Abstract
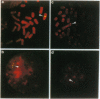
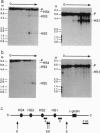
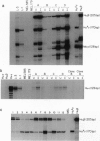
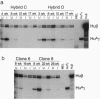
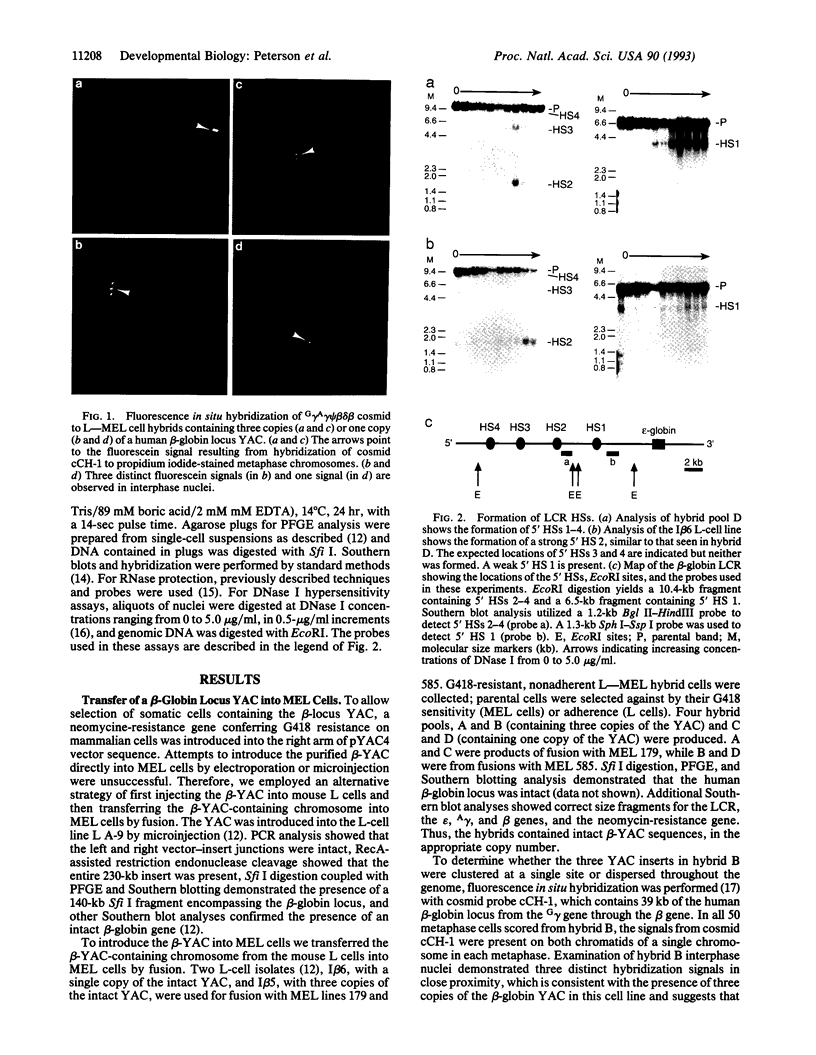
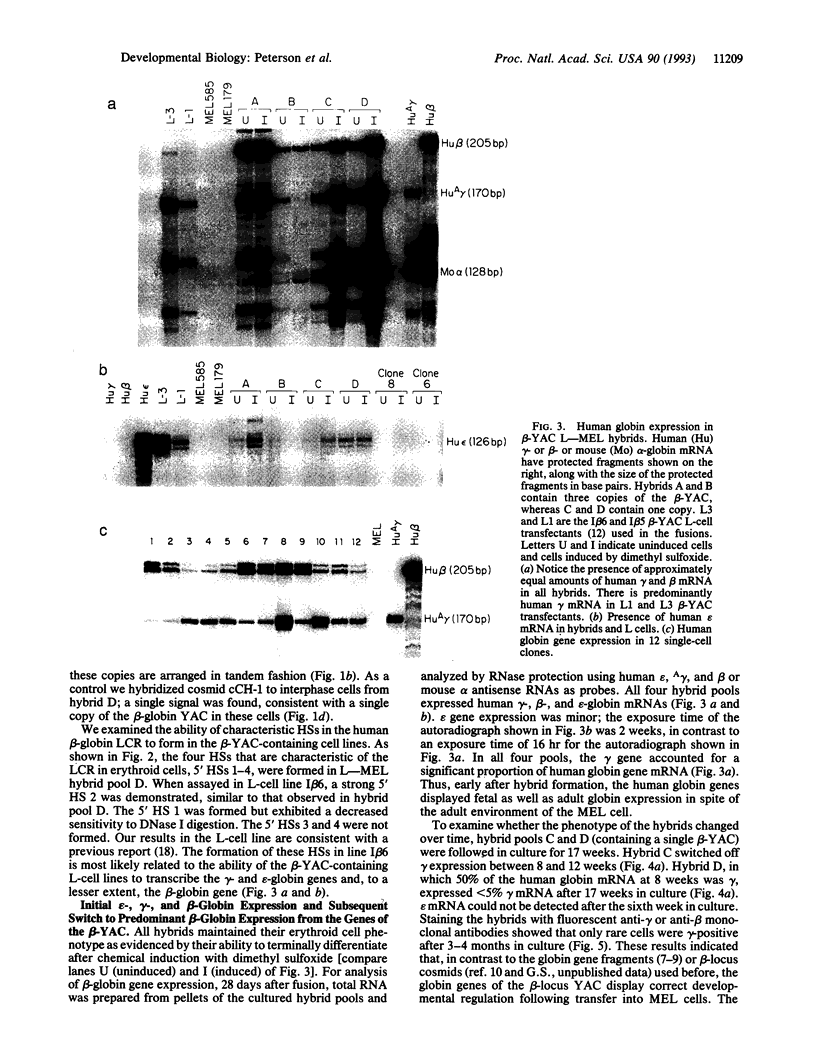
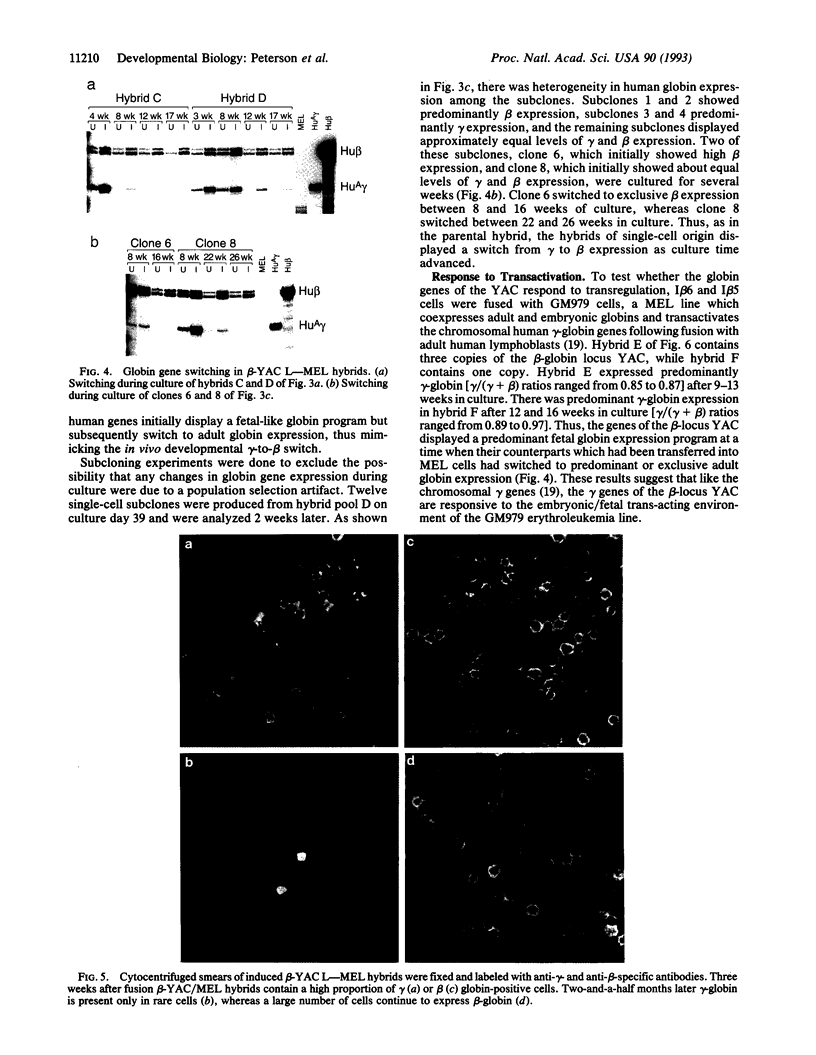
We demonstrate that transfer of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) containing 230 kb of the human beta-globin locus into mouse erythroleukemia cells by fusion results in correct developmental regulation of the human beta-like globin genes. Additionally, we show that early after hybrid formation, human embryonic epsilon- and fetal gamma-globin genes are coexpressed with the adult beta gene but that after 10-20 weeks in culture, globin gene expression switches to predominantly adult. Thus, in contrast to shorter gene constructs, the globin genes of the beta-globin locus YAC are regulated like the chromosomal globin genes. These results indicate that transfer of YACs into established cell lines can be used for the analysis of the developmental control of multigenic and developmentally regulated human loci.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Ryan T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Townes T. M. Human gamma- to beta-globin gene switching in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):380–389. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance P. F., Alderson M. K., Leppig K. A., Lensch M. W., Matsunami N., Smith B., Swanson P. D., Odelberg S. J., Disteche C. M., Bird T. D. DNA deletion associated with hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Henry L. Regulated expression of cloned human fetal A gamma-globin genes introduced into murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):475–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V., Nandi