Abstract
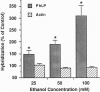
Acute and chronic exposure to ethanol produces specific changes in several signal transduction cascades. Such alterations in signaling are thought to be a crucial aspect of the central nervous system's adaptive response, which occurs with chronic exposure to ethanol. We have recently identified and isolated several genes whose expression is specifically induced by ethanol in neural cell cultures. The product of one of these genes has extensive sequence homology to phosducin, a phosphoprotein expressed in retina and pineal gland that modulates trimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) function by binding to G-protein beta gamma subunits. We identified from a rat brain cDNA library an isolate encoding the phosducin-like protein (PhLP), which has 41% identity and 65% amino acid homology to phosducin. PhLP cDNA is expressed in all tissues screened by RNA blot-hybridization analysis and shows marked evolutionary conservation on Southern hybridization. We have identified four forms of PhLP cDNA varying only in their 5' ends, probably due to alternative splicing. This 5'-end variation generates two predicted forms of PhLP protein that differ by 79 aa at the NH2 terminus. Treatment of NG108-15 cells for 24 hr with concentrations of ethanol seen in actively drinking alcoholics (25-100 mM) causes up to a 3-fold increase in PhLP mRNA levels. Induction of PhLP by ethanol could account for at least some of the widespread alterations in signal transduction and G-protein function that are known to occur with chronic exposure to ethanol.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. H., Müller S., Puzicha M., Pippig S., Obermaier B., Helmreich E. J., Lohse M. J. Phosducin is a protein kinase A-regulated G-protein regulator. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):73–76. doi: 10.1038/358073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck K. J., Harris R. A. Neuroadaptive responses to chronic ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Jun;15(3):460–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charness M. E., Querimit L. A., Henteleff M. Ethanol differentially regulates G proteins in neural cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charness M. E., Simon R. P., Greenberg D. A. Ethanol and the nervous system. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 17;321(7):442–454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908173210706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft C. M., Lolley R. N., Seldin M. F., Lee R. H. Rat pineal gland phosducin: cDNA isolation, nucleotide sequence, and chromosomal assignment in the mouse. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):400–409. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Wrubel B., Estrin W., Gordon A. Basal and adenosine receptor-stimulated levels of cAMP are reduced in lymphocytes from alcoholic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1413–1416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Mellström B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P. Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):80–84. doi: 10.1038/355080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayer G. G., Gordon A., Miles M. F. Ethanol increases tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22279–22284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Collier K., Diamond I. Ethanol regulation of adenosine receptor-stimulated cAMP levels in a clonal neural cell line: an in vitro model of cellular tolerance to ethanol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2105–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Hoek J. B. Ethanol causes desensitization of receptor-mediated phospholipase C activation in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2178–2190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Thomas A. P., Rubin R., Rubin E. Ethanol-induced mobilization of calcium by activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in intact hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):682–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. L., Tabakoff B. Ethanol and guanine nucleotide binding proteins: a selective interaction. FASEB J. 1990 Jun;4(9):2612–2622. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.9.2161371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. H., Taniura H., Watanabe Y., Fukada Y., Yoshizawa T., Miki N. Identification of a retina-specific MEKA protein as a 33 K protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90781-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Brown B. M., Lolley R. N. Protein kinase A phosphorylates retinal phosducin on serine 73 in situ. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15860–15866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Ting T. D., Lieberman B. S., Tobias D. E., Lolley R. N., Ho Y. K. Regulation of retinal cGMP cascade by phosducin in bovine rod photoreceptor cells. Interaction of phosducin and transducin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25104–25112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little H. J. The role of neuronal calcium channels in dependence on ethanol and other sedatives/hypnotics. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;50(3):347–365. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90050-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolley R. N., Craft C. M., Lee R. H. Photoreceptors of the retina and pinealocytes of the pineal gland share common components of signal transduction. Neurochem Res. 1992 Jan;17(1):81–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00966868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. F., Diaz J. E., DeGuzman V. S. Mechanisms of neuronal adaptation to ethanol. Ethanol induces Hsc70 gene transcription in NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2409–2414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. F., Diaz J. E., DeGuzman V. Ethanol-responsive gene expression in neural cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 14;1138(4):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T., Levitt M., Udenfriend S. Conversion of L-tyrosine to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine by cell-free preparations of brain and sympathetically innervated tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:543–549. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L. E., Diamond I., Gordon A. Cultured lymphocytes from alcoholic subjects have altered cAMP signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6973–6976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabe C. S., Giri P. R., Hoffman P. L., Tabakoff B. Effect of ethanol on cyclic AMP levels in intact PC12 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 1;40(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90557-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reig J. A., Yu L., Klein D. C. Pineal transduction. Adrenergic----cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of cytoplasmic 33-kDa protein (MEKA) which binds beta gamma-complex of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5816–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E., Stenstrom S., Forray C., Enloe L., Pfenning M. Effects of chronic exposure to ethanol on the prostaglandin E1 receptor-mediated response and binding in a murine neuroblastoma clone (N1E-115). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):687–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson P., Rodriguez F. D., Loman N., Alling C. G proteins coupled to phospholipase C: molecular targets of long-term ethanol exposure. J Neurochem. 1991 Jun;56(6):2018–2026. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skwish S., Shain W. Ethanol and diolein stimulate PKC translocation in astroglial cells. Life Sci. 1990;47(12):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenstrom S., Richelson E. Acute effect of ethanol on prostaglandin E1-mediated cyclic AMP formation by a murine neuroblastoma clone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 May;221(2):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Visual excitation and recovery. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10711–10714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabakoff B., Hoffman P. L., Lee J. M., Saito T., Willard B., De Leon-Jones F. Differences in platelet enzyme activity between alcoholics and nonalcoholics. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jan 21;318(3):134–139. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198801213180302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twombly D. A., Herman M. D., Kye C. H., Narahashi T. Ethanol effects on two types of voltage-activated calcium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):1029–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand G. S., Diehl A. M., Levine M. A., Wolfgang D., Samy S. Chronic ethanol treatment increases expression of inhibitory G-proteins and reduces adenylylcyclase activity in the central nervous system of two lines of ethanol-sensitive mice. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2595–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand G. S., Levine M. A. Hormonal tolerance to ethanol is associated with decreased expression of the GTP-binding protein, Gs alpha, and adenylyl cyclase activity in ethanol-treated LS mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Aug;15(4):705–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb00583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kawasaki K., Miki N., Kuo C. H. Isolation and analysis of the human MEKA gene encoding a retina-specific protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):951–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92183-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Veale M. A., Horne P., Kelly E. Ethanol differentially regulates guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha subunit expression in NG108-15 cells independently of extracellular adenosine. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;43(2):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]