybbs M, Tavazoie M, Kennedy S, Wang D, Dupuy D, Rual JF, Hill DE, Vidal M, et al. Systematic analysis of genes required for synapse structure and function. Nature. 2005;436:510–517. doi: 10.1038/nature03809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sudhof TC. The presynaptic active zone. Neuron. 2012;75:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Verstreken P, Koh TW, Schulze KL, Zhai RG, Hiesinger PR, Zhou Y, Mehta SQ, Cao Y, Roos J, Bellen HJ. Synaptojanin is recruited by endophilin to promote synaptic vesicle uncoating. Neuron. 2003;40:733–748. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00644-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schuske KR, Richmond JE, Matthies DS, Davis WS, Runz S, Rube DA, van der Bliek AM, Jorgensen EM. Endophilin is required for synaptic vesicle endocytosis by localizing synaptojanin. Neuron. 2003;40:749–762. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00667-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nonet ML, Holgado AM, Brewer F, Serpe CJ, Norbeck BA, Holleran J, Wei L, Hartwieg E, Jorgensen EM, Alfonso A. UNC-11, a Caenorhabditis elegans AP180 homologue, regulates the size and protein composition of synaptic vesicles. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:2343–2360. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schreiber MA, Pierce-Shimomura JT, Chan S, Parry D, McIntire SL. Manipulation of behavioral decline in Caenorhabditis elegans with the Rag GTPase raga-1. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ou CY, Poon VY, Maeder CI, Watanabe S, Lehrman EK, Fu AK, Park M, Fu WY, Jorgensen EM, Ip NY, et al. Two cyclin-dependent kinase pathways are essential for polarized trafficking of presynaptic components. Cell. 2010;141:846–858. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kauffman AL, Ashraf JM, Corces-Zimmerman MR, Landis JN, Murphy CT. Insulin signaling and dietary restriction differentially influence the decline of learning and memory with age. PLoS Biol. 2010;8:e1000372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lakhina V, Arey RN, Kaletsky R, Kauffman A, Stein G, Keyes W, Xu D, Murphy CT. Genome-wide functional analysis of CREB/long-term memory-dependent transcription reveals distinct basal and memory gene expression programs. Neuron. 2015;85:330–345. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stein GM, Murphy CT. C. elegans positive olfactory associative memory is a molecularly conserved behavioral paradigm. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014;115:86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kenyon C, Chang J, Gensch E, Rudner A, Tabtiang R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature. 1993;366:461–464. doi: 10.1038/366461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kappeler L, De Magalhaes Filho C, Dupont J, Leneuve P, Cervera P, Perin L, Loudes C, Blaise A, Klein R, Epelbaum J, et al. Brain IGF-1 receptors control mammalian growth and lifespan through a neuroendocrine mechanism. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Clancy DJ, Gems D, Harshman LG, Oldham S, Stocker H, Hafen E, Leevers SJ, Partridge L. Extension of life-span by loss of CHICO, a Drosophila insulin receptor substrate protein. Science. 2001;292:104–106. doi: 10.1126/science.1057991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C. daf-16: An HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1997;278:1319–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson GI, Lee L, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G. The Fork head transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature. 1997;389:994–999. doi: 10.1038/40194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hsu AL, Murphy CT, Kenyon C. Regulation of aging and age-related disease by DAF-16 and heat-shock factor. Science. 2003;300:1142–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.1083701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bishop NA, Guarente L. Two neurons mediate diet-restriction-induced longevity in C. elegans. Nature. 2007;447:545–549. doi: 10.1038/nature05904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pack-Chung E, Kurshan PT, Dickman DK, Schwarz TL. A Drosophila kinesin required for synaptic bouton formation and synaptic vesicle transport. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:980–989. doi: 10.1038/nn1936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Okada Y, Yamazaki H, Sekine-Aizawa Y, Hirokawa N. The neuron-specific kinesin superfamily protein KIF1A is a unique monomeric motor for anterograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors. Cell. 1995;81:769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90538-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hall DH, Hedgecock EM. Kinesin-related gene unc-104 is required for axonal transport of synaptic vesicles in C. elegans. Cell. 1991;65:837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90391-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Klopfenstein DR, Tomishige M, Stuurman N, Vale RD. Role of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate organization in membrane transport by the Unc104 kinesin motor. Cell. 2002;109:347–358. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00708-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Murphy CT. The search for DAF-16/FOXO transcriptional targets: approaches and discoveries. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41:910–921. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2006.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Murphy CT, McCarroll SA, Bargmann CI, Fraser A, Kamath RS, Ahringer J, Li H, Kenyon C. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2003;424:277–283. doi: 10.1038/nature01789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Celniker SE, Dillon LA, Gerstein MB, Gunsalus KC, Henikoff S, Karpen GH, Kellis M, Lai EC, Lieb JD, MacAlpine DM, et al. Unlocking the secrets of the genome. Nature. 2009;459:927–930. doi: 10.1038/459927a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.