Abstract
The Brazilian South coast seasonally hosts numerous marine species, observed particularly during winter months. Some animals, including fur seals, are found dead or debilitated along the shore and may harbor potential pathogens within their microbiota. In the present study, a metagenomic approach was performed to evaluate the viral diversity in feces of fur seals found deceased along the coast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The fecal virome of two fur seal species was characterized: the South American fur seal (Arctocephalus australis) and the Subantarctic fur seal (Arctocephalus tropicalis). Fecal samples from 10 specimens (A. australis, n = 5; A. tropicalis, n = 5) were collected and viral particles were purified, extracted and amplified with a random PCR. The products were sequenced through Ion Torrent and Illumina platforms and assembled reads were submitted to BLASTx searches. Both viromes were dominated by bacteriophages and included a number of potentially novel virus genomes. Sequences of picobirnaviruses, picornaviruses and a hepevirus-like were identified in A. australis. A rotavirus related to group C, a novel member of the Sakobuvirus and a sapovirus very similar to California sea lion sapovirus 1 were found in A. tropicalis. Additionally, sequences of members of the Anelloviridae and Parvoviridae families were detected in both fur seal species. This is the first metagenomic study to screen the fecal virome of fur seals, contributing to a better understanding of the complexity of the viral community present in the intestinal microbiota of these animals.
Introduction
Every year, hundreds of marine species arrive at the coast of Rio Grande do Sul, the southernmost state in Brazil. Among these species, which include birds, turtles and mammals, fur seals are regular visitors that can be observed near or on-shore. These animals are driven to this region by the Malvinas current, particularly during winter months [1–3]. Although some fur seals may reach the coast to rest, several are found dead or debilitated along the shore and the cause of their weakness or death cannot always be determined [4,5]. Few studies have attempted to identify the pathogens that infect these populations and their roles as etiological agents of diseases and as potential zoonotic agents, especially those concerned with viruses [6–10]. While the virome of marine mammals has already been investigated [11], these studies have been restricted to species native to the northern hemisphere. Little is known about the viruses that infect marine mammals limited to the southern hemisphere and the effects of this geographical difference on their virome profiles.
Here, we evaluated the viral diversity of two species of pinnipeds from the Otariidae family from the southern hemisphere: the South American fur seal (Arctocephalus australis) and the Subantarctic fur seal (Arctocephalus tropicalis). While the South American fur seal is found along the Pacific and Atlantic coast of South America, the Subantarctic fur seal has a broader range that extends from the South Atlantic to Indian ocean islands. The South American fur seal is more frequently sighted in Rio Grande do Sul coast, mostly juveniles, due to the proximity of its closest breeding colony, located in the neighboring country of Uruguay. By contrast, the closest Subantarctic fur seals colonies are located at more than 4,000 km away at the south Atlantic islands of Gough and Tristan da Cunha [3,12]. Juveniles and adults specimens of Subantarctic fur seals reach the Atlantic coast with the help of ocean currents, and it is known that juveniles do not stay in the colonies during breeding seasons, while adults can travel long distances after mating [1,13].
The aim of this study was to examine the fecal virome of two species of fur seals whose cadavers were found along the shore of Rio Grande do Sul state. Anelloviruses, parvoviruses and picornaviruses were identified, as well as potential new members of Sakobuvirus, Picobirnavirus and Rotavirus. A sapovirus very similar to California sea lion sapovirus 1 was found in the Subantarctic fur seal, and a hepevirus-like sequence was identified. The data provides a preliminary characterization of the viruses that occur within fur seals populations of the southern hemisphere.
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
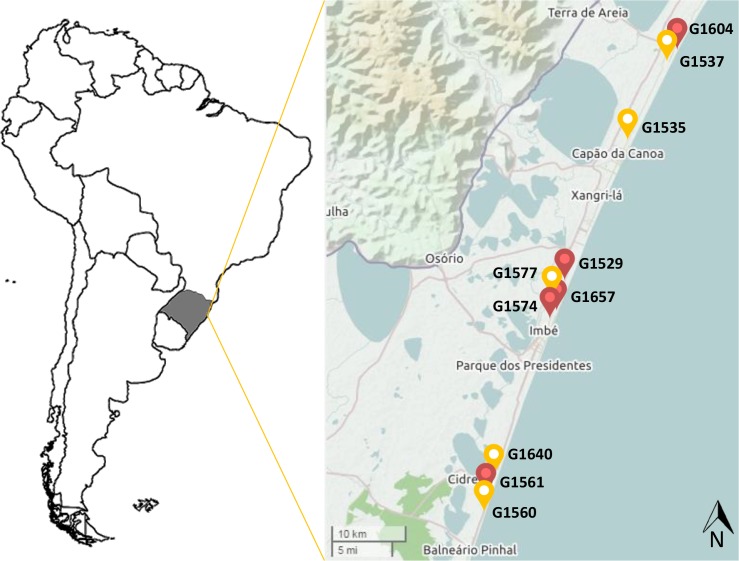
Fecal samples from 10 specimens (A. australis, n = 5; A. tropicalis, n = 5) were collected directly from the intestines of deceased fur seals found along shores between August 2012 and September 2013 by the Center for Coastal, Limnology and Marine Studies (CECLIMAR) team. Samples for each species were pooled and kept at -80°C until processing. All samples from this study were collected in strict accordance with the Brazilian law, and the license for collecting zoological material was granted by SISBIO/Ministry of the Environment (License number: 20185–4). The location and information about the specimens are provided in Table 1 and Fig 1.
Table 1. Samples used in this study.
| Pool no. | No. | Species | Length (cm) | Weight (kg) | Sex | Carcass classification code* | Date of collection (dd/mm/yyyy) | Collection location | Geolocation latitude/ longitude (decimal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G1529 | South American fur seal Arctocephalus australis | 94.2 | 10.6 | Male | 2 | 02/08/2012 | Osório, RS | -29.878119/-50.073224 |
| 1 | G1560 | South American fur seal Arctocephalus australis | 92 | 9.5 | Male | 2 | 09/08/2012 | Cidreira, RS | -30.165946/-50.197728 |
| 1 | G1574 | South American fur seal Arctocephalus australis | 89.4 | 10.8 | Male | 2 | 16/08/2012 | Imbé, RS | -29.94758/-50.105842 |
| 1 | G1604 | South American fur seal Arctocephalus australis | 92 | 15.5 | Male | 2 | 31/08/2012 | Capão da Canoa, RS | -29.657469/-49.954338 |
| 1 | G1657 | South American fur seal Arctocephalus australis | 88 | 12 | Male | 2 | 11/09/2013 | Imbé, RS | -29.94579/-50.10498 |
| 2 | G1535 | Subantarctic fur seal Arctocephalus tropicalis | 91.9 | 8.4 | Male | 2 | 02/08/2012 | Capão da Canoa, RS | -29.730323/-49.995557 |
| 2 | G1537 | Subantarctic fur seal Arctocephalus tropicalis | 90.6 | 9 | Male | 2 | 02/08/2012 | Capão da Canoa, RS | -29.665492/-49.959170 |
| 2 | G1561 | Subantarctic fur seal Arctocephalus tropicalis | 91.9 | 8.8 | Male | 2 | 09/08/2012 | Cidreira, RS | -30.174591/-50.200809 |
| 2 | G1577 | Subantarctic fur seal Arctocephalus tropicalis | 80.5 | 7.1 | Male | 3 | 16/08/2012 | Osório, RS | -29.917806/-50.091768 |
| 2 | G1640 | Subantarctic fur seal Arctocephalus tropicalis | 157.5 | 40.9 | Male | 2 | 25/07/2013 | Tramandaí, RS | -30.13273/-50.18535 |
*Code for carcass classification according to Geraci & Lounsbury (1993)[14]: freshly dead, edible (2); and decomposed, but organs basically intact (3).
Fig 1. Sample location map.
Map indicating the location of where the samples were collected along the coast of the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil (shaded). The map was extracted from the Open Street Map[15] database.
Viral Particle Purification and Nucleic Acid Extraction
Fecal samples were suspended in Hank's balanced salt solution, vigorously vortexed and then centrifuged at 2500 × g for 90 min at 4°C. The supernatant was again centrifuged for 10 min at maximum speed and then filtered through a 0.45 μm syringe filter (MF-Millipore). The viral particles were harvested and pelleted on a 25% sucrose cushion by ultracentrifugation at 190000 × g for 4h at 4°C. The pellet was resuspended in TE buffer and clarified by emulsifying with 1/1 (v/v) chloroform and centrifugation. In order to remove nucleic acids not protected by the capsid, the purified samples were treated with 100 U of DNase I (Roche) and 20 U of RNase (Invitrogen) at 37°C for 2h, as similar to other studies [16,17].
Viral genomes were extracted via commercial kits (PureLink® Viral RNA/DNA Invitrogen for DNA extraction; RNeasy® Mini Kit Qiagen for RNA) and processed as described by [18] with minor modifications. Briefly, a complementary strand of extracted DNA (5 μl) was synthesized using the Klenow fragment DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs) and primer K-randoms (GAC CAT CTA GCG ACC TCC ACM NN MNM) designed by [19]. For the extracted RNA (10 μl), a reverse transcription using the primer K-randoms was carried out prior the second strand synthesis using Klenow fragment DNA polymerase.
