Figure 1. GRP94 and FN14 expression predict brain metastasis progression in breast cancer patients.
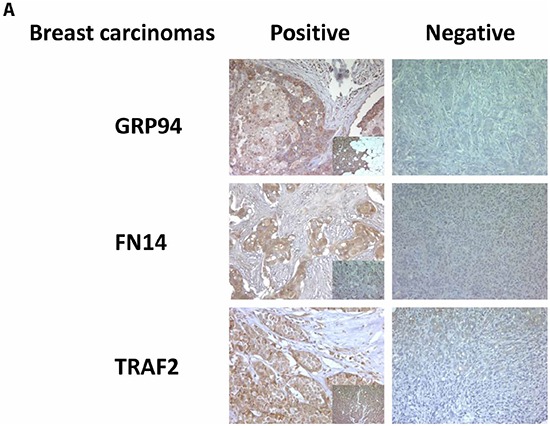
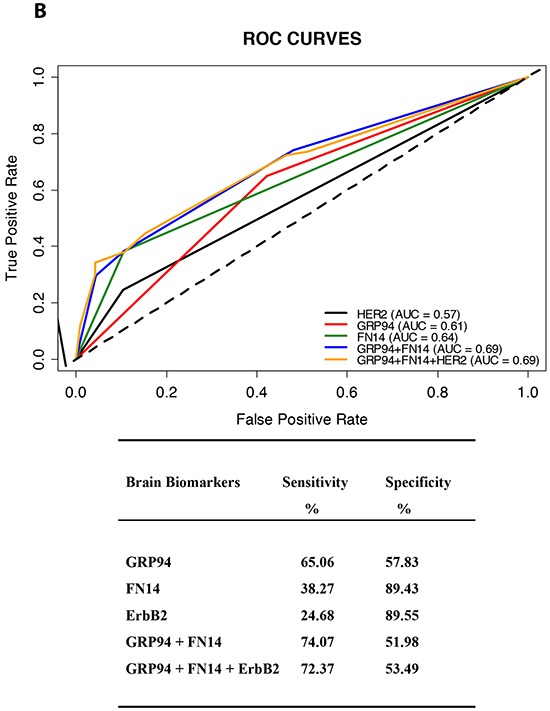
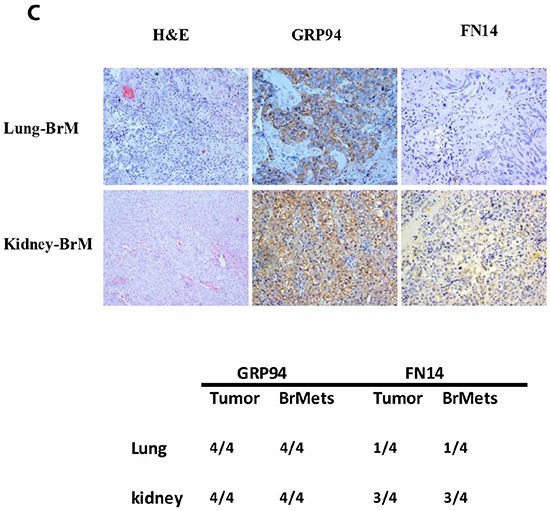
A. TMAs were used to identify the indicated proteins by IHC analysis in paraffin-embedded primary breast carcinomas (x 20). To score the positivity of the three proteins we considered samples with more than 70% of tumor positive cells with high levels of staining to represent positive control samples (small squares in the left column), ignoring samples with less intense staining or fewer positive cells. B. The area under the ROC curve obtained with the integrated predictive indexes. Markers were assessed in a multivariate logistic regression model using a forward stepwise procedure to identify the best combination for predicting brain metastasis. The area under the ROC curve obtained for ErbB2 alone (AUC = 0.57), for GRP94 (AUC = 0.61), FN14 (AUC = 0.64) and the combination of GRP94 and FN14 (AUC = 0.69) and for ErbB2, GRP94 and FN14 (AUC = 0.69), is represented in the upper part of the figure. The sensitivity and specificity of the markers are shown in the lower part of the figure, indicating the most specific GRP94 and the most sensitive FN14, which was similar to ErbB2 in terms of sensitivity and specificity. C. Expression of GRP94 and FN14 in four pairs tumor/BrM of lung and clear cell kidney carcinomas. Representative IHC of BrM are showed in the upper part of the figure and at the bottom the relation of positive samples of each protein.
