Abstract
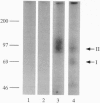
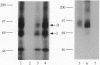
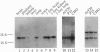
Activin type II receptors are transmembrane protein-serine/threonine kinases. By using a reverse-transcription PCR assay to screen for protein kinase sequences, we isolated a cDNA clone, activin X1 receptor, from rat brain that encodes a 55-kDa transmembrane protein-serine kinase which is structurally related to other receptors in this kinase subfamily. The predicted protein consists of 509 amino acids, and the kinase domain shows 40% and 37% identity to the activin and transforming growth factor beta type II receptors, respectively. No activin-binding was observed when activin X1 receptor was expressed alone in COS-M6 cells; however, coexpression with type II activin receptors gave rise to a 68-kDa affinity-labeled complex in addition to the 85-kDa type II receptor complex. The size of this cross-linked band is consistent with the size of the type I activin receptor; furthermore, activin X1 receptor associated with type II receptors, as judged by coimmunoprecipitation with type II receptor antibodies. These data suggest that activin X1 receptor can serve as an activin type I receptor and that the diverse biological effects of activins may be mediated by a complex formed by the interaction of two transmembrane protein-serine kinases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Novel activin receptors: distinct genes and alternative mRNA splicing generate a repertoire of serine/threonine kinase receptors. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90209-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand T., MacLellan W. R., Schneider M. D. A dominant-negative receptor for type beta transforming growth factors created by deletion of the kinase domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11500–11503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Ebner R., Derynck R. Inactivation of the type II receptor reveals two receptor pathways for the diverse TGF-beta activities. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.8388126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Chen R. H., Shum L., Lawler S., Zioncheck T. F., Lee A., Lopez A. R., Derynck R. Cloning of a type I TGF-beta receptor and its effect on TGF-beta binding to the type II receptor. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1344–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.8388127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgi L. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W. W., Gustafson M. L., Hirobe S., Donahoe P. K. Developmental expression of four novel serine/threonine kinase receptors homologous to the activin/transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor family. Dev Dyn. 1993 Feb;196(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001960207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Melton D. A. A truncated activin receptor inhibits mesoderm induction and formation of axial structures in Xenopus embryos. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):609–614. doi: 10.1038/359609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino M., Tojo A., Miyazono K., Miura Y., Chiba S., Eto Y., Shibai H., Takaku F. Characterization of cellular receptors for erythroid differentiation factor on murine erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10309–10314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Moustakas A., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F., Carr B. I. Growth inhibition by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) type I is restored in TGF-beta-resistant hepatoma cells after expression of TGF-beta receptor type II cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5359–5363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Tashiro K., Fujii G., Asano M., Miyoshi R., Yamada R., Muramatsu M., Shiokawa K. Activin receptor mRNA is expressed early in Xenopus embryogenesis and the level of the expression affects the body axis formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):684–690. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis F. M., Boyd F. T., Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Responsiveness to transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) restored by genetic complementation between cells defective in TGF-beta receptors I and II. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9108–9112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R., Zhou X., Dresback J., Eberspaecher H., McKinney S., Segarini P., de Crombrugghe B. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel rat activin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):672–679. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90535-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Wang X. F., Ng-Eaton E., Weinberg R. A., Lodish H. F. Expression cloning of the TGF-beta type II receptor, a functional transmembrane serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Characterization of type II activin receptors. Binding, processing, and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19013–19018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W., Kintner C. R. Cloning of a second type of activin receptor and functional characterization in Xenopus embryos. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1702–1705. doi: 10.1126/science.1313188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki K., Xu J., Wang F., McKeehan W. L., Krummen L., Kan M. A widely expressed transmembrane serine/threonine kinase that does not bind activin, inhibin, transforming growth factor beta, or bone morphogenic factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12719–12723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Hara T., Kitamura T. Common subunits of cytokine receptors and the functional redundancy of cytokines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Sugino K., Kurosawa N., Sawai M., Takio K., Eto Y., Iwashita S., Muramatsu M., Titani K., Sugino H. Isolation and characterization of activin receptor from mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Identification of its serine/threonine/tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18924–18928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Stein R. W., Moran E., Yaciuk P., Schlegel R., Lyons R. M., Pittelkow M. R., Münger K., Howley P. M., Moses H. L. TGF-beta 1 inhibition of c-myc transcription and growth in keratinocytes is abrogated by viral transforming proteins with pRB binding domains. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90188-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehy D. W., Shao L. E., Yu A. L., Tsai W. M., Yu J. Activin A-induced differentiation in K562 cells is associated with a transient hypophosphorylation of RB protein and the concomitant block of cell cycle at G1 phase. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Nov;50(3):255–265. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ito I., Hasegawa Y., Nakamura K., Igarashi S., Nakamura M., Miyamoto K., Eto Y., Ibuki Y., Minegishi T. Cloning and sequencing of a rat type II activin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 2;312(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81408-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino H., Nakamura T., Hasegawa Y., Miyamoto K., Igarashi M., Eto Y., Shibai H., Titani K. Identification of a specific receptor for erythroid differentiation factor on follicular granulosa cell. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15249–15252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Lewis K. A., Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Molecular characterization of rat transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):790–795. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution and quantitation of the mRNAs for three rat tachykinin receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):751–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Cárcamo J., Zentella A., Doody J., Laiho M., Wang X. F., Massagué J. TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1003–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90395-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]