Library Construction for Metagenomic Sequencing
A random PCR was performed in a final volume of 50 μL, containing 5 μL of template, 0.8 μM of the fixed portion of primer K-randoms (GAC CAT CTA GCG ACC TCC AC), 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 1X PCR Buffer, 2.5 mM MgCl2, and 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase. Amplification conditions consisted of an initial denaturation cycle at 95°C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles for amplification (95°C for 1 min, 53°C for 1 min and 72°C for 1 min), and final extension at 72°C for 7 min. The products were visualized by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, purified and processed for Ion Torrent (Life Technologies, USA) using a 316 Ion chip, which was performed by the Genomic and Molecular Biology Laboratory from the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul. The same process, including the random PCR, was repeated for Illumina MiSeq platform sequencing using Kit v2 in the 300-cycles (2x150) format performed by Fepagro Animal Health Institute of Veterinary Research Desidério Finamor (IPVDF), Eldorado do Sul, Brazil.
Bioinformatics
Ion Torrent reads were trimmed using PRINSEQ (prinseq.sourceforge.net) and the quality of the sequences was analyzed with FastQC (www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Trimmed reads were assembled de novo by using MetaVelvet v1.2.01 (metavelvet.dna.bio.keio.ac.jp) with a k-mer of 51. Illumina reads were trimmed for primers using Geneious 8.1.3 and de novo assembled with St. Petersburg genome assembler (SPAdes) 3.5.0 (bioinf.spbau.ru/spades). The resulting contigs (>100bp) were submitted to BLASTx search against the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) non-redundant database (nr) and its viral database by using an E-value cutoff of 1e-05. The contigs were classified into eukaryotic viruses, bacteriophages, bacterium, eukaryotes and unknown based on lowest E-value. Contigs of eukaryotic viruses were used for sequence and phylogenetic analyses and bacteriophage sequences were not further analyzed. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences derived in this study are: KR261062, KR261063, KR261065, KR816222, KR816223 (fur seal anelloviruses); KR261066-KR261068, KR261070-KR261075, KR261077-KR261079, KR816217, KR816218, KR816220, KR816221 (fur seal parvoviruses); KR106199-KR106202, KR816213, KR816215, KR337994 (fur seal picornaviruses); KR072975-KR072979, KR072981, KR072982, KR072984 (fur seal sakobuvirus); KR106194-KR106196, KR106198, KR816216 (fur seal picobirnavirus); KR072985-KR072990 (fur seal rotavirus), KR827461 (fur seal hepevirus); KR072992, KR072994, KR072995 (fur seal sapovirus). The sequence data obtained from this study is available at the NIH Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the study accession number SRP070196.
Phylogenetic Analysis
Nucleotide or translated amino acid sequences from the contigs of anellovirus, parvovirus, picornavirus, picobirnavirus, rotavirus, sapovirus and hepevirus-like were aligned with MUSCLE (www.drive5.com/muscle) and phylogenetic trees were built using MEGA6 [20]. Trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining (NJ) method [21] with a bootstrap of 1000 replicates, p-distance model, and gaps were treated as pairwise deletion. The contig sequences from this study were compared with other selected gene sequences available in the GenBank.
Results
Overview
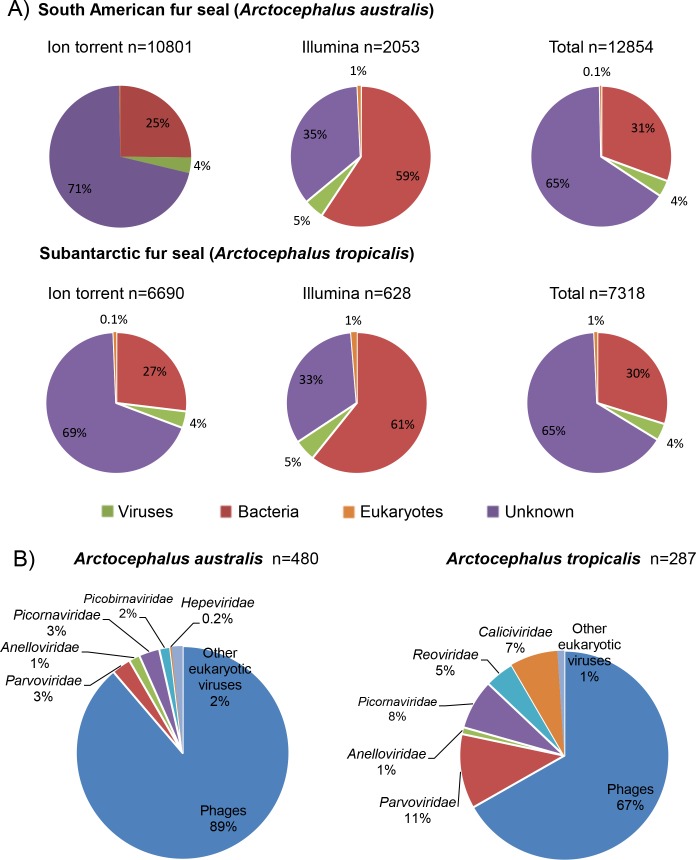
A substantial proportion of the assembled reads detected in both fur seals species have no significant similarity to any of the sequences deposited to date at GenBank. About 70% of the assembled reads from the Ion Torrent platform had no significant hits, whereas in Illumina NGS apparatus the sequences with no identified matches reached 35% (cutoff for significant as <1e-05 BLASTx E score). The same divergence was observed with the number of bacterial hits, however, Ion Torrent had the lowest number of hits (about 25%) when compared to Illumina (about 60%).
The viral component detected in either of the sequencing platforms represented 4–5% of total sequences, regardless of the fur seal species analyzed. Most of the viral hits were from bacteriophages, in agreement with previous studies of bats and dromedary fecal viromes [22–24]. Some of the contigs from eukaryotic viruses displayed low similarity to currently known viruses and, as such, may represent novel viruses. The Subantarctic fur seal was found to carry a larger proportion of identifiable sequences of eukaryotic viruses (95 hits, corresponding to 33% of total assembled reads assigned to viruses) when compared to the South American fur seal (53 hits, corresponding to 11% of total assembled reads assigned to viruses). The proportional taxonomic composition of the assembled reads is shown in Fig 2.
Fig 2. Taxonomic classification of assembled reads (>100bp).
(A) Pie charts of assembled reads based on BLASTx best E-scores (cutoff: 10e-05) against the GenBank non-redundant and viral databases. (B) Taxonomic distribution of viruses for each fur seal species.
South American Fur Seal (Arctocephalus australis)
Ion Torrent sequencing generated a total of 475,511 reads with an average length of 191 bp which were trimmed to a final number of 282,732 reads. MetaVelvet de novo assembly of trimmed reads resulted in 10,801 contigs (>100 bp). Illumina sequencing generated a total of 496,016 paired-end reads (average length of 149 bp) which were trimmed for primers and assembled de novo with St. Petersburg genome assembler (SPAdes) into 2,053 contigs (>100 bp). BLASTx results from the Ion Torrent contigs revealed sequences with similarity to the eukaryotic virus families Parvoviridae (11 contigs), Anelloviridae (5), Picornaviridae (10), Picobirnaviridae (5) and invertebrate virus (1). Illumina contigs displayed similarity to genomes of members of the families Parvoviridae (3), Anelloviridae (3), Picornaviridae (5), Picobirnaviridae (3) and Hepeviridae (1), among other viruses that infect fish, small invertebrates and insects (7). Contigs with significant BLASTx hits and their GenBank accession numbers are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Contigs (>200bp) with significant BLASTx hits to known eukaryotic viruses obtained from the South American fur seals (Arctocephalus australis).
