Abstract
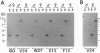
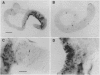
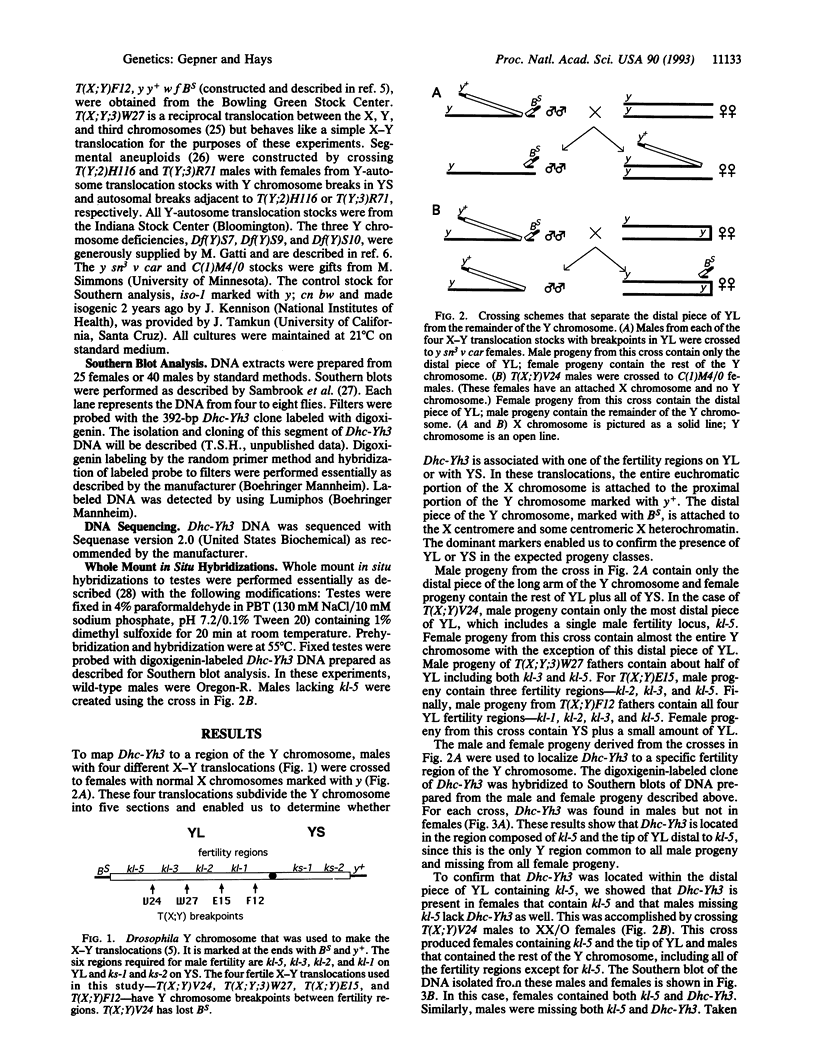
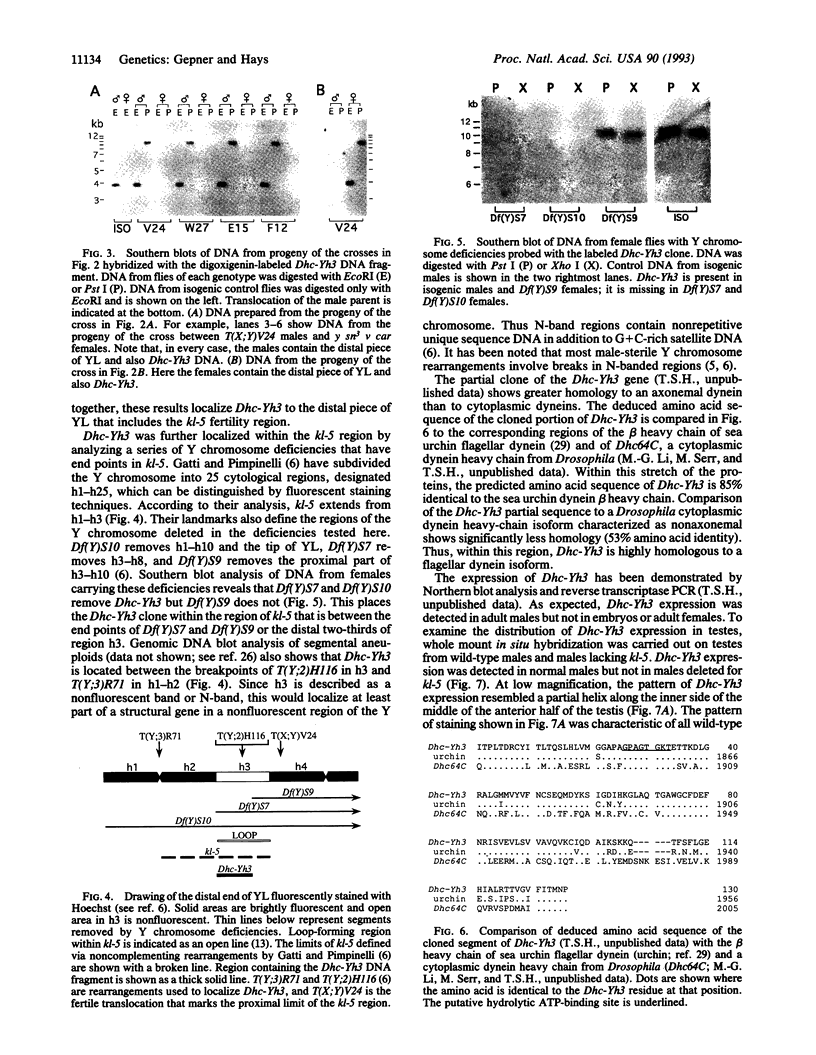
A clone encoding a portion of the highly conserved ATP-binding domain of a dynein heavy-chain polypeptide was mapped to a region of the Drosophila melanogaster Y chromosome. Dyneins are large multisubunit enzymes that utilize the hydrolysis of ATP to move along microtubules. They were first identified as the motors that provide the force for flagellar and ciliary bending. Seven different dynein heavy-chain genes have been identified in D. melanogaster by PCR. In the present study, we demonstrate that one of the dynein genes, Dhc-Yh3, is located in Y chromosome region h3, which is contained within kl-5, a locus required for male fertility. The PCR clone derived from Dhc-Yh3 is 85% identical to the corresponding region of the beta heavy chain of sea urchin flagellar dynein but only 53% identical to a cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain from Drosophila. In situ hybridization to Drosophila testes shows Dhc-Yh3 is expressed in wild-type males but not in males missing the kl-5 region. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the Y chromosome is needed for male fertility because it contains conventional genes that function during spermiogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayles G. B., Sanders T. G., Kiefer B. I., Suzuki D. T. Temperature-sensitive mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. XI. Male sterile mutants of the Y chromosome. Dev Biol. 1973 Jun;32(2):239–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi S., Gatti M., Pisano C., Lohe A. Transcription of a satellite DNA on two Y chromosome loops of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1990 Aug;99(4):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01731701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi S., Lohe A. Fine mapping of satellite DNA sequences along the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: relationships between satellite sequences and fertility factors. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):177–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi S., Pisano C., Puoti F., Gatti M. Y chromosome loops in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1015–1034. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. B. Non-Disjunction as Proof of the Chromosome Theory of Heredity (Concluded). Genetics. 1916 Mar;1(2):107–163. doi: 10.1093/genetics/1.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosseau G E. Genetic Analysis of the Male Fertility Factors on the Y Chromosome of Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1960 Mar;45(3):257–274. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberl D. F., Duyf B. J., Hilliker A. J. The role of heterochromatin in the expression of a heterochromatic gene, the rolled locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):277–292. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M., Pimpinelli S. Functional elements in Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:239–275. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Gibbons B. H., Mocz G., Asai D. J. Multiple nucleotide-binding sites in the sequence of dynein beta heavy chain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):640–643. doi: 10.1038/352640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S., Hardy R. W., Lindsley D. L. Structural genes on the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowen J. W., Gay E. H. Gene Number, Kind, and Size in Drosophila. Genetics. 1933 Jan;18(1):1–31. doi: 10.1093/genetics/18.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstein J. H., Glätzer K. H., Hulsebos T. J. Genetic and cytogenetic analysis of the "Th-Ps" region of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei: evidence for dual functions of the lampbrush loop-forming fertility genes? Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jun;227(2):293–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00259683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Lindsley D. L., Livak K. J., Lewis B., Siversten A. L., Joslyn G. L., Edwards J., Bonaccorsi S. Cytogenetic analysis of a segment of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1984 Aug;107(4):591–610. