Abstract
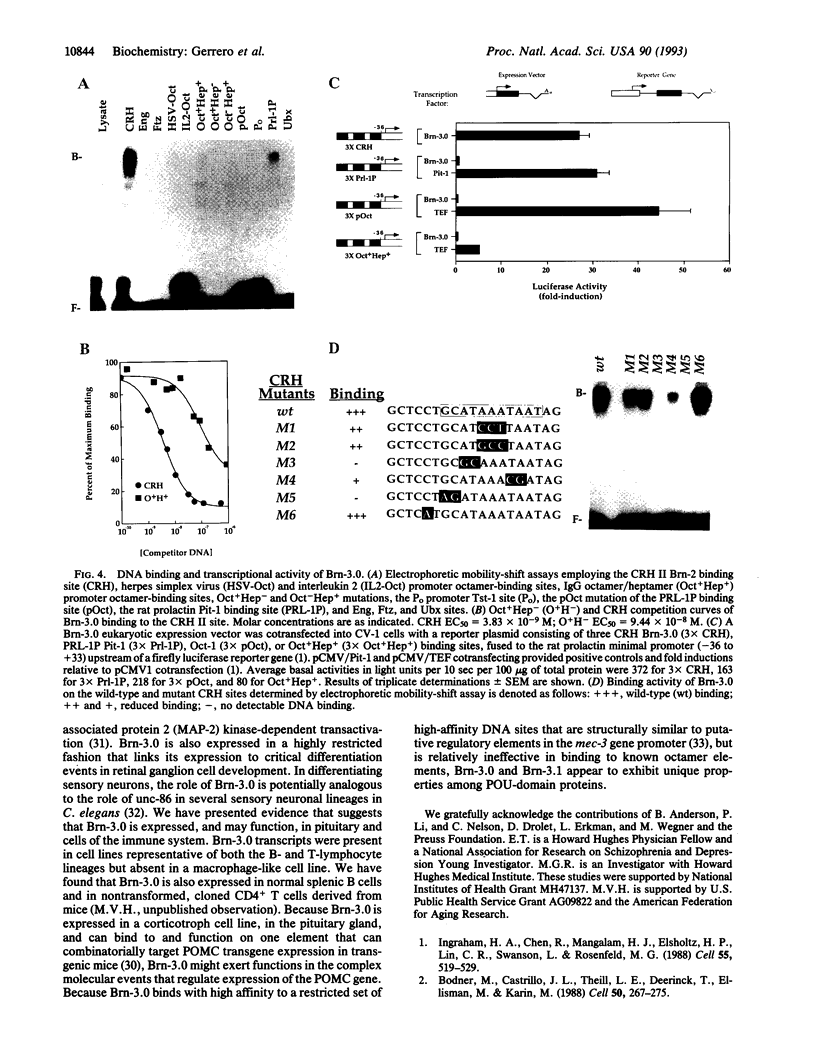
Characterization of Brn-3.0 and identification of a highly related member (Brn-3.1) of the class IV POU-domain family suggest potential roles of Brn-3.0 in the development of retinal ganglion cells and sensory neurons, as well as potential roles in the pituitary gland and the immune system. Brn-3.0 is expressed in the pituitary gland and in a corticotroph cell line. A functional DNA response element has been identified in the proopiomelanocortin promoter. In contrast to previously described mammalian POU-domain proteins, Brn-3.0 binds relatively ineffectively to known octamer DNA motifs, but instead binds with high affinity to a distinct set of DNA elements, functioning as a transcriptional activator. Brn-3.0, Brn-3.1, and the Drosophila tI-POU share an N-terminal region of homology, referred to as the "POU-IV box," which is similar to a conserved functional domain in the c-myc gene family.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B., Schonemann M. D., Flynn S. E., Pearse R. V., 2nd, Singh H., Rosenfeld M. G. Skn-1a and Skn-1i: two functionally distinct Oct-2-related factors expressed in epidermis. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.7682011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Karin M. A pituitary-specific trans-acting factor can stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter in extracts of nonexpressing cells. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G. The unc-86 gene product couples cell lineage and cell identity in C. elegans. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):895–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Rovescalli A. C., Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Structure and evolution of four POU domain genes expressed in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3280–3284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs M. V., Weigle W. O., Noonan D. J., Torbett B. E., McEvilly R. J., Koch R. J., Cardenas G. J., Ernst D. N. Patterns of cytokine gene expression by CD4+ T cells from young and old mice. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3602–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Corcoran L., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D. The promoter of the human interleukin-2 gene contains two octamer-binding sites and is partially activated by the expression of Oct-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5464–5472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. A human protein specific for the immunoglobulin octamer DNA motif contains a functional homeobox domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara T., Weidman T. A. Development of the prenatal rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;13(10):725–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine C., Young W. S., 3rd RHS2, a POU domain-containing gene, and its expression in developing and adult rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3285–3289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Hammer G. D., Rubinstein M., Mortrud M., Low M. J. Identification of DNA elements cooperatively activating proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the pituitary glands of transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3978–3990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. M., Simmons D. M., He X., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Brain 4: a novel mammalian POU domain transcription factor exhibiting restricted brain-specific expression. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2551–2561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Weinmaster G., Trapp B. D., Lemke G. Expression and activity of the POU transcription factor SCIP. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1975954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazawa H., Okamoto K., Ishino F., Ishino-Kaneko T., Takeda S., Toyoda Y., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. The oct3 gene, a gene for an embryonic transcription factor, is controlled by a retinoic acid repressible enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2997–3005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler A., Sievers J. The development of the visual system of the albino rat. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1975;50(3):3–88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Alvarez E., Gupta S., Davis R. J. A phosphorylation site located in the NH2-terminal domain of c-Myc increases transactivation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23521–23524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien M., Drouin J. Pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression requires synergistic interactions of several regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3492–3503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Seasholtz A. F., Herbert E. Rat corticotropin-releasing hormone gene: sequence and tissue-specific expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 May;1(5):363–370. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-5-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beneden R. J., Watson D. K., Chen T. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular myc (c-myc) in fish (rainbow trout): its relationship to other vertebrate myc genes and to the transforming genes of the MC29 family of viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Finney M., Ruvkun G., Chalfie M. Regulation of the mec-3 gene by the C.elegans homeoproteins UNC-86 and MEC-3. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4969–4979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]