Abstract
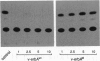
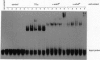
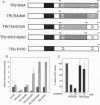
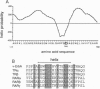
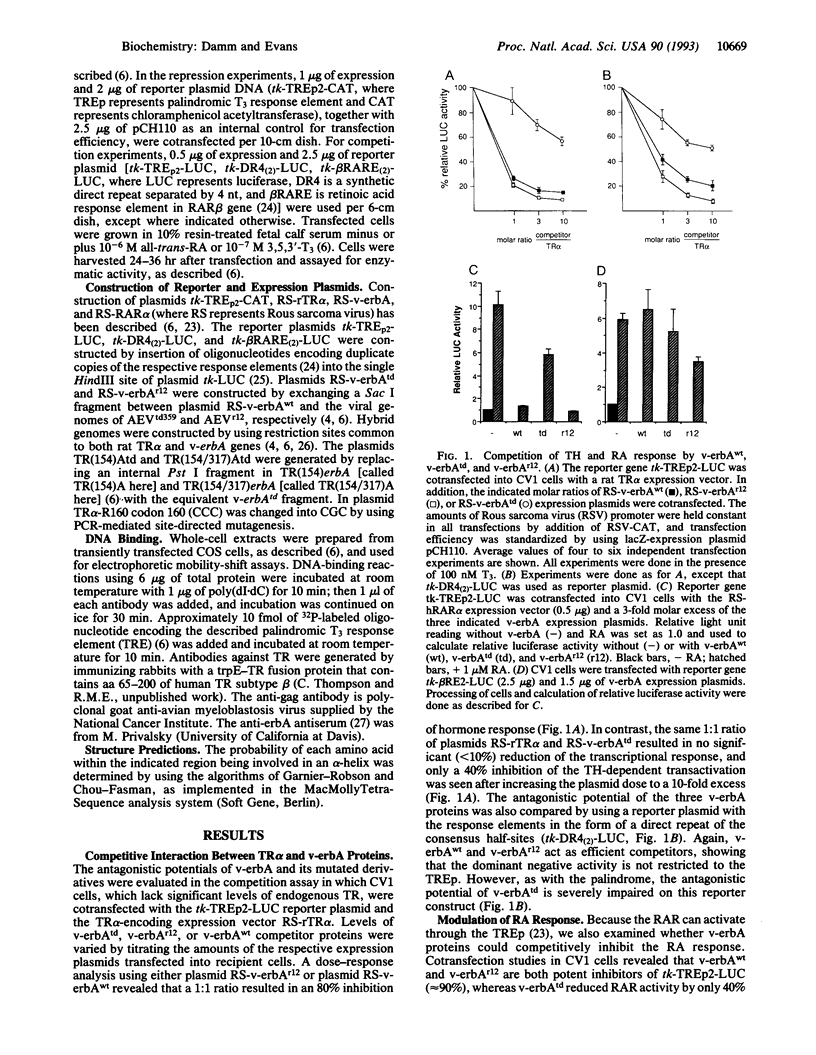
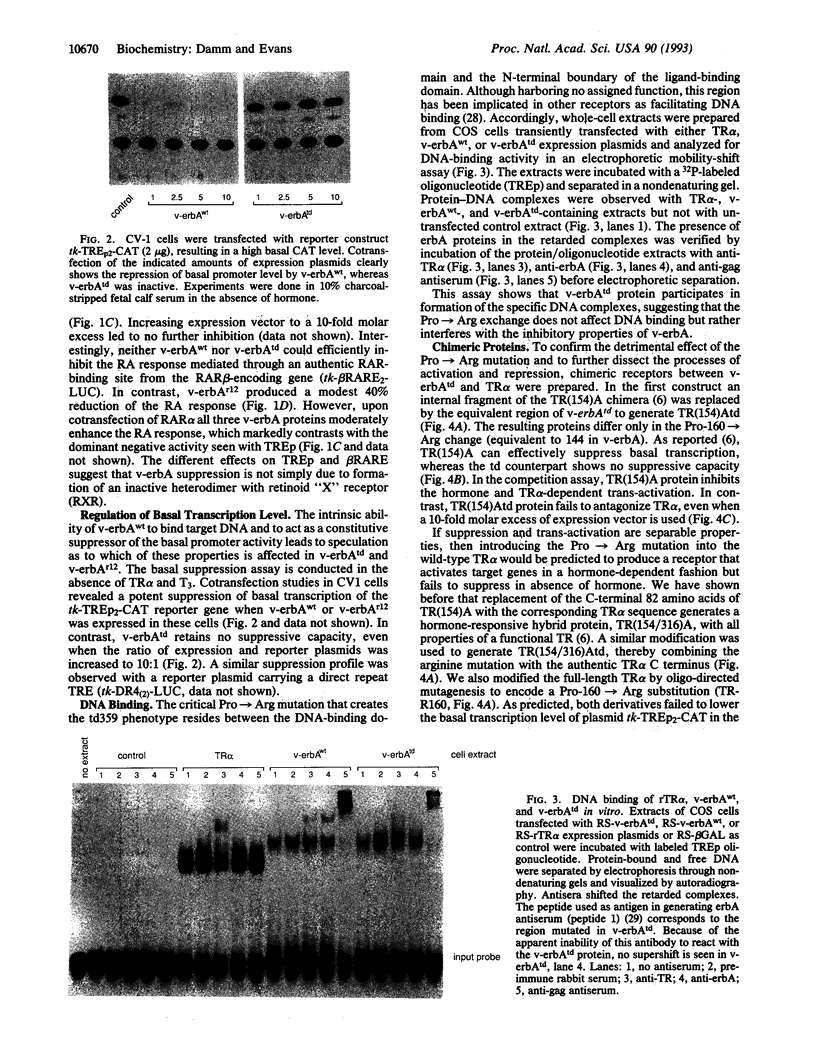
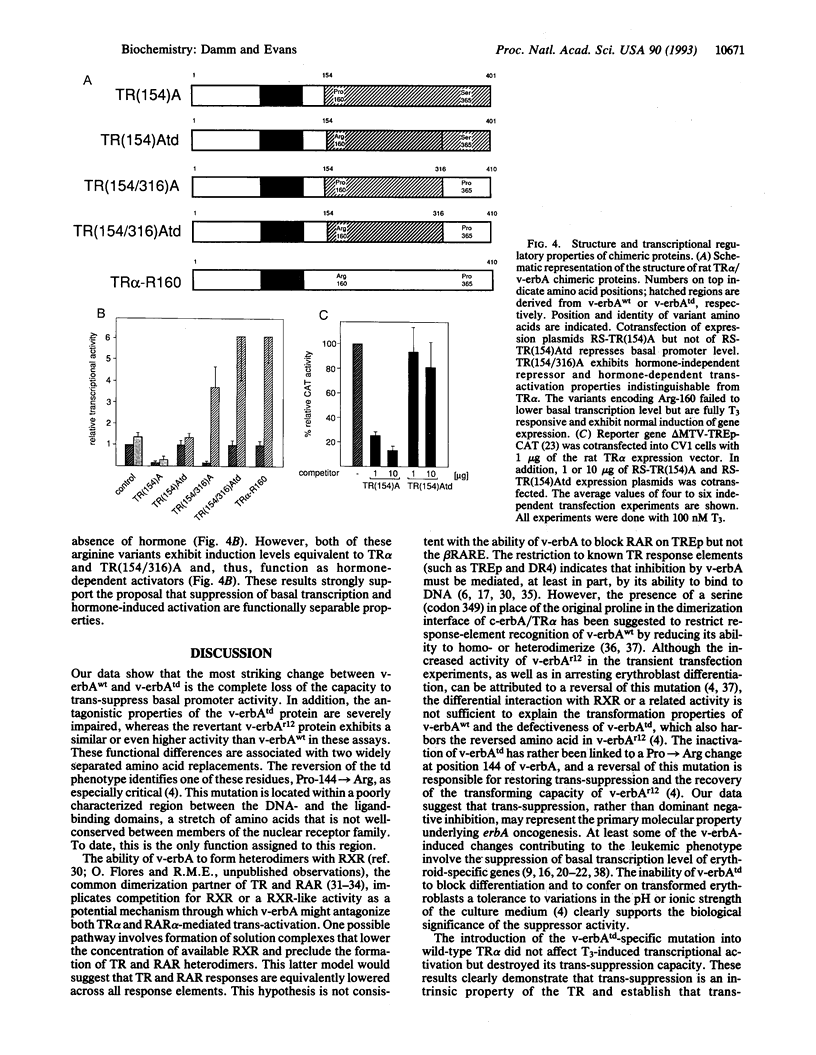
v-erbA, a mutated version of the chicken thyroid hormone (TH) receptor type alpha, can inhibit hormonal induction of target genes. In addition, v-erbA acts as a constitutive repressor of the basal promoter activity. In vivo, v-erbA can arrest the differentiation of erythroid precursor cells and suppresses transcription of erythrocyte-specific genes. We show that the v-erbA protein of the transformation-defective avian erythroblastosis virus mutant (AEVtd359) fails to suppress basal transcription level and exhibits impaired ability in antagonizing the TH and retinoic acid response. The inactivating mutation is a 1-nt change leading to a Pro-->Arg replacement in the "hinge region" of v-erbA protein. Introducing this mutation in the context of TH receptor alpha selectively inactivates the suppressor function, while hormone-binding and transcriptional-activation properties are unaffected. These data suggest that trans-repression rather than a dominant negative block of TH-receptor or retinoic acid-receptor activation may represent the primary molecular property underlying erbA oncogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baniahmad A., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. A transferable silencing domain is present in the thyroid hormone receptor, in the v-erbA oncogene product and in the retinoic acid receptor. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barettino D., Bugge T. H., Bartunek P., Vivanco Ruiz M. D., Sonntag-Buck V., Beug H., Zenke M., Stunnenberg H. G. Unliganded T3R, but not its oncogenic variant, v-erbA, suppresses RAR-dependent transactivation by titrating out RXR. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1343–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonde B. G., Privalsky M. L. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the v-erbA oncogene protein of avian erythroblastosis virus. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1314–1320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1314-1320.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher P., Koning A., Privalsky M. L. The avian erythroblastosis virus erbA oncogene encodes a DNA-binding protein exhibiting distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic subcellular localizations. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):534–544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.534-544.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher P., Privalsky M. L. Mapping of functional domains within the v-erb A oncogene protein: the remnants of the hormone binding domain play multiple, vital roles in protein action. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Beug H., Graf T., Vennström B. A single point mutation in erbA restores the erythroid transforming potential of a mutant avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) defective in both erbA and erbB oncogenes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):375–382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Heyman R. A., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Functional inhibition of retinoic acid response by dominant negative retinoic acid receptor mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disela C., Glineur C., Bugge T., Sap J., Stengl G., Dodgson J., Stunnenberg H., Beug H., Zenke M. v-erbA overexpression is required to extinguish c-erbA function in erythroid cell differentiation and regulation of the erbA target gene CAII. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2033–2047. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondell J. D., Roy A. L., Roeder R. G. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor inhibits formation of a functional preinitiation complex: implications for active repression. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Muñoz A., Raynoschek C., Vennström B., Beug H. Requirement for the C-terminal domain of the v-erbA oncogene protein for biological function and transcriptional repression. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerstenberg S., Beug H., Introna M., Khazaie K., Muñoz A., Ness S., Nordström K., Sap J., Stanley I., Zenke M. Ectopic expression of the erythrocyte band 3 anion exchange protein, using a new avian retrovirus vector. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5891–5902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5891-5902.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerstenberg S., Leitner I., Schroeder C., Schwarz H., Vennström B., Beug H. Transcriptional repression of band 3 and CAII in v-erbA transformed erythroblasts accounts for an important part of the leukaemic phenotype. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3355–3365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandrillon O., Jurdic P., Pain B., Desbois C., Madjar J. J., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., Samarut J. Expression of the v-erbA product, an altered nuclear hormone receptor, is sufficient to transform erythrocytic cells in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90408-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Role of the v-erbA and v-erbB oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus in erythroid cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann T., Hoffmann B., Piedrafita F. J., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. V-erbA requires auxiliary proteins for dominant negative activity. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily interact with TFIIB (S300-II). J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17617–17623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Active repression of transcription by the engrailed homeodomain protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1427–1433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Krasnow M. A. Differential regulation of transcription preinitiation complex assembly by activator and repressor homeo domain proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2177–2189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Zenke M., Gehring U., Sap J., Beug H., Vennström B. Characterization of the hormone-binding domain of the chicken c-erbA/thyroid hormone receptor protein. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):155–159. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. Repression of transcription mediated at a thyroid hormone response element by the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):242–244. doi: 10.1038/340242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Concentration-dependent transcriptional activation or repression by Krüppel from a single binding site. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):563–566. doi: 10.1038/353563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder C., Gibson L., Beug H. The v-erbA oncogene requires cooperation with tyrosine kinases to arrest erythroid differentiation induced by ligand-activated endogenous c-erbA and retinoic acid receptor. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder C., Raynoschek C., Fuhrmann U., Damm K., Vennström B., Beug H. The v-erb A oncogene causes repression of erythrocyte-specific genes and an immature, aberrant differentiation phenotype in normal erythroid progenitors. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1445–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmi S., Samuels H. H. Thyroid hormone receptor/and v-erbA. A single amino acid difference in the C-terminal region influences dominant negative activity and receptor dimer formation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11589–11593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Privalsky M. L. v-erbA oncogene function in neoplasia correlates with its ability to repress retinoic acid receptor action. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Weinberger C., Lebo R., Evans R. M. Identification of a novel thyroid hormone receptor expressed in the mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1610–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.3629259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Paulsen R. E., Padgett K. A., Milbrandt J. Participation of non-zinc finger residues in DNA binding by two nuclear orphan receptors. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):107–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1314418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Muñoz A., Sap J., Vennström B., Beug H. v-erbA oncogene activation entails the loss of hormone-dependent regulator activity of c-erbA. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1035–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90068-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]