Abstract
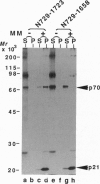
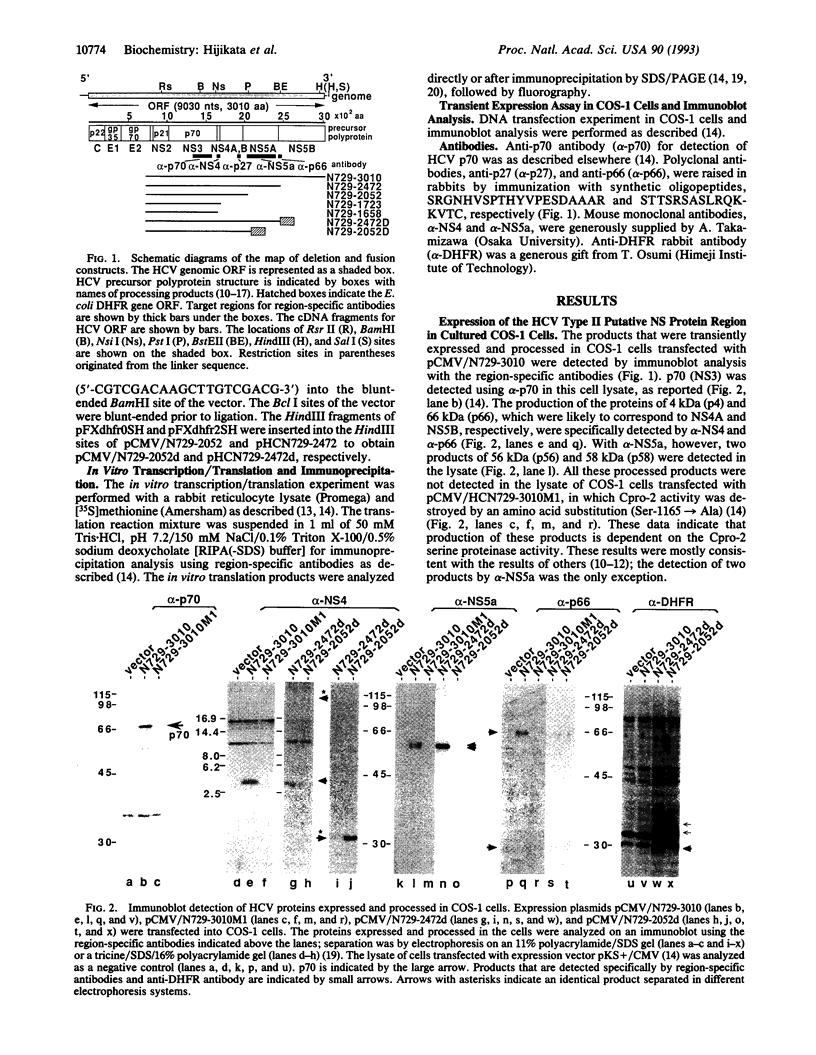
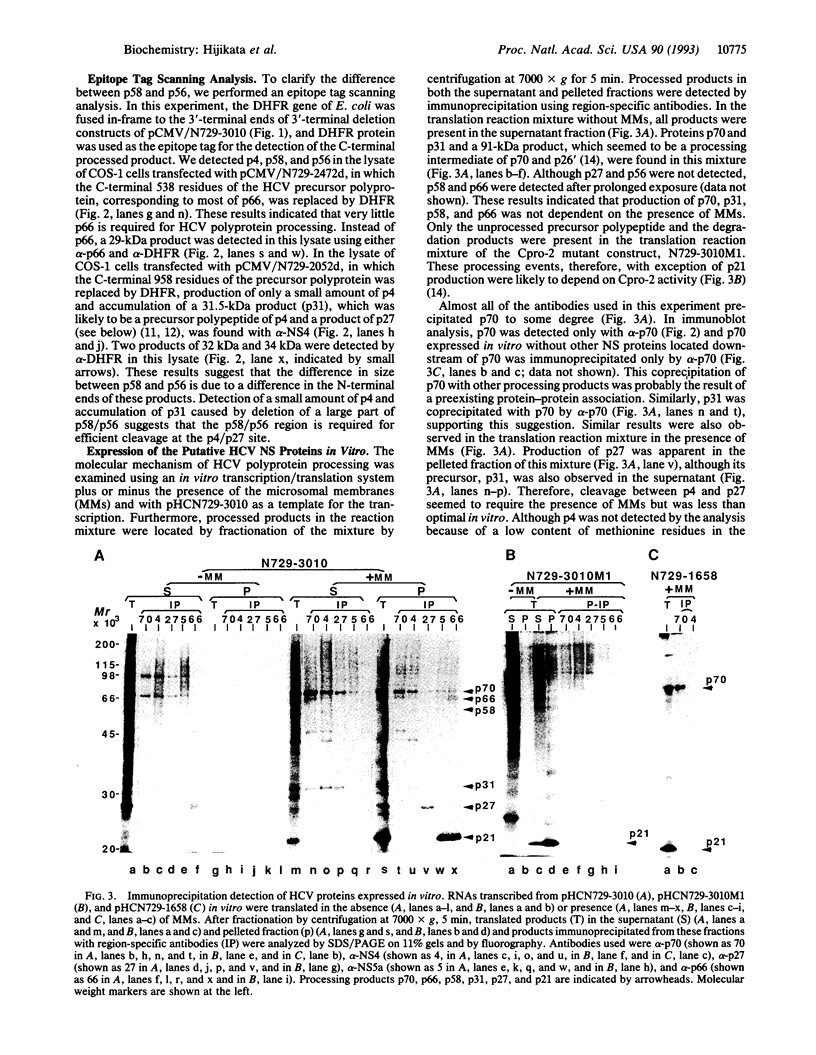
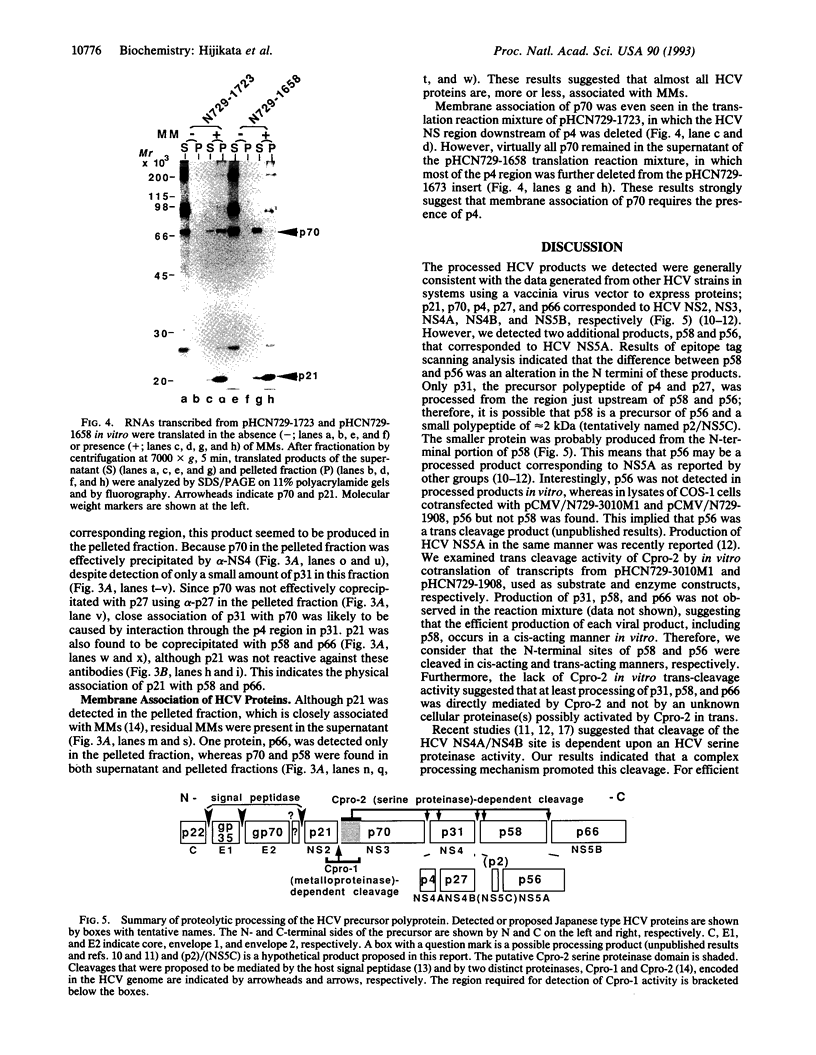
By using a plasmid-based transient protein expression system in cultured cells and an in vitro transcription/translation system, we analyzed the proteolytic processing of the putative nonstructural protein region of the precursor polyprotein from a Japanese type of hepatitis C virus. In addition to the previously reported viral proteins, p21 and p70, we identified products of 4 kDa (p4), 27 kDa (p27), 56 kDa (p56), 58 kDa (p58), and 66 kDa (p66). These products were produced in a viral serine proteinase (proteinase 2)-dependent manner from the region downstream of p70 in the precursor polyprotein and were arranged as NH2-p70-p4-p27-p58(p56)-p66-COOH as determined with region-specific antibodies. We showed that p56 was an N-terminally truncated form of p58, which suggested that a small polypeptide of 2 kDa (p2) was produced from the N-terminal part of p58. Cleavage between p4 and p27 was inefficient in vitro and we saw the 31-kDa precursor polypeptide (p31) accumulate. Furthermore, efficient cleavage at this site in vivo required the presence of p58/p56. Immunoprecipitation analysis in vitro also suggested the mutual interaction of those nonstructural protein products. An especially close association of p4 with p70 may contribute to association of p70 with microsomal membranes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Ahlborn-Laake L., Mous J., Jacobsen H. Nonstructural protein 3 of the hepatitis C virus encodes a serine-type proteinase required for cleavage at the NS3/4 and NS4/5 junctions. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3835–3844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3835-3844.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahour A., Falgout B., Lai C. J. Cleavage of the dengue virus polyprotein at the NS3/NS4A and NS4B/NS5 junctions is mediated by viral protease NS2B-NS3, whereas NS4A/NS4B may be processed by a cellular protease. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1535–1542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1535-1542.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Grakoui A., Rice C. M. Processing of the yellow fever virus nonstructural polyprotein: a catalytically active NS3 proteinase domain and NS2B are required for cleavages at dibasic sites. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6042–6050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6042-6050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Lin M. H., Tai K. F., Liu P. C., Lin C. J., Chen D. S. The Taiwanese hepatitis C virus genome: sequence determination and mapping the 5' termini of viral genomic and antigenomic RNA. