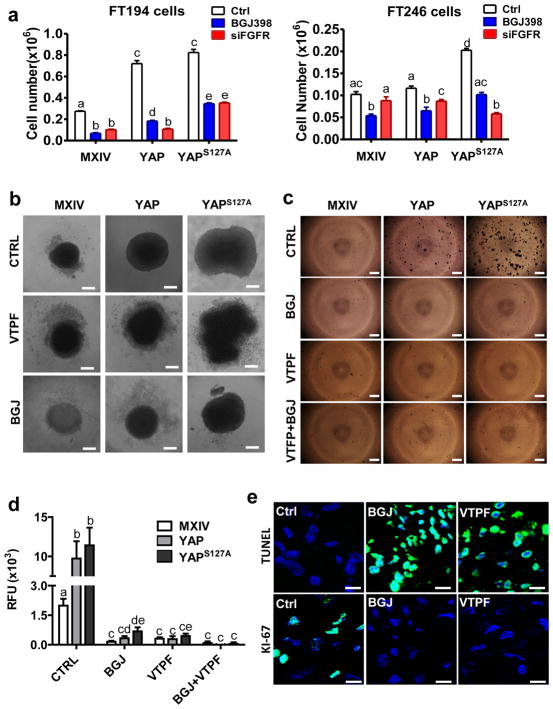
Figure 10. The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with FGF/FGFR pathway to regulate activities of FTSECs.
a) Knockdown of FGFRs in FT194 and FT246 cells using FGFR siRNAs or blockage of FGFR activities using BGJ398 eliminate YAP- or constitutively active YAP-induced cell growth. Each bar represents mean ± SEM of four independent repeats. Bars with different letters are significantly different from each other (p<0.05). b) Verteporfin (YAP antagonist, 5 μM) and BGJ398 (FGFR inhibitor, 1μM) block YAP-induced growth of FT194 cells in a 3D-hanging drop culture system. c) Representative images from the soft agar assays showing that verteporfin and BGJ398 block YAP-induced colony formation in FT194 cells. d) Fluorescence-based quantitative soft agar assay showing that verteporfin and BGJ398 block YAP-induced colony formation in FT194 cells. Each bar represents mean ± SEM of four independent repeats. Bars with different letters are significantly different from each other (p<0.05). e) Representative images showing that treatment of tumor tissues derived from transformed FT194 cell mouse xenografts with BGJ398 (BGJ) or verteporfin (VTPF) suppressed tumor cell growth, which was indicated by the reduced expression of Ki-67 (Ki-67 positive cells are in green) (lower panel), and increased tumor cell apoptosis, which is indicated by TUNEL staining (TUNEL positive tumor cells are in green) (upper panel). Scale bar: 10μm.