| Contig ID | Accession number | Length (nt) | Family/Genus | Genome | Product | Best hit | Amino acid identity (%) | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58 | KR261062 | 1292 | Anelloviridae | ssDNA | putative ORF1 | ORF1 [Seal anellovirus 5] (KM262782) | 35 | 5e-61 |
| 59 | KR261063 | 480 | Anelloviridae | ssDNA | putative ORF1 | ORF1 [Seal anellovirus 5] (KM262782) | 45 | 1e-14 |
| 62 | KR816222 | 1080 | Anelloviridae | ssDNA | putative ORF1 | ORF1 [Torque teno sus virus 1a] (HM633252) | 84 | 0.0 |
| 53 | KR261066 | 616 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | VP2 [Tusavirus 1] (KJ495710) | 46 | 8e-46 |
| 54 | KR261067 | 334 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | capsid protein [Canine parvovirus 2a](HM042734) | 50 | 2e-29 |
| 55 | KR261068 | 460 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | NS1 [Solwezi bufavirus] (LC011438) | 43 | 1e-23 |
| 57 | KR261070 | 237 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | VP2 [Fox parvovirus] (KC692368) | 46 | 3e-11 |
| 63 | KR816220 | 344 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | NS1 [Tusavirus 1] KJ495710) | 82 | 1e-65 |
| 34 | KR106199 | 561 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [Hepatitis A virus] (FJ360731) | 36 | 3e-15 |
| 35 | KR106200 | 707 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | capsid protein [Hepatitis A virus] (AF365952) | 37 | 1e-39 |
| 36 | KR106201 | 519 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | putative 3C [Avian encephalomyelitis virus] (NP_653151) | 39 | 2e-26 |
| 37 | KR106202 | 285 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [Bat picornavirus] (KJ641684) | 38 | 5e-12 |
| 65 | KR816213 | 466 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | 1B VP2 mature peptide [Hepatitis A virus] (NP_041008) | 52 | 2e-50 |
| 67 | KR816215 | 318 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | hypothetical protein [Avian encephalomyelitis virus] (AJ006950) | 32 | 2e-09 |
| 29 | KR106194 | 217 | Picobirnaviridae Picobirnavirus | dsRNA | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | RNA dependent RNA polymerase [Human picobirnavirus] (AB517735) | 52 | 3e-13 |
| 30 | KR106195 | 968 | Picobirnaviridae Picobirnavirus | dsRNA | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Fox picobirnavirus] (KC692366) | 71 | 1e-169 |
| 31 | KR106196 | 240 | Picobirnaviridae Picobirnavirus | dsRNA | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Dromedary picobirnavirus] (KM573806) | 77 | 3e-34 |
| 33 | KR106198 | 293 | Picobirnaviridae Picobirnavirus | dsRNA | capsid protein | hypothetical protein [Human picobirnavirus] (GU968923) | 35 | 1e-08 |
| 64 | KR816216 | 330 | Picobirnaviridae Picobirnavirus | dsRNA | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Dromedary picobirnavirus] (KM573806) | 82 | 3e-61 |
| 73 | KR827461 | 661 | Hepevirus-like | +ssRNA | polyprotein | nonstructural protein [Hepatitis E virus] (JQ026407) | 27 | 4e-07 |
Subantarctic Fur Seal (Arctocephalus tropicalis)
Ion Torrent sequencing generated a total of 784,917 reads with an average length of 184 bp which were trimmed into 288,611 reads. Trimmed reads were de novo assembled with MetaVelvet into 6,690 contigs (>100 bp). Illumina sequencing generated a total of 1,253,988 paired-end reads (average length of 144 bp) which were trimmed for primers and de novo assembled with SPAdes into 628 contigs (>100 bp). For Ion Torrent contigs, the eukaryotic virus families with significant similarity to results from BLASTx searches were Parvoviridae (24 contigs), Anelloviridae (2), Picornaviridae (19), Reoviridae (13), Caliciviridae (18), other insect viruses (2) and a circovirus-like hit (1). Illumina contigs had similarity with Parvoviridae (9), Anelloviridae (1), Picornaviridae (3), Caliciviridae (3) and Reoviridae (1). Contigs with significant BLASTx hits and their GenBank accession numbers are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Contigs (>200bp) with significant BLASTx hits to known eukaryotic viruses obtained from the Subantarctic fur seals (Arctocephalus tropicalis).
| Contig ID | Accession number | Length (nt) | Family/Genus | Genome | Product | Best hit | Amino acid identity (%) | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52 | KR261065 | 347 | Anelloviridae | ssDNA | putative ORF2 | ORF2 [Torque teno zalophus virus 1] (NC_012126) | 78 | 5e-18 |
| 72 | KR816223 | 467 | Anelloviridae | ssDNA | putative ORF2 and ORF1 | ORF1 [Torque teno sus virus 1a] (HM633252) | 88 | 4e-39 |
| 40 | KR261071 | 1519 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | VP2 [Tusavirus 1] (KJ495710) | 39 | 1e-85 |
| 41 | KR261072 | 1648 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | NS1 [Miniopterus schreibersii parvovirus] (KC154061) | 57 | 7e-131 |
| 42 | KR261073 | 628 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | nonstructural protein NS1 [Tumor virus X] (KJ631100) | 44 | 2e-43 |
| 43 | KR261074 | 565 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | NS1 [Turkey parvovirus TP1-2012/HUN] (KF925531) | 36 | 2e-13 |
| 44 | KR261075 | 612 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | putative VP1 [Tusavirus 1] (KJ495710) | 39 | 2e-18 |
| 46 | KR261077 | 349 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | VP protein [Canine parvovirus] (KM235293) | 55 | 2e-26 |
| 47 | KR261078 | 957 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | non-structural protein 1 [Chipmunk parvovirus] (U86868) | 37 | 1e-26 |
| 48 | KR261079 | 301 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | capsid protein [Canine parvovirus 2b] (JQ730016) | 53 | 6e-25 |
| 68 | KR816217 | 438 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | putative VP1 [Tusavirus 1] (KJ495710) | 42 | 1e-18 |
| 69 | KR816218 | 322 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | capsid protein | capsid protein VP2 [Mpulungu bufavirus] (NC_026815) | 36 | 1e-07 |
| 70 | KR816221 | 319 | Parvoviridae | ssDNA | NS1 | NS1 [Miniopterus schreibersii parvovirus] (KC154061) | 41 | 1e-14 |
| 61 | KR337994 | 438 | Picornaviridae | +ssRNA | polyprotein | AEV polyprotein [Avian encephalomyelitis virus] (NC_003990) | 34 | 4e-15 |
| 12 | KR072975 | 1271 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [Feline sakobuvirus A] (NC_022802) | 58 | 6e-126 |
| 13 | KR072976 | 477 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [Kobuvirus SZAL6-KoV/2011/HUN] (KJ934637) | 52 | 4e-12 |
| 14 | KR072977 | 289 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [Feline sakobuvirus A] (NC_022802) | 66 | 3e-22 |
| 15 | KR072978 | 273 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | VP3 [Feline sakobuvirus A] (YP_008802588) | 66 | 1e-34 |
| 16 | KR072979 | 227 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | VP1 [Feline sakobuvirus A] (YP_008802588) | 59 | 2e-12 |
| 18 | KR072981 | 466 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | 2C [Feline sakobuvirus A] (YP_008802588) | 59 | 3e-58 |
| 20 | KR072982 | 767 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | +ssRNA | polyprotein | 3D [Feline sakobuvirus A] (YP_008802588) | 65 | 3e-117 |
| 22 | KR072984 | 430 | Picornaviridae Sakobuvirus | + ssRNA | polyprotein | 3D [Feline sakobuvirus A] (YP_008802588) | 73 | 1e-67 |
| 23 | KR072985 | 469 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | NSP2 | nonstructural protein 2 [Bovine rotavirus C] (AB874653) | 69 | 3e-66 |
| 24 | KR072986 | 412 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | NSP3 | nonstructural protein 3 [Bovine rotavirus C] (AB874654) | 45 | 6e-33 |
| 25 | KR072987 | 928 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | VP1 | VP1 [Bovine rotavirus C] (AB738412) | 69 | 2e-137 |
| 26 | KR072988 | 442 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | VP3 | VP3 [Human rotavirus C] (HQ185645) | 51 | 5e-41 |
| 27 | KR072989 | 357 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | VP3 | viral protein 3 [Bovine rotavirus C] (AB874621) | 65 | 6e-46 |
| 28 | KR072990 | 360 | Reoviridae Rotavirus | dsRNA | VP7 | outer capsid protein VP7 [Human rotavirus C] (JQ177070) | 59 | 9e-42 |
| 02 | KR072992 | 2932 | Caliciviridae Sapovirus | + ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [California sea lion sapovirus 1] (JN420370) | 98 | 0.0 |
| 06 | KR072994 | 1400 | Caliciviridae Sapovirus | + ssRNA | polyprotein | polyprotein [California sea lion sapovirus 1] (JN420370) | 98 | 0.0 |
| 07 | KR072995 | 2408 | Caliciviridae Sapovirus | + ssRNA | polyprotein and VP2 | polyprotein [California sea lion sapovirus 1] (JN420370) | 96 | 0.0 |
Anellovirus
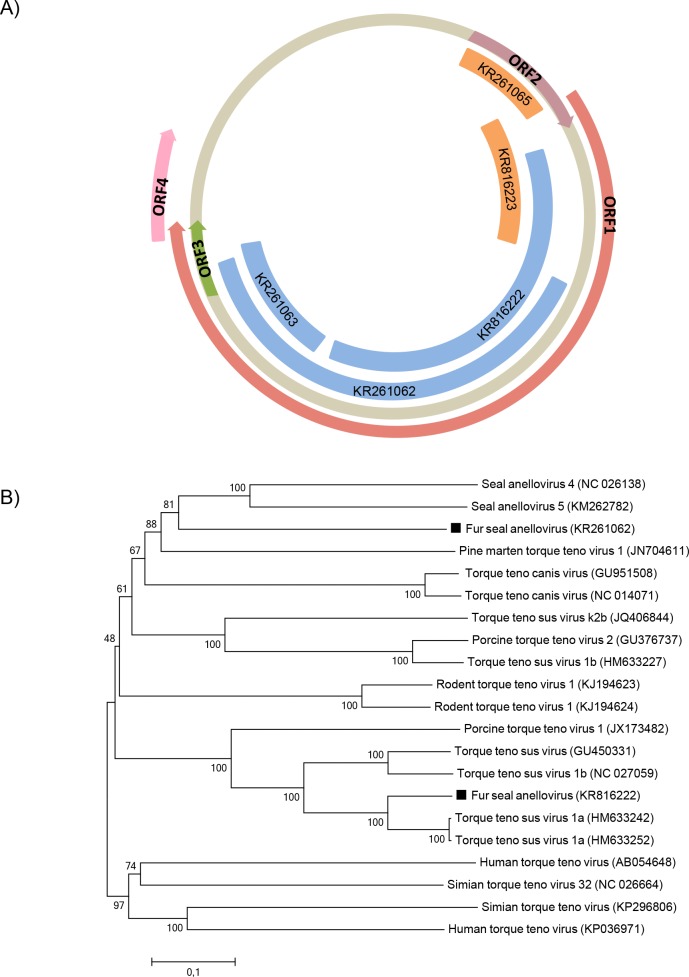
Anelloviruses are small, non-enveloped, circular ssDNA viruses belonging to the Anelloviridae family [25]. Anellovirus genome sequences were detected in both fur seal species (Fig 3A). Few sequences from the South American fur seal had the closest similarity to Seal anellovirus 5, with an amino acid identity ranging from 35–45% and covering up to 65% of ORF1. Another sequence from the Subantarctic fur seal had the closest similarity to Torque teno zalophus virus1 (TTZV), with 78% amino acid identity and covering 69% of ORF2 of TTZV. Both fur seal species had sequences with the closest similarity to Torque teno sus virus 1a, with an amino acid identity ranging from 84–88% and coverage of up to 56% of ORF1.