A., Schildkraut C. L., Skoultchi A. I. Erythroid-specific nuclease-hypersensitive sites flanking the human beta-globin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4324–4333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Brice M., Karlinsey J., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Developmental regulation of fetal to adult globin gene switching in human fetal erythroid x mouse erythroleukemia cell hybrids. Dev Biol. 1991 Nov;148(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90323-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Ebens A. J., Forrester W. C., Stamatoyannopoulos G. The human beta-globin locus activation region alters the developmental fate of a human fetal globin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7033–7037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Raich N., Ebens A. J., Papayannopoulou T., Costantini F., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Developmental regulation of human fetal-to-adult globin gene switching in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):309–313. doi: 10.1038/344309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Elder J. T., Groudine M. A developmentally stable chromatin structure in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler K. M., Burmeister M., Brownstein B. H., Taillon-Miller P., Myers R. M. Physical mapping of yeast artificial chromosomes containing sequences from the human beta-globin gene region. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):976–984. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90188-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Huxley C., Peterson K., Olson M. V. Microinjection of intact 200- to 500-kb fragments of YAC DNA into mammalian cells. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):659–667. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug B. A., Moon A. M., Ley T. J. Structure and function of the murine beta-globin locus control region 5' HS-3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5771–5778. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey C. H., Bodine D. M., Nienhuis A. W. Mechanism of DNase I hypersensitive site formation within the human globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1143–1147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley B. J., Abbott C. A., Wood W. G. Regulation of human fetal and adult globin genes in mouse erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1355–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Brice M., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Analysis of human hemoglobin switching in MEL x human fetal erythroid cell hybrids. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90667-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strouboulis J., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Developmental regulation of a complete 70-kb human beta-globin locus in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1857–1864. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. W., Raich N., Enver T., Anagnou N. P., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Butyrate induces expression of transfected human fetal and endogenous mouse embryonic globin genes in GM 979 erythroleukemia cells. Dev Genet. 1990;11(2):168–174. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020110207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitnik G., Hines P., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Murine erythroleukemia cell line GM979 contains factors that can activate silent chromosomal human gamma-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2530–2534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]