Abstract
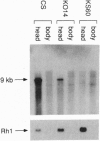
The Drosophila visual mutant, carrying the retinal degeneration A gene (rdgA), has photoreceptor cells that degenerate within a week after eclosion. Morphological studies suggested that this mutant harbors abnormalities in membrane turnover of the photoreceptor cells. Biochemically, the rdgA mutant lacks an eye-specific and membrane-associated diacylglycerol kinase (DGK; EC 2.7.1.107) activity in a gene-dosage-dependent manner, suggesting that rdgA gene encodes a DGK. We report the molecular cloning and characterization of a DGK gene, which maps to the rdgA locus. This gene, designated as DGK2, has a single open reading frame that encodes 1454 amino acids. Like porcine DGK, DGK2 has two cysteine-rich zinc-finger motifs as well as a DGK catalytic domain. The DGK2 protein contains four ankyrin-like repeats at the C-terminal region, suggesting that DGK2 is likely anchored to the membrane or cytoskeleton. Northern blot analysis and tissue in situ hybridization to adult sections revealed that DGK2 is expressed exclusively in the adult retina and that the amount of its mRNA is reduced in some of the rdgA mutant alleles. Furthermore, in two rdgA alleles, rdgA1 and rdgA2, nonsense and missense mutations occur within their DGK2 gene, respectively. Thus, we conclude that rdgA encodes an eye-specific DGK, the absence of which leads to rhabdomere degeneration due to defective phospholipid turnover.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Ankyrins. Adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8703–8706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. NF-kappa B and related proteins: Rel/dorsal homologies meet ankyrin-like repeats. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90321-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes C., Li T., Danciger M., Baxter L. C., Applebury M. L., Farber D. B. Retinal degeneration in the rd mouse is caused by a defect in the beta subunit of rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):677–680. doi: 10.1038/347677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Romero J. M., Doyle S., Elliott R., Murphy G., Carpenter R. floricaula: a homeotic gene required for flower development in antirrhinum majus. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1311–1322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90426-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Reichel E., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Yandell D. W., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):364–366. doi: 10.1038/343364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries P., Kenna P., Farrar G. J. On the molecular genetics of retinitis pigmentosa. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):804–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1589761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Yoshioka T., Hotta Y. Diacylglycerol kinase defect in a Drosophila retinal degeneration mutant rdgA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5996–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Yoshioka T., Hotta Y. Partial purification and characterization of membrane-associated diacylglycerol kinase of Drosophila heads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 31;1122(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90327-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Yamada K., Sakane F. Diacylglycerol kinase: a key modulator of signal transduction? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Feb;15(2):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyatkin N. I., Dulubova I. E., Chekhovskaya I. A., Grishin E. V. Cloning and structure of cDNA encoding alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81250-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masai I., Hosoya T., Kojima S., Hotta Y. Molecular cloning of a Drosophila diacylglycerol kinase gene that is expressed in the nervous system and muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masai I., Hotta Y. Genomic organization of a Drosophila phospholipase C, norpA, and molecular lesions in two temperature-sensitive mutants. J Biochem. 1991 Jun;109(6):867–871. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto-Suzuki E., Hirosawa K., Hotta Y. Structure of the subrhabdomeric cisternae in the photoreceptor cells of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurocytol. 1989 Feb;18(1):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01188427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto E., Hirosawa K., Takagawa K., Hotta Y. Structure of retinular cells in a Drosophila melanogaster visual mutant, rdgA, at early stages of degeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 May;252(2):293–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00214371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Harris G. L., Stevens C. F., Zuker C. S. A Drosophila mutant defective in extracellular calcium-dependent photoreceptor deactivation and rapid desensitization. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):230–232. doi: 10.1038/354230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Yamada K., Kanoh H., Yokoyama C., Tanabe T. Porcine diacylglycerol kinase sequence has zinc finger and E-F hand motifs. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):345–348. doi: 10.1038/344345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Ranganathan R., Hardy R. W., Marx J., Tsuchida T., Zuker C. S. Photoreceptor deactivation and retinal degeneration mediated by a photoreceptor-specific protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1478–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.1962207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Hirosawa K., Hotta Y. Analysis of photoreceptor membrane turnover in a Drosophila visual mutant, rdgA, by electron microscope autoradiography. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1990;39(1):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Brennan M. B., Danielson P. E., Kozak C. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Identification of a photoreceptor-specific mRNA encoded by the gene responsible for retinal degeneration slow (rds). Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):70–73. doi: 10.1038/338070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihtelic T. S., Goebl M., Milligan S., O'Tousa J. E., Hyde D. R. Localization of Drosophila retinal degeneration B, a membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol transfer protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1013–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihtelic T. S., Hyde D. R., O'Tousa J. E. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila retinal degeneration B (rdgB) gene. Genetics. 1991 Apr;127(4):761–768. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Weston K., Greenwald I. The Caenorhabditis elegans lin-12 gene encodes a transmembrane protein with overall similarity to Drosophila Notch. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):547–550. doi: 10.1038/335547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Inoue H., Hotta Y. Absence of diglyceride kinase activity in the photoreceptor cells of Drosophila mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91664-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]