Abstract
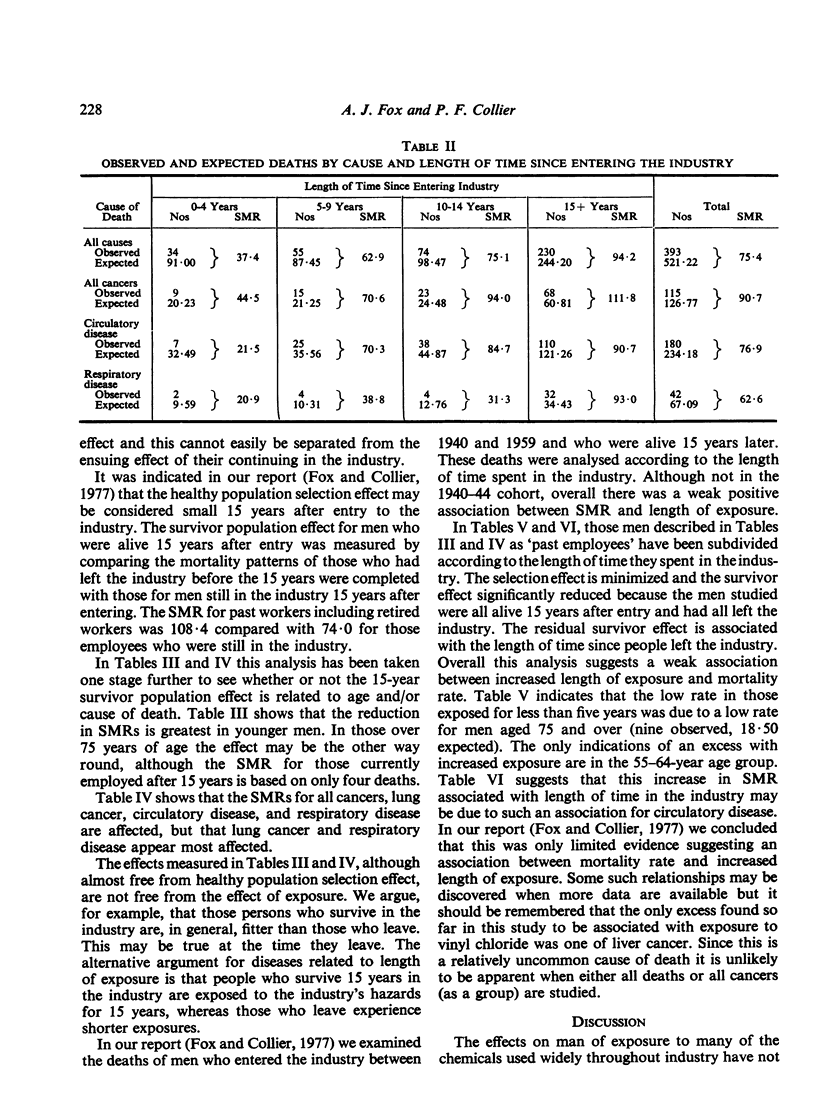
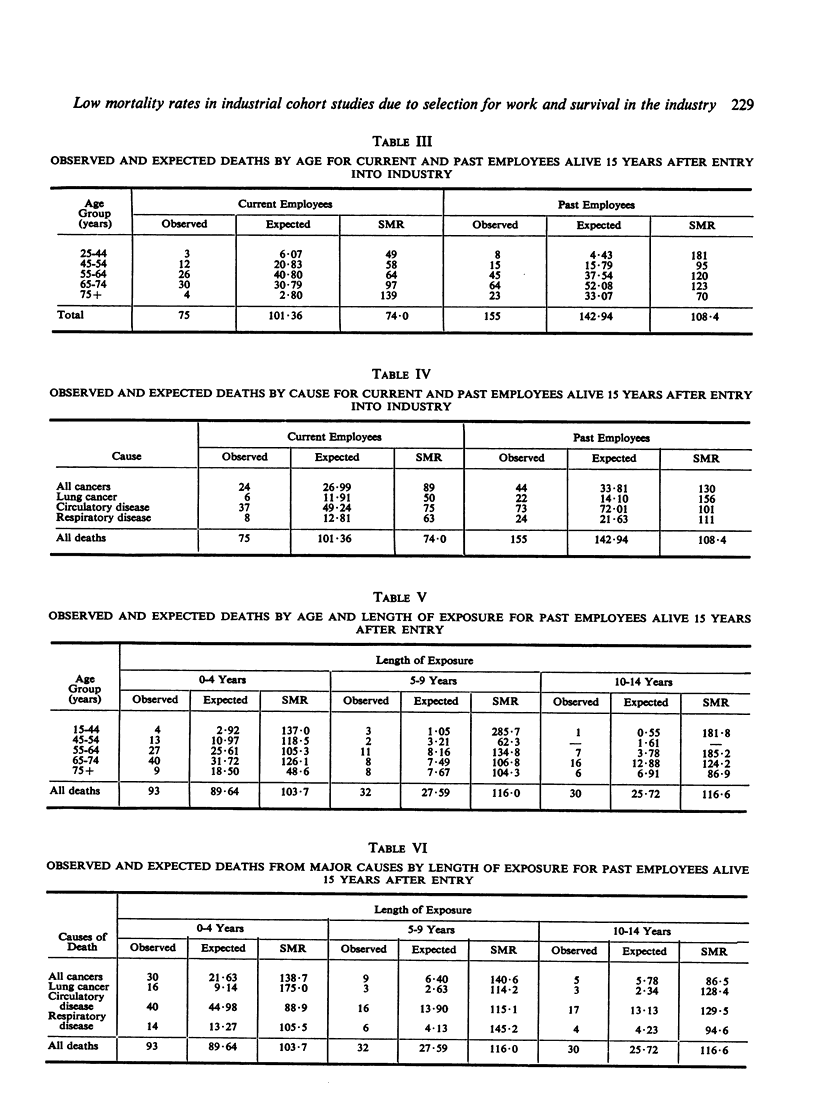
Occupational groups are often described as being relatively healthy because their mortality rates are lower than those of the national average. Although correct this confuses the issue for those who are interested in assessing the effects of exposure to a particular chemical. In a further analysis of data collected in a study of all men ever exposed to vinyl chloride monomer in the manufacture of polyvinyl chloride in Great Britain, three factors have been shown to contribute to the low mortality rates that were observed. The three factors: the selection of a healthy population for employment, the survival in the industry of the healthier men, and the length of time that this population has been pursued, have been quantified. The mortality experience within five years of entering this industry was shown to be as low as 37% of that expected; for circulatory disease and respiratory disease it was as low as 21%. There was a progressive increase in standardized mortality ratio with the length of time since entry so that the effect had almost disappeared 15 years after entry. To avoid confounding the selection effect with the survival effect the latter was measured by separating men who survived 15 years after entering the industry according to whether or not they were still in the industry after this period. Those who had left experienced an overall standardized mortality ratio some 50% higher than those still in the industry. This effect, although consistent in the age groups between 25 and 74 years and for all cause groups studied, was greatest in those aged between 25 and 44 years and for lung cancer and respiratory disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goldsmith J. R. Letter: What do we expect from an occupational cohort? J Occup Med. 1975 Feb;17(2):126–131. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197502000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox E. G. Computer simulation of industrial hazards. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



