Abstract
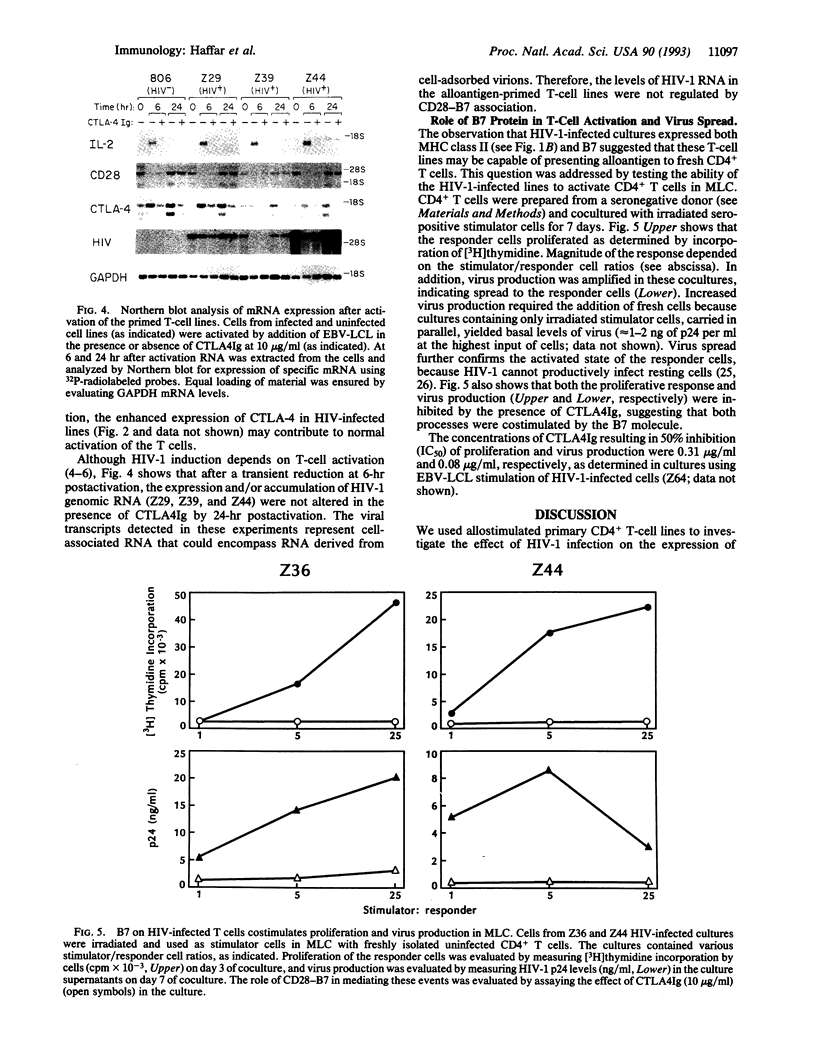
Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) requires T-cell activation. Recent studies have shown that interactions of the T-lymphocyte receptors CD28 and CTLA-4 with their counter receptor, B7, on antigen-presenting cells are required for optimal T-cell activation. Here we show that HIV-1 infection is associated with decreased expression of CD28 and increased expression of B7 on CD4+ T-cell lines generated from seropositive donors by alloantigen stimulation. Loss of CD28 expression was not seen on CD4+ T-cell lines from seronegative donors, but up-regulation of B7 expression was observed upon more prolonged culture. Both T-cell proliferation and interleukin 2 mRNA accumulation in HIV-1-infected cultures required costimulation with exogenous B7 because these events were blocked by CTLA4Ig, a soluble form of CTLA-4 that binds B7 with high avidity. In contrast, levels of HIV-1 RNA were not affected by CTLA4Ig, indicating that regulation of virus transcription in these cultures did not depend upon CD28-B7 engagement. Infected T cells could present alloantigen to fresh, uninfected CD4+ T cells, leading to increased proliferation and virus spread to the activated cells. Both of these events were blocked by CTLA4Ig. Thus, chronic activation of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells reduces expression of CD28 and increases expression of B7, thereby enabling these T cells to become antigen-presenting cells for uninfected CD4+ T cells; this might be another mechanism for HIV-1 transmission via T-cell-T-cell contact.
