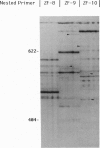
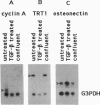
Abstract
RNA fingerprinting using arbitrarily primed PCR (RAP) samples an RNA population and allows the detection of differentially expressed genes between two or more populations. This method was applied to mink lung epithelial cells, which respond to treatment with transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) by undergoing cell cycle arrest at or near the G1/S-phase boundary. The steady-state abundances of approximately 200 RNAs were surveyed, a few of which displayed differential regulation in response to TGF-beta 1. Three products were isolated, cloned, and sequenced. One differentially regulated RNA corresponded to cyclin A, a gene known to be required for the progression of mammalian fibroblasts through S phase. Northern blot analysis confirmed that the cyclin A mRNA steady-state abundance decreased dramatically in response to a 24-hr TGF-beta 1 treatment and also in response to cell cycle arrest caused by contact inhibition. A second RAP product corresponded to a previously unknown 7.5-kb mRNA, the level of which decreased dramatically in response to TGF-beta 1 treatment. Unlike the cyclin A mRNA, the abundance of this transcript did not decrease in response to growth arrest induced by contact inhibition. A third RAP product corresponded to the mRNA for osteonectin, an extracellular matrix protein. The abundance of this mRNA increased at least 2-fold during TGF-beta 1 treatment. This observation is consistent with other reports of increases in extracellular matrix proteins during TGF-beta treatment. RAP should be able to identify many of the genes that change in steady-state expression during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen R. H., Ebner R., Derynck R. Inactivation of the type II receptor reveals two receptor pathways for the diverse TGF-beta activities. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.8388126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell-Crowley L., Solomon M. J., Wei N., Harper J. W. Phosphorylation independent activation of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by cyclin A in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):79–92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Levin A. H., Zhao S., Pardee A. B. Cyclin E and cyclin A as candidates for the restriction point protein. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1493–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stillman B. cdc2 family kinases phosphorylate a human cell DNA replication factor, RPA, and activate DNA replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2189–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini G., Clementi E., Ceci R., Marziali G., Sorrentino V. Expression of a ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ channel that is regulated by TGF-beta. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):91–94. doi: 10.1126/science.1320290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:281–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Draetta G., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibition of p34cdc2 phosphorylation and histone H1 kinase activity is associated with G1/S-phase growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1071–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionov Y., Peinado M. A., Malkhosyan S., Shibata D., Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):558–561. doi: 10.1038/363558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Ohtsuki M., Polyak K., Roberts J. M., Massagué J. Negative regulation of G1 in mammalian cells: inhibition of cyclin E-dependent kinase by TGF-beta. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):536–539. doi: 10.1126/science.8475385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., Koornneef I., de Laat S. W., van den Eijnden-van Raaij A. J. TGF-beta 1 induces phosphorylation of the cyclic AMP responsive element binding protein in ML-CCl64 cells. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1083–1089. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Kellogg D. E., McKinney N., Spasic D., Goda L., Levenson C., Sninsky J. J. Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):999–1005. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesman Y., Pagano M., Draetta G., Rotter V., Fusenig N. E., Kimchi A. Modifications of cell cycle controlling nuclear proteins by transforming growth factor beta in the HaCaT keratinocyte cell line. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1661–1665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Keyomarsi K., Sager R., Pardee A. B. Differential display and cloning of messenger RNAs from human breast cancer versus mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6966–6968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Shon J., Pipas J. M., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product undergoes cell cycle-dependent dephosphorylation and binding to and release from SV40 large T. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90590-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léopold P., O'Farrell P. H. An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marraccino R. L., Firpo E. J., Roberts J. M. Activation of the p34 CDC2 protein kinase at the start of S phase in the human cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):389–401. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Laiho M., Ralph D. A., Weis F. M., Zentella A. Transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:81–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedivi E., Hevroni D., Naot D., Israeli D., Citri Y. Numerous candidate plasticity-related genes revealed by differential cDNA cloning. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):718–722. doi: 10.1038/363718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Rodan G. A. Type beta transforming growth factor (TGF beta) regulation of alkaline phosphatase expression and other phenotype-related mRNAs in osteoblastic rat osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):426–437. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins: in search of an S-phase-promoting factor. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90279-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Tiefenbrun N., Berissi H., Kimchi A. Interferons and interleukin 6 suppress phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein in growth-sensitive hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):402–406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala A., Calabretta B. Regulation of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblast proliferation by B-myb is accompanied by selective activation of cdc2 and cyclin D1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10415–10419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Chada K., Dalal S. S., Cheng R., Ralph D., McClelland M. Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):4965–4970. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.4965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentella A., Weis F. M., Ralph D. A., Laiho M., Massagué J. Early gene responses to transforming growth factor-beta in cells lacking growth-suppressive RB function. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4952–4958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]