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W. The influence of chromosome content on the size and shape of sperm heads in Drosophila melanogaster and the demonstration of chromosome loss during spermiogenesis. Genetics. 1975 Feb;79(2):231–264. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Tokuyasu K. T., Lindsley D. L. Analysis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster bearing deletions for Y-chromosome fertility genes. Chromosoma. 1981;83(5):593–617. doi: 10.1007/BF00328522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J. Genetic analysis of the centromeric heterochromatin of chromosome 2 of Drosophila melanogaster: deficiency mapping of EMS-induced lethal complementation groups. Genetics. 1976 Aug;83(4):765–782. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennison J. A. Analysis of Y-Linked Mutations to Male Sterility in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1983 Feb;103(2):219–234. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennison J. A. The Genetic and Cytological Organization of the Y Chromosome of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):529–548. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer B. I. Ultrastructural Abnormalities in Developing Sperm of X/0 DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1966 Dec;54(6):1441–1452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.6.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Dynein from Dictyostelium: primary structure comparisons between a cytoplasmic motor enzyme and flagellar dynein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley D. L., Sandler L., Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Denell R. E., Hall J. C., Jacobs P. A., Miklos G. L., Davis B. K., Gethmann R. C. Segmental aneuploidy and the genetic gross structure of the Drosophila genome. Genetics. 1972 May;71(1):157–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J. Detailed structure of the Drosophila melanogaster stellate genes and their transcripts. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):303–316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchant G. E., Holm D. G. Genetic Analysis of the Heterochromatin of Chromosome 3 in Drosophila Melanogaster. II. Vital Loci Identified through Ems Mutagenesis. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):519–532. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Wieschaus E. Is sex determination in germ line and soma controlled by separate genetic mechanisms? Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):249–251. doi: 10.1038/272249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Paschal B. M., Mazumdar M., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the retrograde transport motor cytoplasmic dynein (MAP 1C). Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90195-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K. Four ATP-binding sites in the midregion of the beta heavy chain of dynein. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):643–645. doi: 10.1038/352643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano C., Bonaccorsi S., Gatti M. The kl-3 loop of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster binds a tektin-like protein. Genetics. 1993 Mar;133(3):569–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Johnson K. A. Dynein structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:119–151. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M., SPIEGELMAN S. LOCALIZATION OF DNA COMPLEMENTARY TO RIBOSOMAL RNA IN THE NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGION OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:737–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. H. Allelic complementation between mutants in the fertility factyors of the Y chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):43–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00270442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. H. Ethyl methanesulfonate-induced mutants in the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat Res. 1970 Dec;10(6):597–605. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]