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90739-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckart M. R., Selby M., Masiarz F., Lee C., Berger K., Crawford K., Kuo C., Kuo G., Houghton M., Choo Q. L. The hepatitis C virus encodes a serine protease involved in processing of the putative nonstructural proteins from the viral polyprotein precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):399–406. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Wychowski C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus-encoded serine proteinase: determination of proteinase-dependent polyprotein cleavage sites. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2832–2843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2832-2843.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., Wychowski C., Lin C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Expression and identification of hepatitis C virus polyprotein cleavage products. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1385–1395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1385-1395.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Kato N., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Shimotohno K. Gene mapping of the putative structural region of the hepatitis C virus genome by in vitro processing analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Kato N., Sato T., Kagami Y., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for a novel phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-responsive gene that is highly expressed in an adult T-cell leukemia cell line. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4632–4639. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4632-4639.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Mizushima H., Akagi T., Mori S., Kakiuchi N., Kato N., Tanaka T., Kimura K., Shimotohno K. Two distinct proteinase activities required for the processing of a putative nonstructural precursor protein of hepatitis C virus. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4665–4675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4665-4675.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hijikata M., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Ohkoshi S., Sugimura T., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of the human hepatitis C virus genome from Japanese patients with non-A, non-B hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Kurai K., Okada S., Yamamoto K., Lizuka H., Tanaka T., Fukuda S., Tsuda F., Mishiro S. Full-length sequence of a hepatitis C virus genome having