Full text
PDF
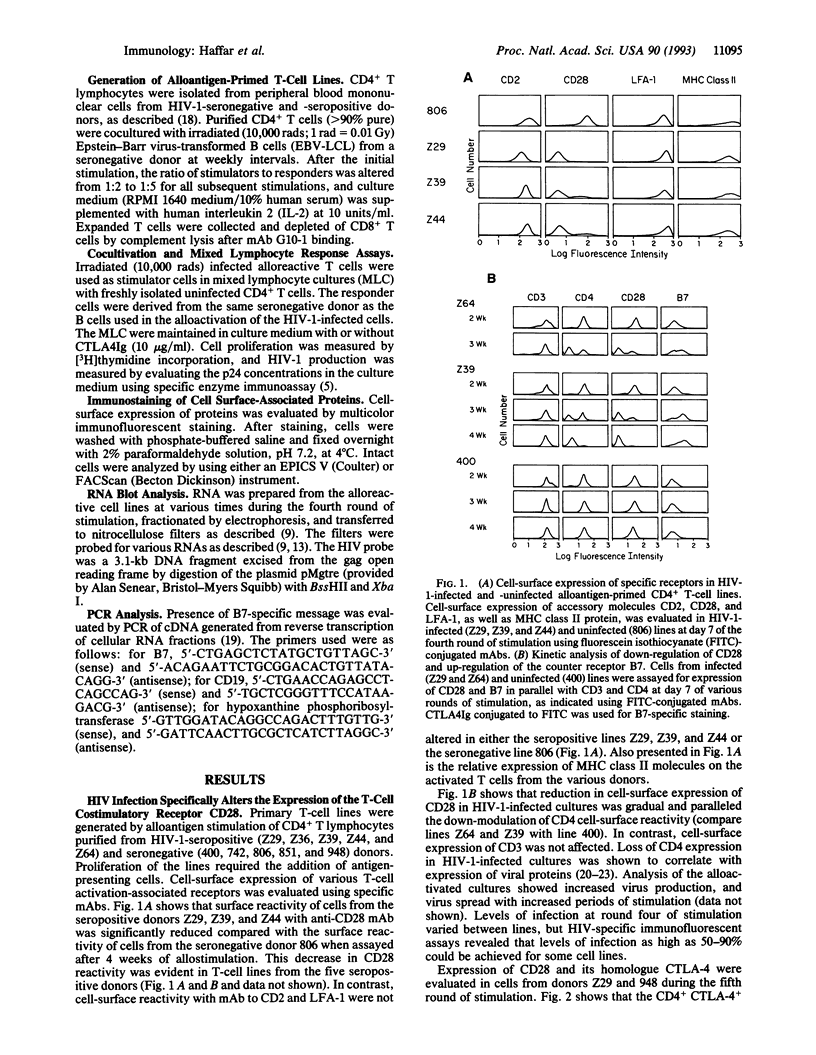
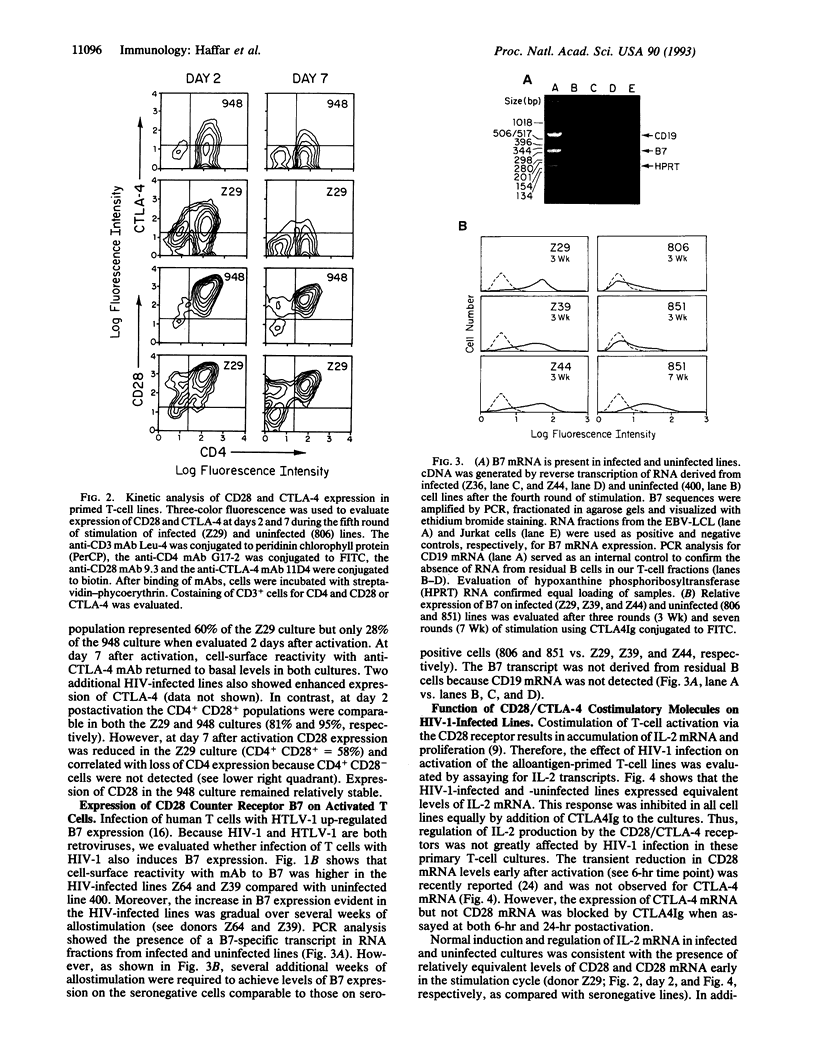

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma M., Cayabyab M., Buck D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. CD28 interaction with B7 costimulates primary allogeneic proliferative responses and cytotoxicity mediated by small, resting T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):353–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma M., Yssel H., Phillips J. H., Spits H., Lanier L. L. Functional expression of B7/BB1 on activated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):845–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Denizot F., Luciani M. F., Roux-Dosseto M., Suzan M., Mattei M. G., Golstein P. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily--CTLA-4. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):267–270. doi: 10.1038/328267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Klussman K., Aruffo A. Intercellular adhesion molecule-2, a second counter-receptor for CD11a/CD18 (leukocyte function-associated antigen-1), provides a costimulatory signal for T-cell receptor-initiated activation of human T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):665–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegel M. L., Moran P. A., Gilliland L. K., Damle N. K., Hayden M. S., Zarling J. M., Ledbetter J. A. Regulation of HIV production by blood mononuclear cells from HIV-infected donors: II. HIV-1 production depends on T cell-monocyte interaction. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 May;9(5):465–473. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Gray G. S., Gimmi C. D., Lombard D. B., Zhou L. J., White M., Fingeroth J. D., Gribben J. G., Nadler L. M. Structure, expression, and T cell costimulatory activity of the murine homologue of the human B lymphocyte activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):625–631. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Lombard D. B., Gimmi C. D., Brod S. A., Lee K., Laning J. C., Hafler D. A., Dorf M. E., Gray G. S., Reiser H. CTLA-4 and CD28 mRNA are coexpressed in most T cells after activation. Expression of CTLA-4 and CD28 mRNA does not correlate with the pattern of lymphokine production. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3795–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Alfano J., Miller A. D. The negative effect of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef on cell surface CD4 expression is not species specific and requires the cytoplasmic domain of CD4. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1511–1516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1511-1516.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groux H., Torpier G., Monté D., Mouton Y., Capron A., Ameisen J. C. Activation-induced death by apoptosis in CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus-infected asymptomatic individuals. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):331–340. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley R. J., Ikeuchi K., Byrn R. A., Anderson K., Groopman J. E. CD4+ lymphocyte function with early human immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1993–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Moran P. A., Smithgall M. D., Diegel M. L., Sridhar P., Ledbetter J. A., Zarling J. M., Hu S. L. Inhibition of virus production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1-seropositive donors by treatment with recombinant HIV-like particles. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4279–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4279-4287.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildreth J. E., Orentas R. J. Involvement of a leukocyte adhesion receptor (LFA-1) in HIV-induced syncytium formation. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1075–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.2543075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Alpers J. D., Rackowski J. L., Huebner K., Haggarty B. S., Cedarbaum A. J., Reed J. C. Alterations in T4 (CD4) protein and mRNA synthesis in cells infected with HIV. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3095925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Depper J. M., Greene W. C., Whalen G., Waldmann T. A., Fauci A. S. Qualitative analysis of immune function in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for a selective defect in soluble antigen recognition. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):79–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linette G. P., Hartzman R. J., Ledbetter J. A., June C. H. HIV-1-infected T cells show a selective signaling defect after perturbation of CD3/antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.2899908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Bradshaw J., Urnes M., Grosmaire L., Ledbetter J. A. CD28 engagement by B7/BB-1 induces transient down-regulation of CD28 synthesis and prolonged unresponsiveness to CD28 signaling. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3161–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Grosmaire L., Aruffo A., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. Binding of the B cell activation antigen B7 to CD28 costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 mRNA accumulation. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):721–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Urnes M., Grosmaire L. S., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. CTLA-4 is a second receptor for the B cell activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):561–569. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. T-cell antigen CD28 mediates adhesion with B cells by interacting with activation antigen B7/BB-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Tan P., Bradshaw J., Ledbetter J. A., Anasetti C., Damle N. K. Coexpression and functional cooperation of CTLA-4 and CD28 on activated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P. A., Diegel M. L., Sias J. C., Ledbetter J. A., Zarling J. M. Regulation of HIV production by blood mononuclear cells from HIV-infected donors: I. Lack of correlation between HIV-1 production and T cell activation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 May;9(5):455–464. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Freeman G. J., Gault A., Godfrey D., Nadler L. M., Glimcher L. H. Signalling through the MHC class II cytoplasmic domain is required for antigen presentation and induces B7 expression. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):266–268. doi: 10.1038/360266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranheim E. A., Kipps T. J. Activated T cells induce expression of B7/BB1 on normal or leukemic B cells through a CD40-dependent signal. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):925–935. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon P., Olivier R., Riviere Y., Brisson E., Gluckman J. C., Kieny M. P., Montagnier L., Klatzmann D. Loss of CD4 membrane expression and CD4 mRNA during acute human immunodeficiency virus replication. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):1953–1969. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom D. M., Hall N. D. B7/BB1, the ligand for CD28, is expressed on repeatedly activated human T cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):295–298. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1349–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.2113314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Meier C., Mann A. M., Chapman N., Wasiak A. Envelope glycoprotein of HIV induces interference and cytolysis resistance in CD4+ cells: mechanism for persistence in AIDS. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Lamonica C. A. HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T cell activation and proviral integration. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington F. W., Brady W., Linsley P. S. Expression and function of B7 on human epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1286–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallé A., Aubry J. P., Durand I., Banchereau J. IL-4 and IL-2 upregulate the expression of antigen B7, the B cell counterstructure to T cell CD28: an amplification mechanism for T-B cell interactions. Int Immunol. 1991 Mar;3(3):229–235. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.3.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallé A., Garrone P., Yssel H., Bonnefoy J. Y., Freedman A. S., Freeman G., Nadler L. M., Banchereau J. mAb 104, a new monoclonal antibody, recognizes the B7 antigen that is expressed on activated B cells and HTLV-1-transformed T cells. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):531–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Alaverdi N., Wade W. F., Linsley P. S. Induction of costimulatory molecule B7 in M12 B lymphomas by cAMP or MHC-restricted T cell interaction. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2192–2202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]