Abstract
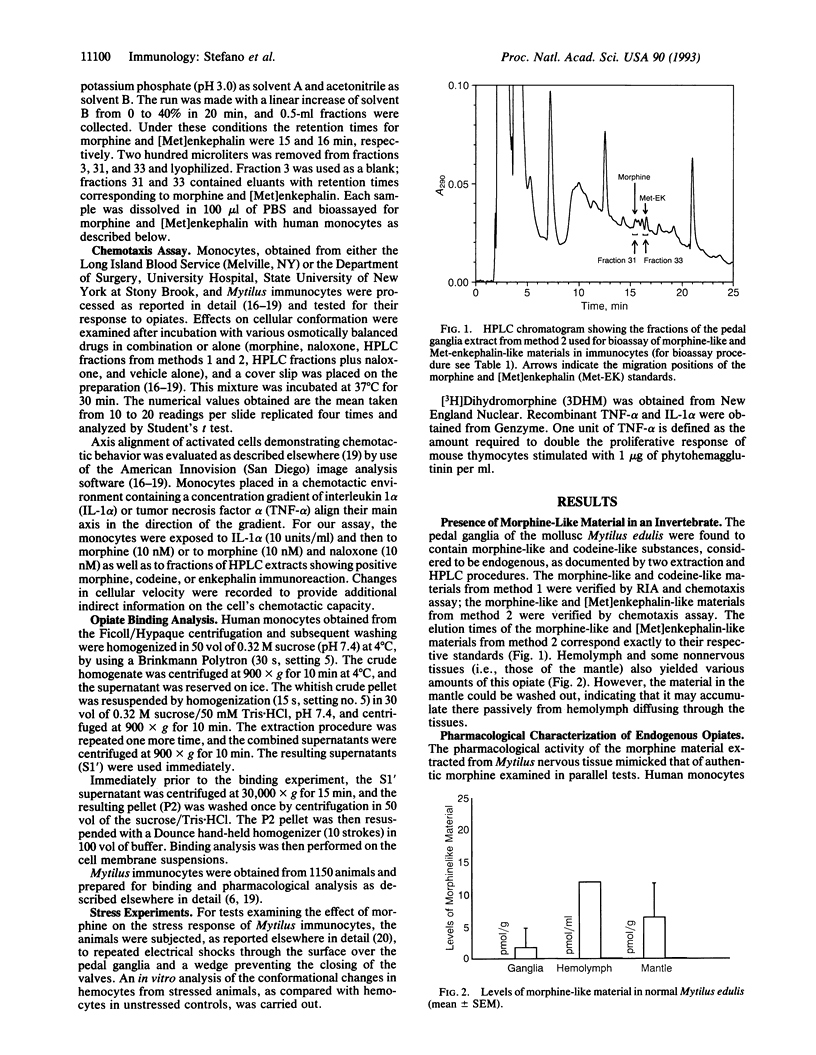
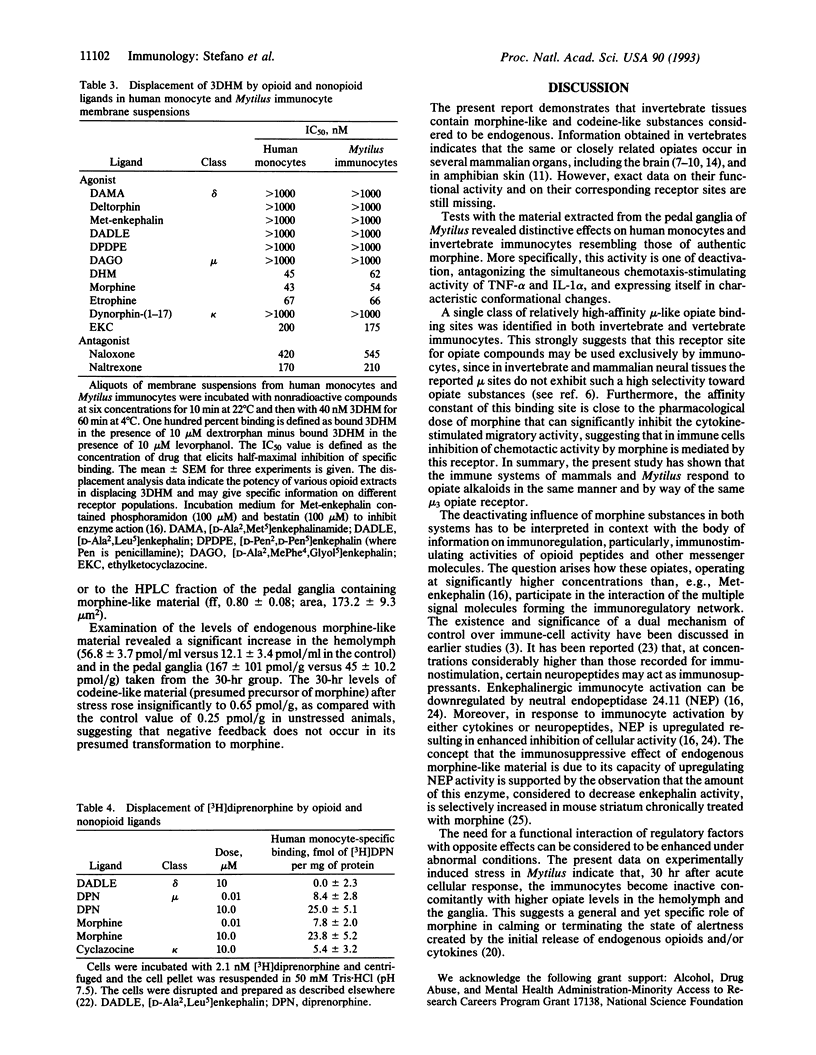
The presence of morphine-like and codeine-like substances was demonstrated in the pedal ganglia, hemolymph, and mantle tissues of the mollusc Mytilus edulis. The pharmacological activities of the endogenous morphine-like material resemble those of authentic morphine. Both substances were found to counteract, in a dose-dependent manner, the stimulatory effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha or interleukin 1 alpha on human monocytes and Mytilus immunocytes, when added simultaneously to the incubation medium. The immunosuppressive effect of this opiate material expresses itself in a lowering of chemotactic activity, cellular velocity, and adherence. Codeine mimics the activity of authentic morphine, but only at much higher concentrations. Specific high-affinity receptor sites (mu 3) for morphine have been identified on human monocytes and Mytilus immunocytes. In Mytilus recovering from experimentally induced stress, the return of "altered" immunocytes to a more inactive state appears to be due to a significant rise in the content of morphine-like material in the pedal ganglia and hemolymph at this time. Thus, morphine may have a role in calming or terminating the state of immune alertness.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cardinale G. J., Donnerer J., Finck A. D., Kantrowitz J. D., Oka K., Spector S. Morphine and codeine are endogenous components of human cerebrospinal fluid. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 19;40(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruciani R. A., Dvorkin B., Morris S. A., Crain S. M., Makman M. H. Direct coupling of opioid receptors to both stimulatory and inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in F-11 neuroblastoma-sensory neuron hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3019–3023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Cardinale G., Coffey J., Lisek C. A., Jardine I., Spector S. Chemical characterization and regulation of endogenous morphine and codeine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Aug;242(2):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Oka K., Brossi A., Rice K. C., Spector S. Presence and formation of codeine and morphine in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4566–4567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Barrett R. W., James I. F., Lowney L. I., Weitz C. J., Knipmeyer L. L., Rapoport H. Morphine and other opiates from beef brain and adrenal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5203–5207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira H., Lisek C. A., Jardine I., Arimura A., Spector S. Identification of the convulsant opiate thebaine in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):716–719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira H., Spector S. Transformation of thebaine to oripavine, codeine, and morphine by rat liver, kidney, and brain microsomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1267–1271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream R. M., Zukin R. S., Stefano G. B. Demonstration of two classes of opiate binding sites in the nervous tissue of the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Positive homotropic cooperativity of lower affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9218–9224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung M. K., Stefano G. B. Comparative neurobiology of opioids in invertebrates with special attention to senescent alterations. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(2):131–159. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Kantrowitz J. D., Spector S. Isolation of morphine from toad skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1852–1854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Kantrowitz J. D., Spector S. Isolation of morphine from toad skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1852–1854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Castrillón J. L., Pérez-Arellano J. L., García-Palomo J. D., Jiménez-López A., De Castro S. Opioids depress in vitro human monocyte chemotaxis. Immunopharmacology. 1992 Jan-Feb;23(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(92)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., D'Adamio L., Switzer S. N., Howard F. D., Sinisterra J., Scharrer B., Reinherz E. L. Downregulation of enkephalin-mediated inflammatory responses by CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):394–396. doi: 10.1038/347394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Hughes T. K., Jr, Hashemi F., Stefano G. B. Immunosuppressive effects of corticotropin and melanotropin and their possible significance in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Cadet P., Dokun A., Scharrer B. A neuroimmunoregulatory-like mechanism responding to stress in the marine bivalve Mytilus edulis. Brain Behav Immun. 1990 Dec;4(4):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(90)90035-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Cadet P., Scharrer B. Stimulatory effects of opioid neuropeptides on locomotory activity and conformational changes in invertebrate and human immunocytes: evidence for a subtype of delta receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6307–6311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B. Comparative aspects of opioid-dopamine interaction. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1982 Sep;2(3):167–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00711145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Kream R. M., Zukin R. S. Demonstration of stereospecific opiate binding in the nervous tissue of the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 13;181(2):440–445. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90626-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Leung M. K., Zhao X. H., Scharrer B. Evidence for the involvement of opioid neuropeptides in the adherence and migration of immunocompetent invertebrate hemocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Melchiorri P., Negri L., Hughes T. K., Jr, Scharrer B. [D-Ala2]deltorphin I binding and pharmacological evidence for a special subtype of delta opioid receptor on human and invertebrate immune cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9316–9320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Paemen L. R., Hughes T. K., Jr Autoimmunoregulation: differential modulation of CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11 by tumor necrosis factor and neuropeptides. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Nov;41(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90189-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B. Role of opioid neuropeptides in immunoregulation. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;33(2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(89)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz C. J., Lowney L. I., Faull K. F., Feistner G., Goldstein A. Morphine and codeine from mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9784–9788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