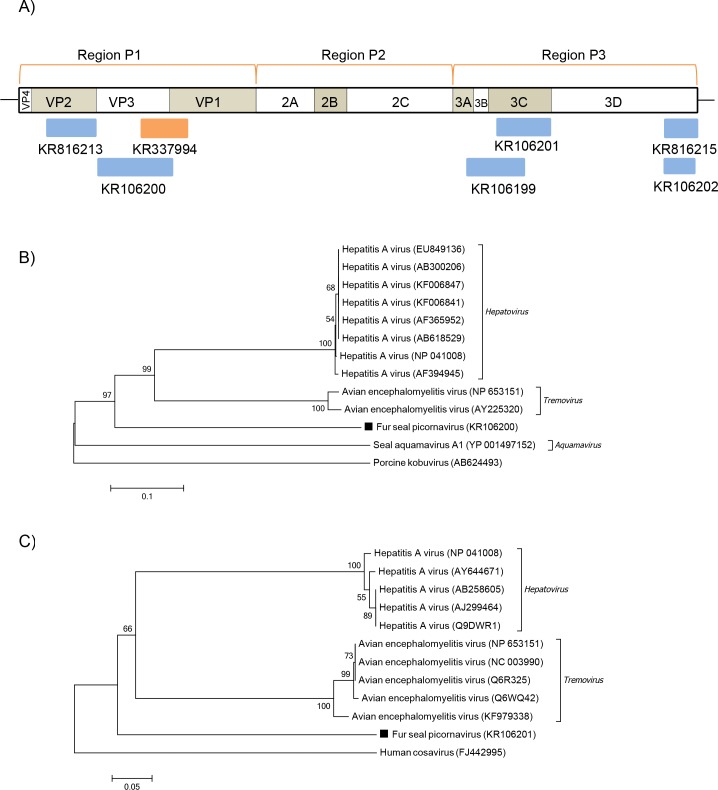
Fig 3. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal anellovirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of anelloviruses using as example the torque teno virus (~3.8 kb). The blue bars represent the contigs from South American fur seal and the orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (233 aa) from the ORF1 of 21 anelloviruses. Human and simian torque teno viruses were used as outgroup. The anellovirus sequences from South American fur seal identified in this study are labeled with black squares. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Due to the high divergence within anelloviruses, ORF1 sequences are the most indicative to phylogenetic analyses [25]. Phylogenetic trees of partial ORF1 amino acid sequences obtained from South American fur seals showed that distinct anelloviruses grouped in different clusters: one most closely related to seal anelloviruses, whereas the other sequence was placed on the same clade as swine torque teno viruses (Fig 3B).
Parvovirus
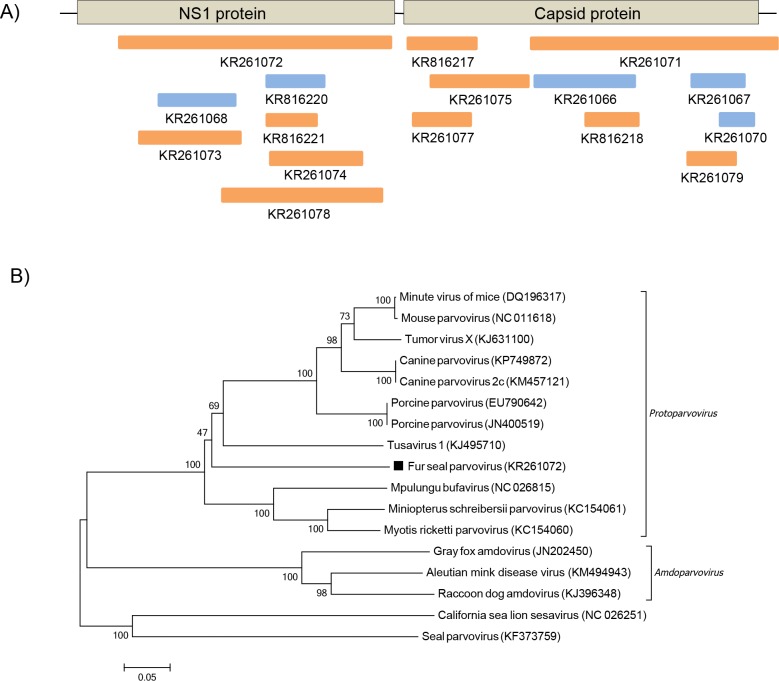
Parvoviruses are non-enveloped linear ssDNA viruses, members of the Parvoviridae family. In this study, both fur seals species had sequences (Fig 4A) more closely related to mammal parvoviruses of the Parvovirinae, a subfamily that infects vertebrates and is currently divided into eight genera [26,27]. The amino acid identity of those sequences with members of the Parvovirinae ranged from 36–82%. Phylogenetic analysis of partial NS1 sequence, conserved within parvoviruses, showed that the fur seal parvovirus clustered with members of the Protoparvovirus genus, distant from previously described pinniped parvorviruses (Fig 4B).
Fig 4. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal parvovirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of parvoviruses using as example the tusavirus (~4.4 kb). The blue bars represent the contigs from South American fur seal and the orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (261 aa) from the NS1 protein of 17 parvoviruses. Seal parvovirus and California sea lion sesavirus were used as outgroup. The parvovirus sequence from Subantarctic fur seal identified in this study is labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Picornavirus
Picornaviruses are small, non-enveloped, positive sense ssRNA viruses of the Picornaviridae family, which has, to date, 29 recognized genera, though often increasing [28–30]. Picornavirus sequences more related to Hepatitis A (HAV) and Avian encephalomyelitis viruses (AEV) were detected in both fur seal species examined (Fig 5A). HAV belongs to Hepatovirus and AEV to Tremovirus, which are closely related genera [31]. The polyprotein sequences obtained here displayed between 32–39% of amino acid identity to both Hepatovirus and Tremovirus members, and one sequence shared 52% amino acid identity with HAV VP2. Phylogenetic analyses were based on the picornavirus polyprotein functional regions: P1, which encodes for structural proteins, and P2-P3, which encode for proteins involved in replication [28]. The analysis of partial P1 sequences identified here showed the fur seal picornavirus forming a monophyletic group with the Hepatovirus and Tremovirus genera, but on a different branch (Fig 5B). When partial sequences of P3 region were analyzed they still shared the same root, with the fur seal picornavirus placed in a similar way (Fig 5C).
Fig 5. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal picornavirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of picornaviruses using as an example the hepatits A virus (~7.4 kb). The blue bars represent the contigs from South American fur seal and the orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (219 aa) from the P1 region of the polyprotein of 13 picornaviruses. Porcine kobuvirus was used as outgroup. (C) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (122 aa) from the P3 region of the polyprotein of 12 picornaviruses. Human cosavirus was used as outgroup. The picornavirus sequences from South American fur seal identified in this study are labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
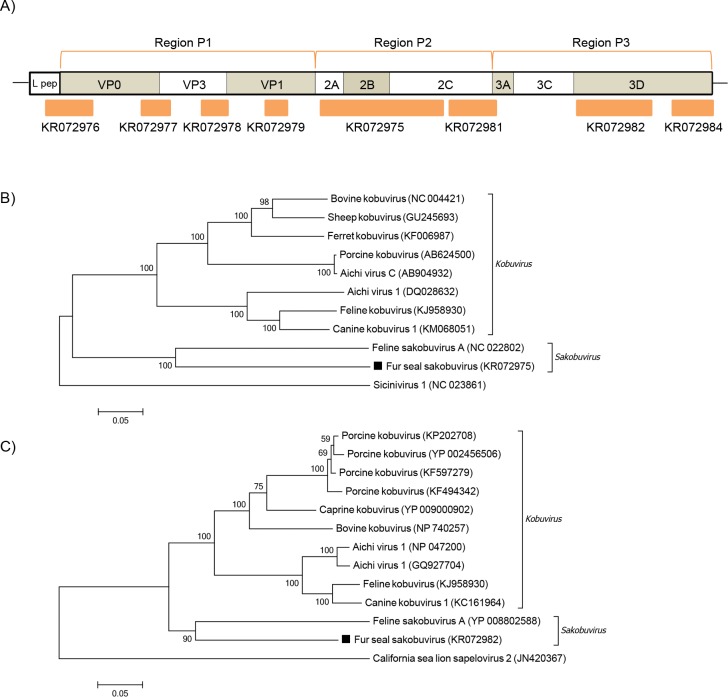
In addition to the above-mentioned picornaviruses, distinct members of this family were found only in Subantarctic fur seals. With the exception of one sequence whose best BLASTx hit had 52% of amino acid identity to a kobuvirus, all other contigs displayed the highest amino acid identity to Feline sakobuvirus A (FSVA), which ranged from 58–73% with a total coverage of 59% of its polyprotein (Fig 6A). One sequence displayed 59% of amino acid identity to FSVA VP1, and the amino acid identity of VP3 was of 66%. The sequence covering the 2C region had 59% of amino acid identity, while the two 3D sequences here identified ranged from 65–73% of FSVA 3D region. Phylogenetic analyses of partial P2 and P3 regions (Fig 6B and 6C, respectively) showed the fur seal picornavirus, temporarily named Fur seal sakobuvirus (FSSV), clustered with FSVA, member of the Sakobuvirus genus.
