Abstract
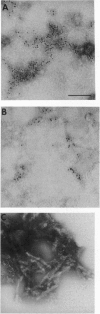
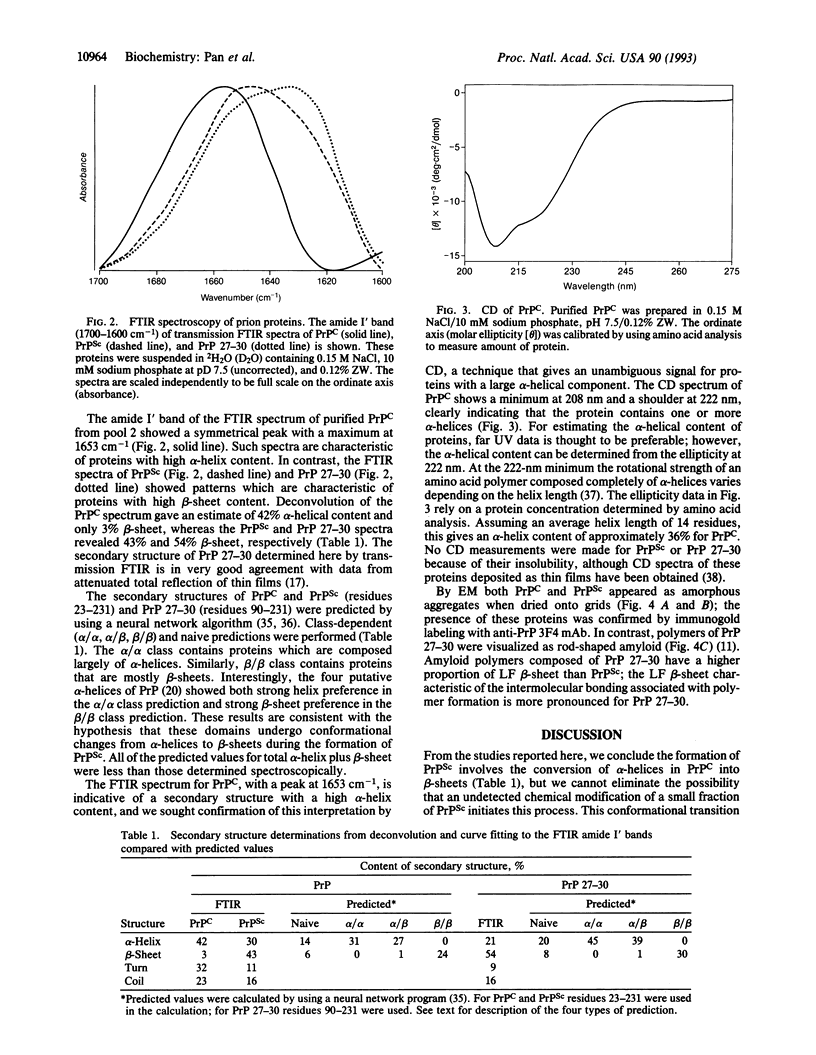
Prions are composed largely, if not entirely, of prion protein (PrPSc in the case of scrapie). Although the formation of PrPSc from the cellular prion protein (PrPC) is a post-translational process, no candidate chemical modification was identified, suggesting that a conformational change features in PrPSc synthesis. To assess this possibility, we purified both PrPC and PrPSc by using nondenaturing procedures and determined the secondary structure of each. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy demonstrated that PrPC has a high alpha-helix content (42%) and no beta-sheet (3%), findings that were confirmed by circular dichroism measurements. In contrast, the beta-sheet content of PrPSc was 43% and the alpha-helix 30% as measured by FTIR. As determined in earlier studies, N-terminally truncated PrPSc derived by limited proteolysis, designated PrP 27-30, has an even higher beta-sheet content (54%) and a lower alpha-helix content (21%). Neither PrPC nor PrPSc formed aggregates detectable by electron microscopy, while PrP 27-30 polymerized into rod-shaped amyloids. While the foregoing findings argue that the conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets underlies the formation of PrPSc, we cannot eliminate the possibility that an undetected chemical modification of a small fraction of PrPSc initiates this process. Since PrPSc seems to be the only component of the "infectious" prion particle, it is likely that this conformational transition is a fundamental event in the propagation of prions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Predicted secondary structure and membrane topology of the scrapie prion protein. Protein Eng. 1987 Feb-Mar;1(2):125–135. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Seligman S. J., Bablanian G., Windsor D., Scala L. J., Kim K. S., Chen C. M., Kascsak R. J., Bendheim P. E. Molecular location of a species-specific epitope on the hamster scrapie agent protein. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3667–3675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3667-3675.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchelt D. R., Scott M., Taraboulos A., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins differ in their kinetics of synthesis and topology in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):743–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Aguzzi A., Sailer A., Greiner R. A., Autenried P., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaccia-Bonnefil P., Kascsak R. J., Fersko R., Callahan S., Carp R. I. Brain regional distribution of prion protein PrP27-30 in mice stereotaxically microinjected with different strains of scrapie. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):7–12. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B. W., Dong A., Bhat K. S., Ernst D., Hayes S. F., Caughey W. S. Secondary structure analysis of the scrapie-associated protein PrP 27-30 in water by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 6;30(31):7672–7680. doi: 10.1021/bi00245a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J. The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18217–18223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Come J. H., Fraser P. E., Lansbury P. T., Jr A kinetic model for amyloid formation in the prion diseases: importance of seeding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5959–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Yang S. L., Lee A., Bowler R., Taraboulos A., Groth D., Prusiner S. B. Three scrapie prion isolates exhibit different accumulation patterns of the prion protein scrapie isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6449–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Meikle V. M., Fraser H. Identification of a gene which controls the incubation period of some strains of scrapie agent in mice. J Comp Pathol. 1968 Jul;78(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(68)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forloni G., Angeretti N., Chiesa R., Monzani E., Salmona M., Bugiani O., Tagliavini F. Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):543–546. doi: 10.1038/362543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. E., Nguyen J. T., Surewicz W. K., Kirschner D. A. pH-dependent structural transitions of Alzheimer amyloid peptides. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1190–1201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82154-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Purified prion proteins and scrapie infectivity copartition into liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Fletterick R. J., Prusiner S. B. Perturbation of the secondary structure of the scrapie prion protein under conditions that alter infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Lloyd D. H., Gabriel J. M., Holtzman D. M., Cohen F., Fletterick R., Prusiner S. B. Predicted alpha-helical regions of the prion protein when synthesized as peptides form amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10940–10944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Eanes E. D., Bladen H. A., Linke R. P., Termine J. D. Beta-pleated sheet fibrils. A comparison of native amyloid with synthetic protein fibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1141–1158. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Brown P., Haltia M., Ghiso J., Frangione B., Gajdusek D. C. Synthetic peptides corresponding to different mutated regions of the amyloid gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease show enhanced in vitro formation of morphologically different amyloid fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4451–4454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goormaghtigh E., Cabiaux V., Ruysschaert J. M. Secondary structure and dosage of soluble and membrane proteins by attenuated total reflection Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy on hydrated films. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):409–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraguchi T., Fisher S., Olofsson S., Endo T., Groth D., Tarentino A., Borchelt D. R., Teplow D., Hood L., Burlingame A. Asparagine-linked glycosylation of the scrapie and cellular prion proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W. Z., Newell W. R., Haris P. I., Chapman D., Barber J. Protein secondary structure of the isolated photosystem II reaction center and conformational changes studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4552–4559. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker R., Taraboulos A., Scott M., Pan K. M., Yang S. L., Torchia M., Jendroska K., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Replication of distinct scrapie prion isolates is region specific in brains of transgenic mice and hamsters. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1213–1228. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemström C., Virtanen A., Bridge E., Ketner G., Pettersson U. Adenovirus E4-dependent activation of the early E2 promoter is insufficient to promote the early-to-late-phase transition. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1440–1449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1440-1449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbich C., Kisters-Woike B., Reed J., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Aggregation and secondary structure of synthetic amyloid beta A4 peptides of Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90881-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K., Baker H. F., Crow T. J., Poulter M., Owen F., Terwilliger J. D., Westaway D., Ott J., Prusiner S. B. Linkage of a prion protein missense variant to Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):342–345. doi: 10.1038/338342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett J. T., Lansbury P. T., Jr Seeding "one-dimensional crystallization" of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie? Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1055–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Tashima T., Takeshita I., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Amyloid plaques in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease stain with prion protein antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):204–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneller D. G., Cohen F. E., Langridge R. Improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by an enhanced neural network. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90154-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P. Are prions misfolded molecular chaperones? FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 9;294(3):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80657-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Langer T., Boteva R., Schramel A., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding at the surface of groEL through a 'molten globule'-like intermediate. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):36–42. doi: 10.1038/352036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Braunfeld M. B., Bellinger C. G., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of prion rods purified from scrapie-infected hamster brains. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):110–120. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Taraboulos A., Kenaga L., Serban D., Stieber A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Gonatas N. Ultrastructural localization of scrapie prion proteins in cytoplasmic vesicles of infected cultured cells. Lab Invest. 1991 Dec;65(6):622–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottonen J., Strand A., Symersky J., Sweet R. M., Danley D. E., Geoghegan K. F., Gerard R. D., Goldsmith E. J. Structural basis of latency in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):270–273. doi: 10.1038/355270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
