Abstract
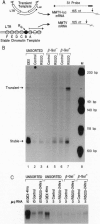
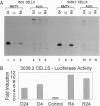
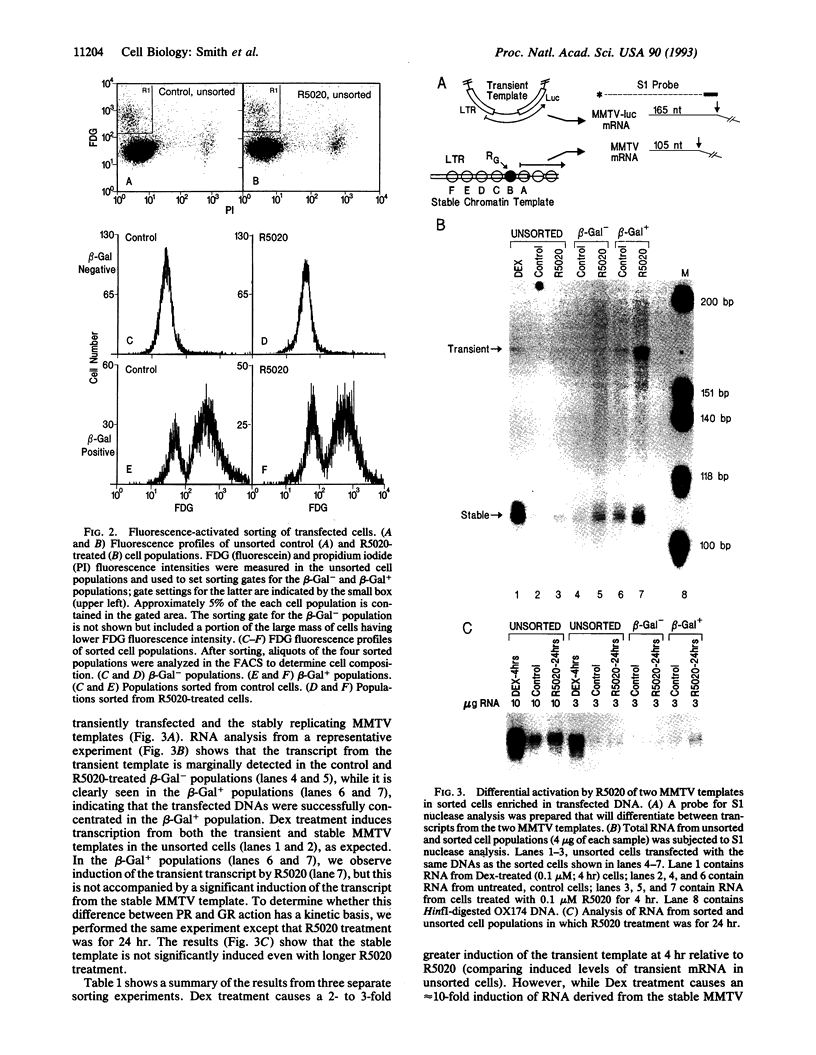
During development and differentiation, the expression of transcription factors is regulated in a temporal fashion. Newly expressed transcription factors must interact productively with target genes organized in chromatin. Although the mechanisms governing factor binding to chromatin templates are not well understood, it is now clear that template access can be dramatically influenced by nucleoprotein structure. We have examined the ability of a well characterized transactivator, the progesterone receptor (PR), to activate the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter organized either in stable, replicating templates that have a highly ordered nucleosome structure or as transiently transfected DNA, which adopts a less-defined structure. If the PR is transiently expressed in cells harboring both replicated and transient MMTV receptor constructs, it cannot significantly activate the stable replicated MMTV template. In contrast, when PR cDNA is stably inserted into the same cells and constitutively expressed, it gains the ability to activate both chromosomal and transiently introduced templates. These results demonstrate that newly expressed PR is not competent to activate the MMTV template in its native nucleoprotein conformation but acquires this ability upon prolonged expression in replicating cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Lefebvre P., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1347958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Tam S. P., Deugau K. V., Deeley R. G. Apolipoprotein C-II mRNA levels in primate liver. Induction by estrogen in the human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1676–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Bustin M., Marsaud V., Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. The transcriptionally-active MMTV promoter is depleted of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):273–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr K. D., Richard-Foy H. Glucocorticoids locally disrupt an array of positioned nucleosomes on the rat tyrosine aminotransferase promoter in hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9300–9304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Henderson D., Ponta H. The hormone response element of the mouse mammary tumour virus DNA mediates the progestin and androgen induction of transcription in the proviral long terminal repeat region. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):363–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Hager G. L. Binding of multiple factors to the MMTV promoter in crude and fractionated nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):609–628. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Northrop J. P., Nolan G. P., Mattila P. S., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. Single cell assay of a transcription factor reveals a threshold in transcription activated by signals emanating from the T-cell antigen receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1823–1834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowland P. L., Buetti E. Mutations in the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus differentially affect the response to progestins, androgens, and glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3999–4008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Loosfelt H., Lescop P., Sar S., Atger M., Perrot-Applanat M., Milgrom E. Mechanisms of nuclear localization of the progesterone receptor: evidence for interaction between monomers. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1147–1154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen J., Shastri N. Measurement of ligand-induced activation in single viable T cells using the lacZ reporter gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3972–3976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Greene G. L. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):745–747. doi: 10.1038/307745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S., Nakauchi H., Takahashi N. The dose dependence of glucocorticoid-inducible gene expression results from changes in the number of transcriptionally active templates. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2835–2842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Threshold phenomena and long-distance activation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1682–1685. doi: 10.1126/science.1388287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P., Berard D. S., Cordingley M. G., Hager G. L. Two regions of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat regulate the activity of its promoter in mammary cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2529–2537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A., Hager G. L. Induction of multiple replacement mutations by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis with extended mismatch primers. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Nov-Dec;4(6):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Kumar V., Chambon P., Yamamoto K. R. Signal transduction by steroid hormones: nuclear localization is differentially regulated in estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. Cell Regul. 1990 Feb;1(3):291–299. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese J. C., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Examination of the DNA-binding ability of estrogen receptor in whole cells: implications for hormone-independent transactivation and the actions of antiestrogens. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4531–4538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik A., Schütz G., Stewart A. F. Glucocorticoids are required for establishment and maintenance of an alteration in chromatin structure: induction leads to a reversible disruption of nucleosomes over an enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strair R. K., Towle M., Smith B. R. Retroviral mediated gene transfer into bone marrow progenitor cells: use of beta-galactosidase as a selectable marker. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4759–4762. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straka C., Hörz W. A functional role for nucleosomes in the repression of a yeast promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Wills K. N., Graupner G., Pfahl M. The human estrogen receptor has transcriptional activator and repressor functions in the absence of ligand. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nolan G. P., Pollock R., Prockop S., Li S. C., Herzenberg L. A., Alt F. W. A novel fluorescence-based system for assaying and separating live cells according to VDJ recombinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I., Yamamoto K. R. Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598–1604. doi: 10.1126/science.1360703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]