Fig 6. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal sakobuvirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the sakobuvirus genome using Feline sakobuvirus A (~7.8 kb—NC_022802) as a reference. The orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (409 aa) from the P2 region of the polyprotein of 11 picornaviruses. Sicinivirus 1 was used as outgroup. (C) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial amino acid sequences (255 aa) from the 3D region of the polyprotein of 13 picornaviruses. California sea lion sapelovirus 2 was used as outgroup. The sakobuvirus sequences from the Subantarctic fur seal from this study used in phylogenetic analyses are labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Picobirnavirus
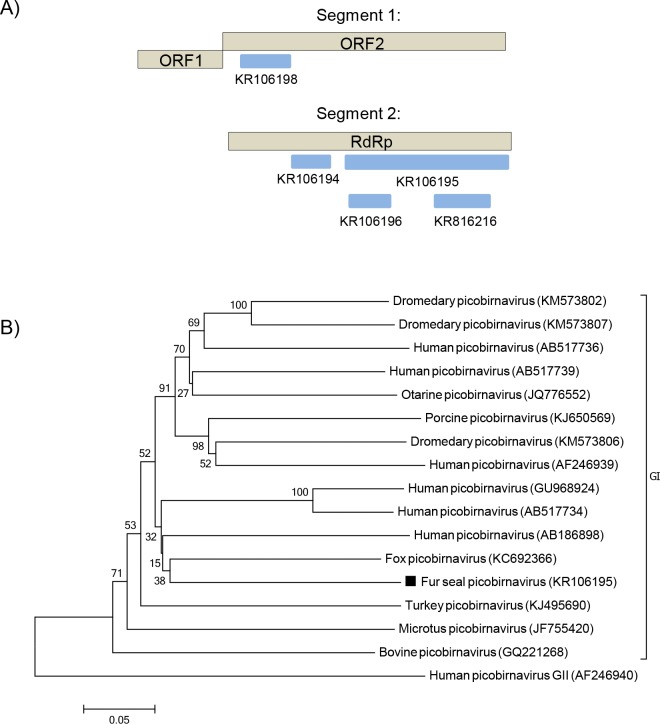
Picobirnaviruses are small, non-enveloped, bisegmented dsRNA viruses of the Picobirnaviridae family. These highly variable viruses are classified in a sole genus, Picobirnavirus, which on its turn is divided into two genogroups (I and II), based on sequence similarities of the RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase gene (RdRp) [32,33]. Sequences of picobirnavirus RdRp and capsid protein were detected in the South American fur seal samples (Fig 7A), having the highest similarity with members of genogroup I, with an amino acid identity ranging from 35–82%. Phylogenetic analyses of the partial RdRp gene (743 bp, which corresponds to 44% of the RdRp gene) confirmed that the fur seal picobirnavirus identified here clustered with members of genogroup I, with a nucleotide identity ranging from 60–68% (Fig 7B).
Fig 7. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal picobirnavirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of picobirnaviruses using as an example the human picobirnavirus (~4.2 kb). The blue bars represent the contigs from South American fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial nucleotide sequences (743 bp) from the RdRp gene of 17 picobirnaviruses. Human picobirnavirus GII was used as outgroup. The picobirnavirus sequence from South American fur seal identified in this study is labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Rotavirus
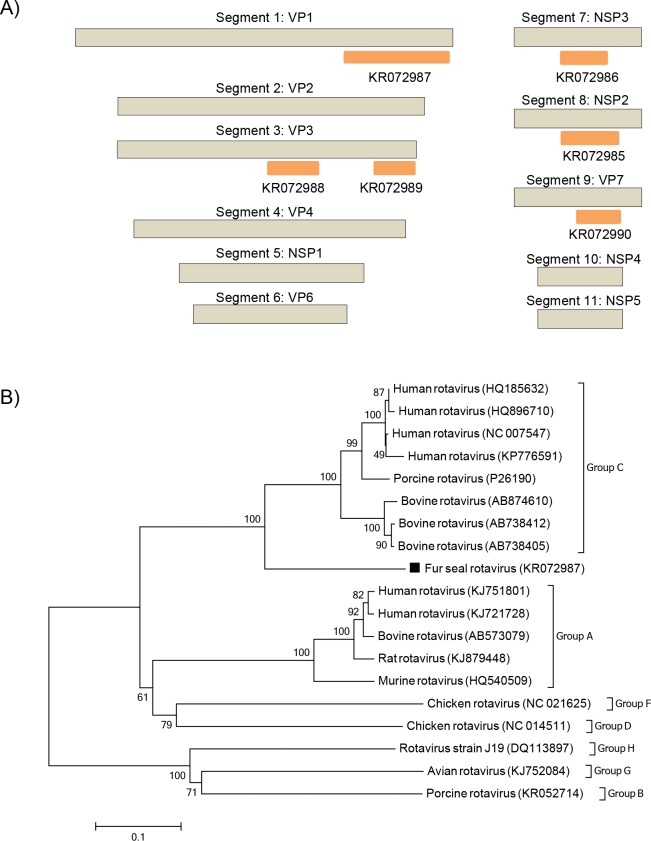
Rotaviruses are non-enveloped segmented dsRNA viruses from the Reoviridae family. They belong to the Rotavirus genus and their genomes contain 11 segments. Based on sequence and serological analyses of the structural protein VP6, there are seven species, also known as groups, of rotaviruses (A-G), and recently a new group H has been proposed [34]. Rotavirus sequences were detected in the Subantarctic fur seal (Fig 8A) with an amino acid identity from 45–69% to group C rotaviruses. The phylogenetic analysis, performed with a partial VP1 sequence, covering 30% of the complete gene, confirmed closer relatedness to group C rotaviruses (Fig 8B). The VP1 gene, which encodes the RdRp, is well conserved within the genus and may be also used for to differentiate rotavirus species [35,36].
Fig 8. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal rotavirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of rotaviruses using as an example the group C rotavirus (~17.9 kb). The orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (307 aa) from the RpRd (segment 1) of 19 rotaviruses. Sequences of groups B, G and H were used as outgroup. The rotavirus sequence from Subantarctic fur seal identified in this study is labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Hepevirus
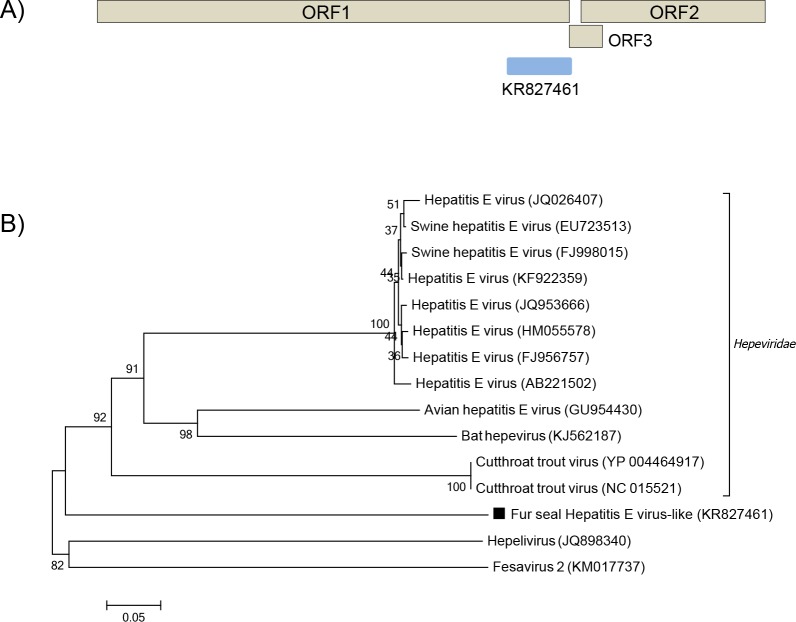
Hepeviruses are non-enveloped, positive sense ssRNA viruses from the Hepeviridae family, which is divided in two genera: Orthohepevirus and Piscihepevirus [37,38]. In this study, a sequence of 661bp with low amino acid identity (27%) to the polyprotein gene of hepeviruses was detected in the South American fur seal (Fig 9A). Phylogenetic analysis of partial sequences of the polyprotein of hepeviruses and hepevirus-like viruses was performed (Fig 9B).