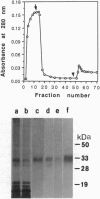
- Pan K. M., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Purification and properties of the cellular prion protein from Syrian hamster brain. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1343–1352. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell S. R., Cohen B. I., Cohen F. E. MacMatch: a tool for pattern-based protein secondary structure prediction. Comput Appl Biosci. 1993 Jun;9(3):373–374. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/9.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D., Serban A., Koehler R., Foster D., Torchia M., Burton D., Yang S. L., DeArmond S. J. Ablation of the prion protein (PrP) gene in mice prevents scrapie and facilitates production of anti-PrP antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10608–10612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Scott M., Foster D., Pan K. M., Groth D., Mirenda C., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban D., Carlson G. A. Transgenetic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90134-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeber A. J., Borchelt D. R., Scott M., Prusiner S. B. Attempts to convert the cellular prion protein into the scrapie isoform in cell-free systems. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6155–6163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6155-6163.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Kinzel V. Primary structure elements responsible for the conformational switch in the envelope glycoprotein gp120 from human immunodeficiency virus type 1: LPCR is a motif governing folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6761–6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Lofthouse R., Allsop D., Landon M., Kidd M., Prusiner S. B., Crow T. J. CNS amyloid proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1534–1540. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safar J., Roller P. P., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Conformational transitions, dissociation, and unfolding of scrapie amyloid (prion) protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20276–20284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitta B., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Human alpha 2(VI) collagen gene. Heterogeneity at the 5'-untranslated region generated by an alternate exon. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6188–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M., Groth D., Foster D., Torchia M., Yang S. L., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Propagation of prions with artificial properties in transgenic mice expressing chimeric PrP genes. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90275-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Baldwin M. A., Teplow D. B., Hood L., Gibson B. W., Burlingame A. L., Prusiner S. B. Structural studies of the scrapie prion protein using mass spectrometry and amino acid sequencing. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1991–2002. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Prusiner S. B. Differential release of cellular and scrapie prion proteins from cellular membranes by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5405–5412. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Prelli F., Ghiso J., Bugiani O., Serban D., Prusiner S. B., Farlow M. R., Ghetti B., Frangione B. Amyloid protein of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana kindred) is an 11 kd fragment of prion protein with an N-terminal glycine at codon 58. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Jendroska K., Serban D., Yang S. L., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Regional mapping of prion proteins in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7620–7624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Raeber A. J., Borchelt D. R., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Synthesis and trafficking of prion proteins in cultured cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):851–863. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk E., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Purification and properties of the cellular and scrapie hamster prion proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Use of polylysine for adsorption of nuclei acids and enzymes to electron microscope specimen films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Wu C. S., Martinez H. M. Calculation of protein conformation from circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:208–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]