poor homology to reported isolates: comparative study of four distinct genotypes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90762-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Kurai K., Iizuka H., Machida A., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus isolated from a human carrier: comparison with reported isolates for conserved and divergent regions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2697–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Tsukamoto T., Hata S., Yokota S., Miura S., Fujiki Y., Hijikata M., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Amino-terminal presequence of the precursor of peroxisomal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase is a cleavable signal peptide for peroxisomal targeting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92028-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Choo Q. L., Berger K., Kuo G., Glazer E., Eckart M., Lee C., Chien D., Kuo C., Houghton M. Expression, identification and subcellular localization of the proteins encoded by the hepatitis C viral genome. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):1103–1113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Eylar O. R., Silverman D. J. Dengue virus-induced modifications of host cell membranes. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1017–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1017-1026.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa A., Mori C., Fuke I., Manabe S., Murakami S., Fujita J., Onishi E., Andoh T., Yoshida I., Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1105-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kato N., Nakagawa M., Ootsuyama Y., Cho M. J., Nakazawa T., Hijikata M., Ishimura Y., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of hepatitis C virus genome from a single Japanese carrier: sequence variation within the same individual and among infected individuals. Virus Res. 1992 Apr;23(1-2):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90066-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomei L., Failla C., Santolini E., De Francesco R., La Monica N. NS3 is a serine protease required for processing of hepatitis C virus polyprotein. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4017–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4017-4026.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Mohan P. M., Padmanabhan R. Processing and localization of Dengue virus type 2 polyprotein precursor NS3-NS4A-NS4B-NS5. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7549–7554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7549-7554.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]