Fig 9. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal hepevirus-like.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of hepeviruses using as an example the hepatitis E virus (~7.2 kb). The blue bar represents the contig from South American fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of partial amino acid sequences (182 aa) from the polyprotein of 15 hepeviruses. Hepelivirus and Fesavirus 2 were used as outgroup. The hepevirus-like virus sequence from South American fur seal identified in this study is labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Sapovirus
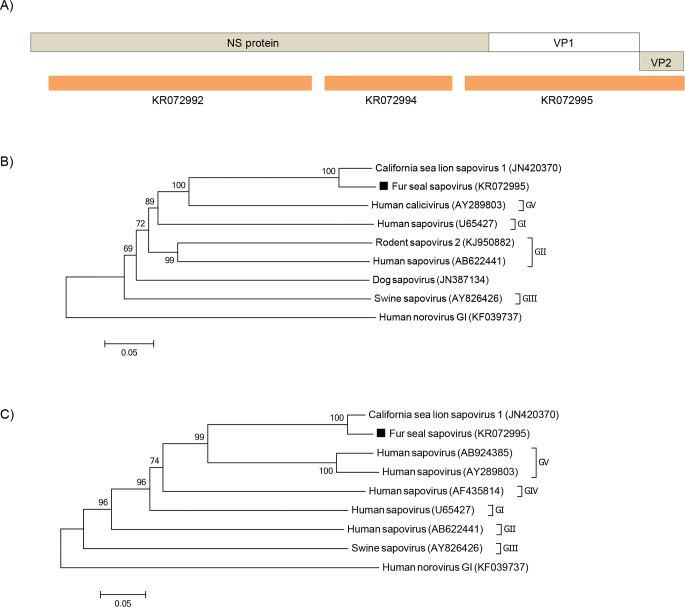
The genus Sapovirus consists of non-enveloped, positive sense ssRNA viruses of the Caliciviridae family. At present, five genogroups have been recognized based on VP1 sequence analyses [39]. Sapovirus sequences were detected in the Subantarctic fur seal samples and results include contigs covering over 90% of the California sea lion sapovirus 1 (CslSaV1) genome (Fig 10A) while sharing 98% amino acid identity and 89% nucleotide sequence identity. Phylogenetic analysis of complete VP1 gene and nearly complete VP2 are shown in Fig 10B and 10C, respectively.
Fig 10. Phylogenetic analysis of fur seal sapovirus.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome of sapoviruses using California sea lion sapovirus 1 (~7.5 kb—JN420370.2) as a reference. The orange bars represent the contigs from Subantarctic fur seal. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on complete nucleotide sequences from the VP1 gene of 9 caliciviruses. Human norovirus was used as outgroup. (C) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the alignment of nearly-complete nucleotide sequences from the VP2 gene of 9 caliciviruses. Human norovirus was used as outgroup. The sapovirus sequences from Subantarctic fur seal from this study used in phylogenetic analyses are labeled with a black square. The GenBank accession numbers of the viral sequences are shown in parentheses.
Discussion
This study has detected enteric viruses in the fecal samples of two species of fur seals that occur in the coast of Rio Grande do Sul, South of Brazil. Such viruses belong to families whose members are either apathogenic or known to cause disease in mammals. Anelloviruses were detected in both species of fur seals examined. Based on anelloviruses demarcation criteria, ORF1 sequences must have a divergence higher than 56 and 35% for genus and species, respectively [25].The sequences with the highest similarity to seal anelloviruses displayed a 60% divergence, suggesting that we found a new genus of Anelloviridae. For the sequences with higher similarity to Torque teno sus virus 1a, the divergence was of 26%, which may indicate they belong to the same genus, Iotatorquevirus. Anelloviruses, which in most cases are not associated to any particular disease, have been detected in seals and sea lions involved in mortality events and virus-specific seroconversion of seals has been demonstrated, suggesting that such animals are indeed susceptible to a productive infection following natural contact with the virus [11,40–42].
Parvovirus sequences were detected in the two species of fur seals. Members of a same genus within the Parvoviridae should share at least 30% amino acid identity in the predicted NS1 sequence, and less than 30% identity when compared to other genera [26]. Although only partial sequences from NS1 were detected in both species, all of them share more than 30% amino acid identity with members of the Protoparvovirus genus, which was also shown by phylogenetic analysis, suggesting a new species within the genus. Parvoviruses have been detected in pinnipeds [43,44], and members of different genera, including bocaviruses, dependoviruses and a novel parvovirus named Sesavirus have been detected in California sea lions [11,45]. Parvoviruses cause infections that can manifest through a variety of illnesses including leukopenia, myocarditis, gastroenteritis, as well as asymptomatically, and have been detected in healthy and debilitated pinnipeds [44–48]. Parvoviruses are also known to be transmitted between wild and domestic species [49,50].
Picornaviruses, which have been found in marine mammals [51], have also been detected in this study. Here, two distinct picornaviruses were detected: one more similar to HAV and AEV and other similar to FSVA. According to the Picornaviridae genus demarcation criteria, different genera should share less than 40%, 40% and 50% amino acid identity in P1, P2 and P3, respectively [30]. Analyses of partial sequences of the polyprotein of the picornavirus similar to HAV and AEV showed that the amino acids identities to members of Hepatovirus and Tremovirus genera were below these cut-offs. The only exception was one sequence that shared 52% amino acid identity with HAV VP2. A higher identity in this region, however, can be expected within members of Hepatovirus and Tremovirus according to previous studies [31]. Based on these values, a possible novel picornavirus more closely related to HAV and AEV was detected in both fur seal species.
In addition, a new putative species within the recently recognized genus Sakobuvirus was identified in the Subantarctic fur seal, here named Fur seal sakobuvirus (FSSV). These share an amino acid identity of at least 50% with Feline sakobuvirus A when comparing all polyprotein coding regions, indicating that FSSV belongs to the same genus. To date, FSVA was the sole member of the genus; the genome reported here corresponds to the first description of a sakobuvirus in another animal species, which was first found in cat feces [52].
Other potential novel enteric virus was also identified. A genogroup I picobirnavirus was detected in South American fur seals. This fur seal picorbirnavirus is distinct from the Otarine picobirnavirus previously found in California sea lions [53] and may represent a new species within the genus. Picobirnaviruses have been detected both in asymptomatic and symptomatic animals, including humans, and an etiologic association with diarrhea is not fully established. However, coinfections of picobirnaviruses with other enteric viruses are not uncommon, can be opportunistic, and may also have a synergistic effect [54–57].
A rotavirus related to group C was found in Subantarctic fur seals. Group C rotaviruses have been associated with sporadic outbreaks in humans and other animals such as pigs and bovines [58–61]. Other studies have detected rotaviruses in marine mammals: anti-group A rotavirus antibodies were first found in Galapagos sea lions and fur seals [62] and RNA sequences from rotaviruses related to lineage B were also detected in California sea lions [11]. Here, results show that more groups of rotaviruses, other than groups A and B, can circulate in marine mammals.
A hepevirus-like sequence was detected in South American fur seals. Hepeviruses, such as Hepatitis E virus (HEV), have been detected in mammals and birds [37,63]. HEVs can cause asymptomatic infections to acute hepatitis and are known zoonotic agents [64]. Recently, a new member of the Hepeviridae family was identified in cutthroat trout, a fish that occurs in the Pacific ocean in North America [65] and unclassified hepevirus-like sequences named hepelivirus and fesavirus-2 were detected in untreated sewage and cat feces, respectively [66,67]. Phylogenetic analysis of the predicted partial polyprotein sequences of the hepevirus-like identified here showed closer relatedness to other members of the Hepeviridae family than to the unclassified hepelivirus and fesavirus-2. Although its low amino acid identity (<30%) might indicate a novel member of the Hepeviridae family, more parts of the polyprotein would need to be sequenced to better taxonomically allocate it.
A sapovirus was detected in samples from Subantarctic fur seals, which is genetically closely related to CslSaV1 that was previously detected in a California sea lion with severe osteomyelitis and nephrolithiasis [11]. Subantarctic fur seals are found in South Atlantic and Indian oceans and our data shows that a very similar sapovirus circulates among fur seals from the southern hemisphere, in addition to the ones that occur in the northern hemisphere. Caliciviruses have been isolated from marine mammals and are known to cause vesicular lesions and diarrhea in those animals [10,44,68]. Sapoviruses can cause gastroenteritis and have been associated with diarrhea in animals [69–71].
Knowledge on viruses in wildlife is still a barely explored field. Occasionally, viral infections have been associated to epidemics in marine mammals, such as anelloviruses infections, whose pathogenic role remains to be determined [41,42]. Additionally, marine mammals may on occasions be exposed to humans, farm animals or pets, which may represent a risk of cross-species transmission of pathogens and zoonoses [10]. Such risk of transmission to humans, for example, was reported with an avian influenza virus isolated from harbor seals [72]. Besides, it is not uncommon to find dogs in contact with carcasses of these animals found ashore, which may give rise to emerging infectious diseases and transmission of known viruses, as already reported with morbilliviruses [73]. An historical example of cross-species transmission occurred with San Miguel sea lion virus that infects marine mammals. This calicivirus is nearly identical to Vesicular exanthema of swine virus, eradicated in swine since 1956, and was able to cause an identical disease in pigs fed with infected carcasses of pinnipeds [74]. Sequences of viruses belonging to viral families known to be transmitted between wild, domestic and farm animals were detected in the present study: parvoviruses, hepeviruses and caliciviruses.
