Abstract
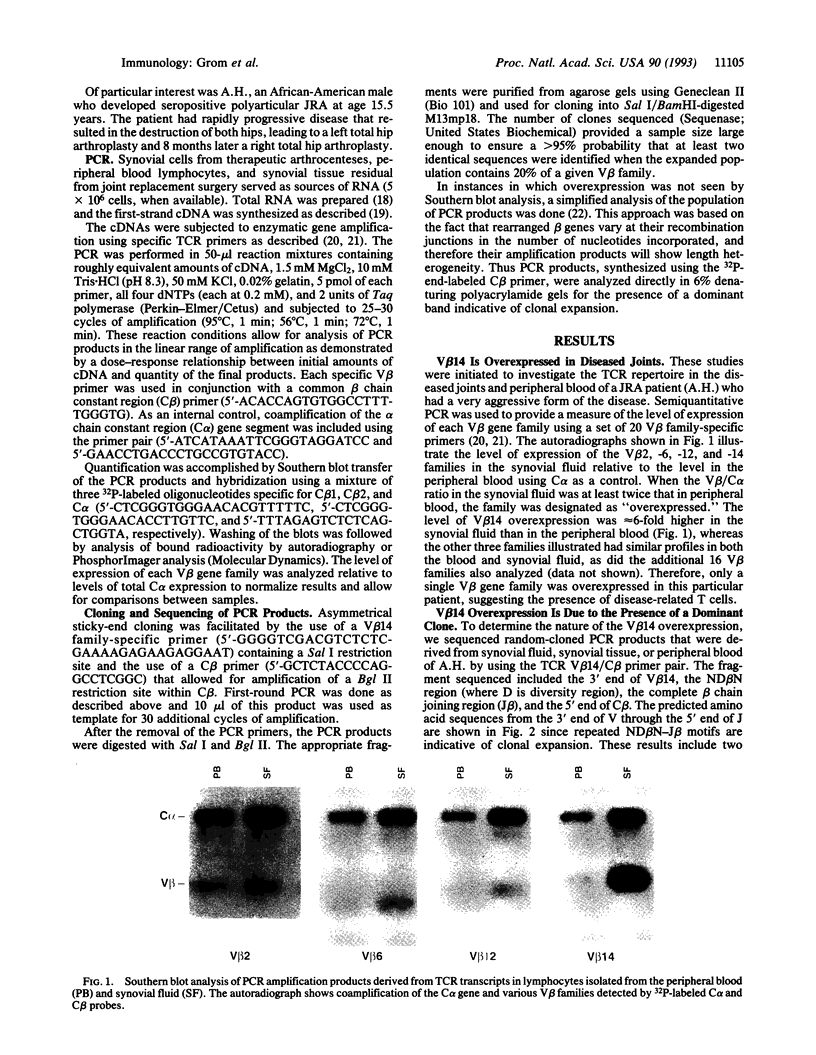
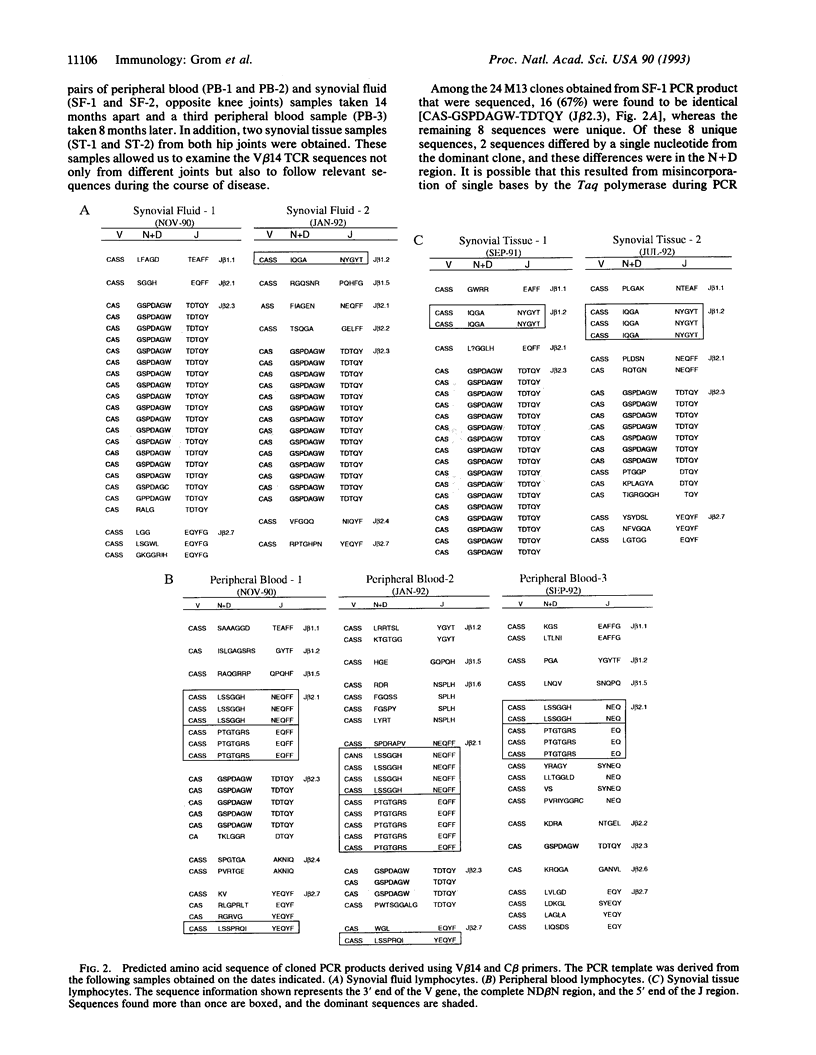
The characteristic histopathology and major histocompatibility complex associations in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis suggest an oligoclonal antigen-specific T-cell population may be critical to pathogenesis. To test this, we analyzed the T-cell repertoire of a polyarticular HLA-DR4+ juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient with an aggressive form of disease that required arthrocentesis of the knee joints and early replacement of both hip joints. A comparison of T-cell-receptor beta chain variable region (V beta) gene expression in peripheral blood and synovial fluid performed by semiquantitation of cDNA samples amplified by the PCR revealed overexpression of the T-cell-receptor V beta 14 gene family. To determine the nature of V beta 14 overexpression, we sequenced randomly cloned amplification products derived from two synovial fluid, two synovial tissue, and three peripheral blood samples by using a V beta 14/beta chain constant region primer pair. Sequence data showed that the T-cell response in the synovia was oligoclonal. Of four clones found, one was present in all joints examined and persisted over time. This clone accounted for 67% and 74% of all V beta 14+ clones sequenced in two synovial fluid samples and 75% and 40% in two synovial tissue samples. This clone was also found at a lesser frequency in peripheral blood samples. Further studies provided evidence for the presence of oligoclonally expanded populations of T cells utilizing the V beta 14 T-cell receptor in 6 of 27 patients examined. In contrast to the remaining patients studied, 3 with a late onset polyarticular course who exhibited especially marked clonality were characterized by features typical of adult rheumatoid arthritis (IgM rheumatoid factor-positive and HLA-DR4+). These data suggest a role for V beta 14+ T cells in a group of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe J., Kotzin B. L., Jujo K., Melish M. E., Glode M. P., Kohsaka T., Leung D. Y. Selective expansion of T cells expressing T-cell receptor variable regions V beta 2 and V beta 8 in Kawasaki disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acha-Orbea H., Mitchell D. J., Timmermann L., Wraith D. C., Tausch G. S., Waldor M. K., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptors from lymphocytes mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis allows specific immune intervention. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Levinson J. E., Bass J. C., Baum J., Brewer E. J., Jr, Fink C. W., Hanson V., Jacobs J. C., Masi A. T., Schaller J. G. A study of classification criteria for a diagnosis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;29(2):274–281. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. M., Dier D. L., Roessner K. D., Budd R. C., Nicklas J. A. Diversity of rheumatoid synovial tissue T cells by T cell receptor analysis. Oligoclonal expansion in interleukin-2-responsive cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):537–546. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian H., Band H., Brenner M. B. Increased frequency of T cell receptor V alpha 12.1 expression on CD8+ T cells: evidence that V alpha participates in shaping the peripheral T cell repertoire. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):639–648. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duby A. D., Sinclair A. K., Osborne-Lawrence S. L., Zeldes W., Kan L., Fox D. A. Clonal heterogeneity of synovial fluid T lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Zvaifler N. J. How important are T cells in chronic rheumatoid synovitis? Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):768–773. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O., Dobloug J. H., Natvig J. B. Augmented numbers of HLA-DR-positive T lymphocytes in the synovial fluid and synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: in vivo-activated T lymphocytes are potent stimulators in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Feb;15(2):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D., Litvin D., Wallace K., Chylack L., Garovoy M., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Early-onset pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis associated with human leukocyte antigen-DRw5, iritis, and antinuclear antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):426–429. doi: 10.1172/JCI109872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Diveley J. P., Lundeen K. A., Esty A., Winters S. T., Carlo D. J., Brostoff S. W. Limited T-cell receptor beta-chain heterogeneity among interleukin 2 receptor-positive synovial T cells suggests a role for superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10921–10925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Steere A. C., Fox R. I., Butcher E. C. A distinct endothelial cell recognition system that controls lymphocyte traffic into inflamed synovium. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3726548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Fryer P., Griffiths S., Harding B., Dixey J., Mansell B. Class II antigens on dendritic cells from the synovial fluids of patients with inflammatory arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Oct;78(1):19–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyrink L., Gabriel C. A., Thompson S. D., Grom A. A., Maksymowych W. P., Choi E., Glass D. N. Reduced expression of a human V beta 6.1 T-cell receptor allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick C. A., Dudley E. C., Viney J. L., Owen M. J., Hayday A. C. Rearrangement and diversity of T cell receptor beta chain genes in thymocytes: a critical role for the beta chain in development. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90138-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom B. S., Nepom G. T., Mickelson E., Schaller J. G., Antonelli P., Hansen J. A. Specific HLA-DR4-associated histocompatibility molecules characterize patients with seropositive juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):287–291. doi: 10.1172/JCI111413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., West S. G., Lafferty J. A., Clements J. R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Kotzin B. L. Evidence for the effects of a superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):325–329. doi: 10.1126/science.1857971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Nag B., Su X. M., Green D., Spack E., Clark B. R., Sriram S. Antigen-specific therapy of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by soluble class II major histocompatibility complex-peptide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11465–11469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Suleyman S., Vinje O., Natvig J. B., Førre O. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptor variable region gene usage in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis synovial T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2413–2418. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Stegagno M., Wright K. A., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., Colvin R. B., Duquesnoy R. J., Kurnick J. T. Clonal dominance among T-lymphocyte infiltrates in arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Fink C. W. Different HLA-D associations in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):124–130. doi: 10.1172/JCI109265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Wege H., Straus A., Ott M., Bannwarth W., Lanchbury J., Panayi G., Steinmetz M. The T-cell-receptor repertoire in the synovial fluid of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis is polyclonal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8534–8538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Roberts C. R., Anderson C. H., Turano A. M., Baron M. Light- and electron-microscopic findings of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis synovium: comparison with normal juvenile synovium. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1978 May;7(4):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(78)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff M. Role of the endothelium in chronic inflammatory synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1345–1352. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