Indisputably, factors such as diet, age and different geographical distributions factors could have contributed to the virome profile of both fur seal species [75]. Based on their lengths and weight, most of the fur seals were classified as juveniles—only one Subantarctic fur seal was an adult animal–and one can expect that juvenil animals are more susceptible to viral infections than adults [76]. Fur seals are carnivores and can feed on a variety of preys. Subtantarctic fur seals mostly feed on fish and cephalopods whereas South American fur seals main diet consists of fish and crustaceans [12,77,78]. Their diet can impact on the virome of each fur seal species and could explain, for example, the detection of eukaryotic viruses that do not infect mammals. The use of fecal samples can allow the detection of sequences that may be originated from different hosts rather than the fur seals. Rotaviruses and sapoviruses were only detected in Subantarctic fur seals whereas picobirnaviruses and a hepevirus-like were only found in South American fur seals. Sequences of anelloviruses, parvoviruses and picornaviruses were detected in both species of fur seals. These have also been reported in seals from the northern hemisphere, indicating the widespread distributions of viruses of such families in pinnipeds [11,41,42,51]. Furthermore, the occurrence of a very genetically closely related sapovirus that infects California sea lions in Subantarctic fur seals shows that viruses previously isolated in the North can also circulate in the South, infecting pinniped populations over a large geographical range.
Although the nucleotide sequences reported in this study do not comprise full genomes, this initial characterization contributes to the knowledge of the viral populations that occur in fur seals, and has identified potential novel viruses that may be of interest for future studies. This is the first study to use next generation sequencing to explore the viral diversity of southern hemisphere marine mammals. The findings presented here are expected to help to understand how viral infections in pinnipeds may impact the health of the pinniped population and its potential as sources of viruses which may potentially infect other animal species.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank CECLIMAR for kindly providing the samples used in this study and the laboratories from PUCRS and IPVDF for performing next-generation sequencing. We also thank the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) Supercomputing National Center (CESUP) for allowing access to run the metagenomic analyses.
Data Availability
All sequence data is available from the NIH Sequence Read Archive (SRA—http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/) database (accession number SRP070196).
Funding Statement
The research leading to these results has received funding from the National Council for the Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES—http://www.capes.gov.br/), the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq—http://www.cnpq.br/), and the Study and Project Funding Agency (FINEP—http://www.finep.gov.br/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Ferreira JM, De Oliveira LR, Wynen L, Bester MN, Guinet C, Moraes-Barros N, et al. Multiple origins of vagrant Subantarctic fur seals: A long journey to the Brazilian coast detected by molecular markers. Polar Biol. 2008;31: 303–308. 10.1007/s00300-007-0358-z [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moura JF, Siciliano S. Straggler subantarctic fur seal (Arctocephalus tropicalis) on the coast of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Lat Am J Aquat Mamm. 2007;6: 103–107. 10.5597/lajam00114 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pinedo MC. Ocorrência de pinípedes na costa brasileira. Gracia Orla Série Zool. 1990;15: 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Oliveira A, Kolesnikovas CKM, Serafini PP, Moreira LMP, Pontalti M, Simões-Lopes PC, et al. Occurrence of pinnipeds in Santa Catarina between 2000 and 2010. Lat Am J Aquat Mamm. 2011;9: 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Simões-Lopes PC, Drebmer CJ, Ott PH. Nota sobre os otariidae e phocidae (mammalia: carnivora) da costa norte do Rio Grande do Sul e Santa catarina, Brasil. Biociências. 1995. pp. 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arbiza J, Blanc A, Castro-Ramos M, Katz H, León AP de, Clara M. Uruguayan Pinnipeds (Arctocephalus australis and Otaria flavescens): Evidence of Influenza Virus and Mycobacterium pinnipedii Infections. New Approaches to Study Mar Mamm. 2012;2: 151–182. 10.5772/54214 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.de Bruyn PJN, Bastos ADS, Eadie C, Tosh CA, Bester MN. Mass mortality of adult male subantarctic fur seals: Are alien mice the culprits? PLoS One. 2008;3: e3757 10.1371/journal.pone.0003757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Katz H, Morgades D, Castro-Ramos M. Pathological and Parasitological Findings in South American Fur Seal Pups (Arctocephalus australis) in Uruguay. ISRN Zool. 2012;2012: 1–7. 10.5402/2012/586079 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sikorski A, Dayaram A, Varsani A. Identification of a Novel Circular DNA Virus in New Zealand Fur Seal (Arctocephalus forsteri) Fecal Matter. Genome Announc. 2013;1: 2012–2013. 10.1099/vir.0.052654-0.17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Waltzek TB, Cortés-Hinojosa G, Wellehan JFX, Gray GC. Marine mammal zoonoses: a review of disease manifestations. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012;59: 521–535. 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2012.01492.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li L, Shan T, Wang C, Côté C, Kolman J, Onions D, et al. The fecal viral flora of california sea lions. J Virol. 2011;85: 9909–9917. 10.1128/JVI.05026-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vaz-Ferreira R. Arctocephalus australis (Zimmermann), South American fur seal In: Ser FF, editor. Mammals in the seas. Rome: FAO; 1982. pp. 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Riedman M. The Pinnipeds: Seals, Sea Lions, and Walruses. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Geraci JR, Lounsbury VJ. Marine Mammals Ashore: A Field Guide for Strandings. 1st ed. Galveston, TX: Texas A&M Sea Grant; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Open Street Map [Internet]. p. https://www.openstreetmap.org.
- 16.Donaldson EF, Haskew AN, Gates JE, Huynh J, Moore CJ, Frieman MB. Metagenomic analysis of the viromes of three North American bat species: viral diversity among different bat species that share a common habitat. J Virol. 2010;84: 13004–13018. 10.1128/JVI.01255-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Victoria JG, Kapoor A, Li L, Blinkova O, Slikas B, Wang C, et al. Metagenomic analyses of viruses in stool samples from children with acute flaccid paralysis. J Virol. 2009;83: 4642–4651. 10.1128/JVI.02301-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Allander T, Tammi MT, Eriksson M, Bjerkner A, Tiveljung-Lindell A, Andersson B. Cloning of a human parvovirus by molecular screening of respiratory tract samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102: 12891–12896. 10.1073/pnas.0504666102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stang A, Korn K, Wildner O, Uberla K. Characterization of virus isolates by particle-associated nucleic acid PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43: 716–720. 10.1128/JCM.43.2.716-720.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30: 2725–2729. 10.1093/molbev/mst197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4: 406–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.He B, Li Z, Yang F, Zheng J, Feng Y, Guo H, et al. Virome Profiling of Bats from Myanmar by Metagenomic Analysis of Tissue Samples Reveals More Novel Mammalian Viruses. PLoS One. 2013;8: e61950 10.1371/journal.pone.0061950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu Z, Ren X, Yang L, Hu Y, Yang J, He G, et al. Virome Analysis for Identification of Novel Mammalian Viruses in Bat Species from Chinese Provinces. J Virol. 2012;86: 10999–11012. 10.1128/JVI.01394-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Teng JLL, Tsang AKL, Joseph M, Wong EYM, et al. Metagenomic analysis of viromes of dromedary camel fecal samples reveals large number and high diversity of circoviruses and picobirnaviruses. Virology. 2014;473: 117–125. 10.1016/j.virol.2014.09.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Biagini P, Bendinelli M, Hino S, Kakkola L, Mankertz A, Niel C, et al. Anelloviridae In: King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 326–341. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cotmore SF, Agbandje-McKenna M, Chiorini JA, Mukha D V, Pintel DJ, Qiu J, et al. The family Parvoviridae. Arch Virol. 2014;159: 1239–1247. 10.1007/s00705-013-1914-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tijssen P, Agbandje-McKenna M, Almendral J, Bergoin M, Flegel T, Hedman K, et al. Parvoviridae In: King A, Lefkowitz E, Adams M, Carstens E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 405–425. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Knowles N, Hovi T, Hyypiä T, King A, Lindberg A, Pallansch M, et al. Picornaviridae In: King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 855–880. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ, Bamford DH, Breitbart M, Davison AJ, et al. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2015). Arch Virol. 2015;160: 1837–50. 10.1007/s00705-015-2425-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.The Pirbright Institute. The Picornavirus Pages [Internet]. 2015. Available: http://www.picornaviridae.com
- 31.Marvil P, Knowles NJ, Mockett AP, Britton P, Brown TD, Cavanagh D. Avian encephalomyelitis virus is a picornavirus and is most closely related to hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1999;80: 653–662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Delmas B. Picobirnaviridae In: King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ganesh B, Masachessi G, Mladenova Z. Animal picobirnavirus. Virus Dis. 2014;25: 223–238. 10.1007/s13337-014-0207-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Matthijnssens J, Otto PH, Ciarlet M, Desselberger U, van Ranst M, Johne R. VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Arch Virol. 2012;157: 1177–1182. 10.1007/s00705-012-1273-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Attoui H, Mertens P, Becnel J, Belaganahalli S, Bergoin M, Brussaard C, et al. Reoviridae In: King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 541–637. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ogden KM, Johne R, Patton JT. Rotavirus RNA polymerases resolve into two phylogenetically distinct classes that differ in their mechanism of template recognition. Virology. 2012;431: 50–57. 10.1016/j.virol.2012.05.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Meng XJ. Recent advances in Hepatitis E virus. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17: 153–161. 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01257.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith DB, Simmonds P, Jameel S, Emerson SU, Harrison TJ, Meng X-J, et al. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J Gen Virol. 2014;95: 2223–32. 10.1099/vir.0.068429-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Clarke I, Estes M, Green K, Hansman G, Knowles N, Koopmans M, et al. Caliciviridae In: King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1st ed. San Diego: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fahsbender E, Rosario K, Cannon JP, Gulland F, Dishaw LJ, Breitbart M. Development of a Serological Assay for the Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) Anellovirus, ZcAV. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 9637 10.1038/srep09637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ng TFF, Suedmeyer WK, Wheeler E, Gulland F, Breitbart M. Novel anellovirus discovered from a mortality event of captive California sea lions. J Gen Virol. 2009;90: 1256–1261. 10.1099/vir.0.008987-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ng TFF, Wheeler E, Greig D, Waltzek TB, Gulland F, Breitbart M. Metagenomic identification of a novel anellovirus in Pacific harbor seal (Phoca vitulina richardsii) lung samples and its detection in samples from multiple years. J Gen Virol. 2011;92: 1318–1323. 10.1099/vir.0.029678-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bodewes R, García AR, Wiersma LCM, Getu S, Beukers M, Schapendonk CME, et al. Novel B19-like parvovirus in the brain of a harbor seal. PLoS One. 2013;8: 1–9. 10.1371/journal.pone.0079259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Burek K a, Gulland FMD, Sheffield G, Beckmen KB, Keyes E, Spraker TR, et al. Infectious disease and the decline of Steller sea lions (Eumetopias jubatus) in Alaska, USA: insights from serologic data. J Wildl Dis. 2005;41: 512–524. 10.7589/0090-3558-41.3.512 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Phan TG, Gulland F, Simeone C, Deng X, Delwart E. Sesavirus: prototype of a new parvovirus genus in feces of a sea lion. Virus Genes. 2014;50: 134–136. 10.1007/s11262-014-1123-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ikeda Y, Nakamura K, Miyazawa T, Tohya Y, Takahashi E, Mochizuki M. Feline host range of Canine parvovirus: Recent emergence of new antigenic types in cats. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8: 341–346. 10.3201/eid0804.010228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Steinel a, Parrish CR, Bloom ME, Truyen U. Parvovirus infections in wild carnivores. J Wildl Dis. 2001;37: 594–607. 10.7589/0090-3558-37.3.594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hoelzer K, Parrish CR. The emergence of parvoviruses of carnivores. Vet Res. 2010;41: 39 10.1051/vetres/2010011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Allison a. B, Harbison CE, Pagan I, Stucker KM, Kaelber JT, Brown JD, et al. Role of Multiple Hosts in the Cross-Species Transmission and Emergence of a Pandemic Parvovirus. J Virol. 2012;86: 865–872. 10.1128/JVI.06187-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Allison AB, Kohler DJ, Fox K a, Brown JD, Gerhold RW, Shearn-Bochsler VI, et al. Frequent Cross-Species Transmission of Parvoviruses among Diverse Carnivore Hosts. J Virol. 2013;87: 2342–2347. 10.1128/jvi.02428-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kapoor a, Victoria J, Simmonds P, Wang C, Shafer RW, Nims R, et al. A highly divergent picornavirus in a marine mammal. J Virol. 2008;82: 311–320. 10.1128/JVI.01240-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ng TFF, Mesquita JR, Nascimento MSJ, Kondov NO, Wong W, Reuter G, et al. Feline fecal virome reveals novel and prevalent enteric viruses. Vet Microbiol. 2014;171: 102–111. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Bai R, Teng JLL, Lee P, Martelli P, et al. Complete Genome Sequence of a Novel Picobirnavirus, Otarine Picobirnavirus, Discovered in California Sea Lions. J Virol. 2012;86: 6377–6378. 10.1128/JVI.00686-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Giordano MO, Masachessi G, Martinez LC, Barril PA, Ferreyra LJ, Isa MB, et al. Two instances of large genome profile picobirnavirus occurrence in Argentinian infants with diarrhea over a 26-year period (1977–2002). J Infect. 2008;56: 371–375. 10.1016/j.jinf.2008.02.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bhattacharya R, Sahoo GC, Nayak MK, Rajendran K, Dutta P, Mitra U, et al. Detection of Genogroup I and II human picobirnaviruses showing small genomic RNA profile causing acute watery diarrhoea among children in Kolkata, India. Infect Genet Evol. 2007;7: 229–238. 10.1016/j.meegid.2006.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Carruyo-Núñez GM, Alcalá-Aristiguieta AC, Liprandi-Fraire F, Ludert-Leon JE. Porcine picobirnavirus infection in venezuelan farms. Rev Cient. 2014;XXIV: 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Malik YS, Kumar N, Sharma K, Dhama K, Shabbir MZ, Ganesh B, et al. Epidemiology, Phylogeny, and Evolution of Emerging Enteric Picobirnaviruses of Animal Origin and Their Relationship to Human Strains. Biomed Res Int. Hindawi Publishing Corporation; 2014;2014: 780752 10.1155/2014/780752 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gabbay YB, Jiang B, Oliveira CS, Mascarenhas JD, Leite JP, Glass RI, et al. An outbreak of group C rotavirus gastroenteritis among children attending a day-care centre in Belém, Brazil. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1999;17: 69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Esona MD, Humphrey CD, Dennehy PH, Jiang B. Prevalence of group C rotavirus among children in Rhode Island, United States. J Clin Virol. 2008;42: 221–224. 10.1016/j.jcv.2008.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kim Y, Chang KO, Straw B, Saif LJ. Characterization of group C rotaviruses associated with diarrhea outbreaks in feeder pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37: 1484–1488. 0095-1137/99 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mawatari T, Taneichi A, Kawagoe T, Hosokawa M, Togashi K, Tsunemitsu H. Detection of a bovine group C rotavirus from adult cows with diarrhea and reduced milk production. J Vet Med Sci. 2004;66: 887–890. 10.1292/jvms.66.887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Coria-Galindo E, Rangel-Huerta E, Verdugo-Rodríguez A, Brousset D, Salazar S, Padilla-Noriega L. Rotavirus infections in Galapagos sea lions. J Wildl Dis. 2009;45: 722–728. 10.7589/0090-3558-45.3.722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Haqshenas G, Shivaprasad HL, Woolcock PR, Read DH, Meng XJ. Genetic identification and characterization of a novel virus related to human hepatitis E virus from chickens with hepatitis-splenomegaly syndrome in the United States. J Gen Virol. 2001;82: 2449–2462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bihl F, Negro F. Hepatitis E virus: A zoonosis adapting to humans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65: 817–821. 10.1093/jac/dkq085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Batts W, Yun S, Hedrick R, Winton J. A novel member of the family Hepeviridae from cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii). Virus Res. Elsevier B.V.; 2011;158: 116–123. 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.03.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ng TFF, Marine R, Wang C, Simmonds P, Kapusinszky B, Bodhidatta L, et al. High Variety of Known and New RNA and DNA Viruses of Diverse Origins in Untreated Sewage. J Virol. 2012;86: 12161–12175. 10.1128/JVI.00869-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhang W, Li L, Deng X, Kapusinszky B, Pesavento P a., Delwart E. Faecal virome of cats in an animal shelter. J Gen Virol. 2014;95: 2553–2564. 10.1099/vir.0.069674-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Smith AW, Akers TG, Madin SH, Vedros NA. San Miguel sea lion virus isolation, preliminary characterization and relationship to vesicular exanthema of swine virus. Nature. 1973;244: 108–110. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4583480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Li L, Pesavento P a., Shan T, Leutenegger CM, Wang C, Delwart E. Viruses in diarrhoeic dogs include novel kobuviruses and sapoviruses. J Gen Virol. 2011;92: 2534–2541. 10.1099/vir.0.034611-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Soma T, Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Mochizuki M. Detection of Norovirus and Sapovirus from diarrheic dogs and cats in Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 2015;59: 123–128. 10.1111/1348-0421.12223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wang QH, Souza M, Funk J a., Zhang W, Saif LJ. Prevalence of noroviruses and sapoviruses in swine of various ages determined by reverse transcription-PCR and microwell hybridization assays. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44: 2057–2062. 10.1128/JCM.02634-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Karlsson EA, Ip HS, Hall JS, Yoon SW, Johnson J, Beck MA, et al. Respiratory transmission of an avian H3N8 influenza virus isolated from a harbour seal. Nat Commun. 2014;5: 4791 10.1038/ncomms5791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kennedy S, Kuiken T, Jepson PD, Deaville R, Forsyth M, Barrett T, et al. Mass die-Off of Caspian seals caused by canine distemper virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6: 637–639. 10.3201/eid0606.000613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gelberg HB, Dieterich RA, Lewis RM. Vesicular Exanthema of Swine and San Miguel Sea Lion Virus: Experimental and Field Studies in Otarid Seals, Feeding Trials in Swine. Vet Pathol. 1982;19: 413–423. 10.1177/030098588201900407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Dierauf L, Gulland FMD. CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine: Health, Disease, and Rehabilitation, Second Edition. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Barry AF, Ribeiro J, Alfieri AF, van der Poel WHM, Alfieri AA. First detection of kobuvirus in farm animals in Brazil and the Netherlands. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11: 1811–1814. 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.06.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bester M. Subantarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus tropicalis, at Gough Island (Tristan da Cunha group). In: Croxall J, Gentry R, editors. Status, biology, and ecology of fur seals: proceedings of an international symposium and workshop Cambridge, England: 23–27 April 1984. Springfield: NOAA Tech Rep NMFS 51; 1987. pp. 57–60.
- 78.Kerley G. Subantarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus tropicalis, at Gough Island (Tristan da Cunha group). In: Croxall J, Gentry R, editors. Status, biology, and ecology of fur seals: proceedings of an international symposium and workshop Cambridge, England: 23–27 April 1984. Springfield: NOAA Tech Rep NMFS 51; 1987. pp. 61–64.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All sequence data is available from the NIH Sequence Read Archive (SRA—http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/) database (accession number SRP070196).